
(a)
Find the current through the emf device and each resistor in circuit 1.
(a)
Answer to Problem 39PQ
The current through the Emf device and each resistor in circuit 1 is
Explanation of Solution
According to Kirchhoff’s junction rule, in any junction, the sum of the all the currents entering the junction equals the sum of all the currents exiting the junction.
Redraw the circuit 1 and labeled it as given below
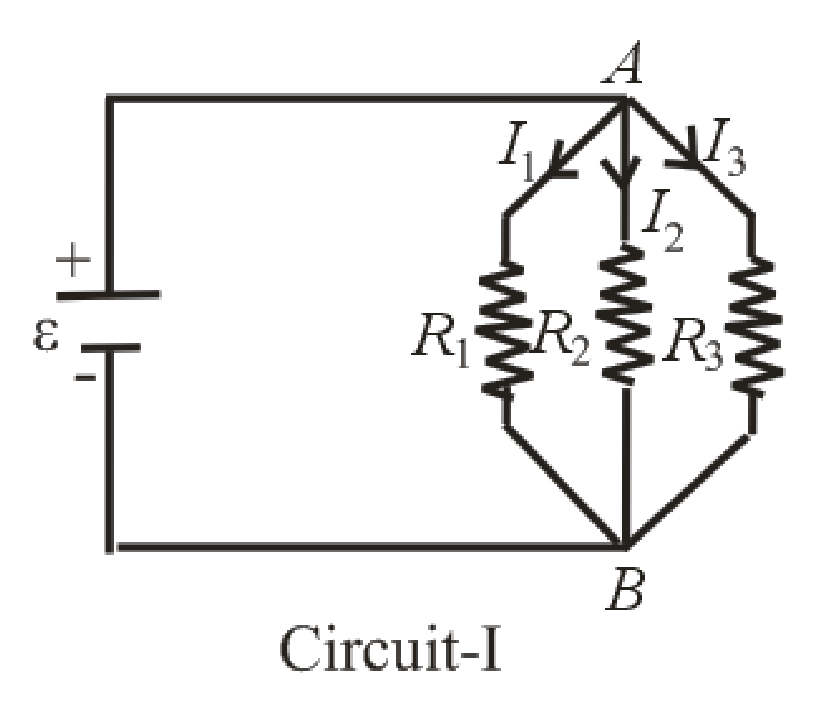
In parallel circuit, voltage across all three resistors is same that means potential difference between node A and node B is same (
According to Ohm’s law,
Here,
Rearrange the equation (I) in terms of total current
Write the expression for equivalent resistance as.
Rearrange the above expression.
Write the expression for current
Here,
Write the expression for current
Here,
Write the expression for current
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the current in circuit 1 is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the current through the Emf device and each resistor in circuit 1 is
(b)
Find the current through the emf device and each resistor in circuit 2 refer to figure P29.28.
(b)
Answer to Problem 39PQ
The current through the Emf device and each resistor in circuit 2 is
Explanation of Solution
According to Kirchhoff’s junction rule, in any junction, the sum of the all the currents entering the junction equals the sum of all the currents exiting the junction.
Redraw the circuit 2 and labeled it as given below.
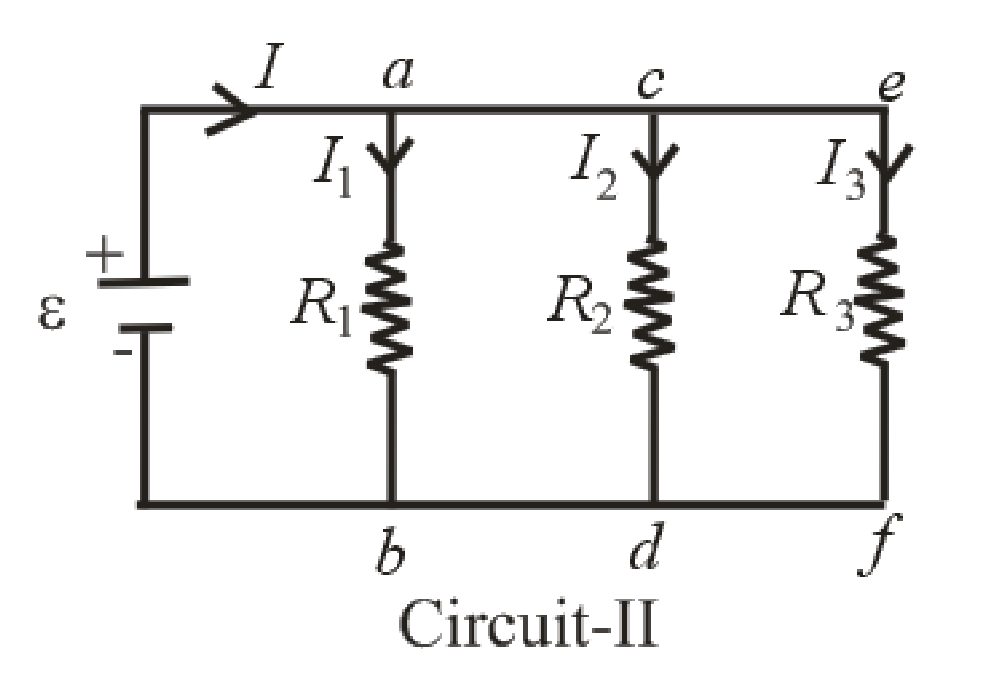
In parallel circuit 2, voltage across all three resistors is same that means potential difference between node a and node b, node c & node d and node e & node f are same
Write the expression for current
Here,
Write the expression for current
Here,
Write the expression for current
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the current in circuit 1 is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the current for the given circuit resistance is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 29 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- In Figure P29.81, N real batteries, each with an emf and internal resistance r, are connected in a closed ring. A resistor R can be connected across any two points of this ring, causing there to be n real batteries in one branch and N n resistors in the other branch. Find an expression for the current through the resistor R in this case.arrow_forwardIn the circuit of Figure P27.25, the switch S has been open for a long time. It is then suddenly closed. Take = 10.0 V, R1 = 50.0 k, R2 = 100 k, and C = 10.0 F. Determine the time constant (a) before the switch is closed and (b) after the switch is closed. (c) Let the switch be closed at t = 0. Determine the current in the switch as a function of time. Figure P27.25 Problems 25 and 26.arrow_forwardThree resistors with resistances R1 = R/2 and R2 = R3 = R are connected as shown, and a potential difference of 225 V is applied across terminals a and b (Fig. P29.49). a. If the resistor R1 dissipates 75.0 W of power, what is the value of R? b. What is the total power supplied to the circuit by the emf? c. What is the potential difference across each of the three resistors?arrow_forward
- Figure P29.41 shows three resistors (R1 = 14.0 , R2 = 8.00 , and R3 = 10.0 ) and two batteries connected in a circuit. a. What is the current in each of the resistors? b. How much power is delivered to each of the resistors?arrow_forwardThe circuit shown in Figure P28.78 is set up in the laboratory to measure an unknown capacitance C in series with a resistance R = 10.0 M powered by a battery whose emf is 6.19 V. The data given in the table are the measured voltages across the capacitor as a function of lime, where t = 0 represents the instant at which the switch is thrown to position b. (a) Construct a graph of In (/v) versus I and perform a linear least-squares fit to the data, (b) From the slope of your graph, obtain a value for the time constant of the circuit and a value for the capacitance. v(V) t(s) In (/v) 6.19 0 5.56 4.87 4.93 11.1 4.34 19.4 3.72 30.8 3.09 46.6 2.47 67.3 1.83 102.2arrow_forwardIn the circuit of Figure P27.25, the switch S has been open for a long time. It is then suddenly closed. Determine the time constant (a) before the switch is closed and (b) after the switch is closed. (c) Let the switch be closed at t = 0. Determine the current in the switch as a function of time. Figure P27.25 Problems 25 and 26.arrow_forward
- Two circuits made up of identical ideal emf devices ( = 1.67 V) and resistors (R = 35.9 ) are shown in Figure P29.8. What is the potential difference Vb Va a. for circuit 1 and b. for circuit 2? What is the current in the resistor c. in circuit 1 and d. in circuit 2?arrow_forwardEach resistor shown in Figure P29.36 has a resistance of 100.0 . An ideal emf device (120.0 V) is connected to points a and b via two leads (not shown in the figure). Find the current that flows through the emf device.arrow_forwardIn The circuit given in pic, the current passed through the resistance 1 is i1=2A and theresistance are R1=2.00 Ω, R2=3.00 Ω, R3=2.50 Ω, R4=6.0 Ω, R5=4.00 Ω and R6=3.50 Ω. a) What is the equivalent resistance of the circuit? b) What is the emf of the battery?arrow_forward
- If you have a circuit like the one in the figure with E=51.0V, R1=793.2Ω, R2=781.3Ω, R3=534.9Ω and R4=793.2Ω, determine the current in amps passing through the resistor R1 (Write your answer to 3 significant figures)arrow_forwardAn initially uncharged capacitor with a capacitance of C = 5.00 µF is connected in series with a resistor with a resistance of R = 4.5 k. If this series combination of circuit elements is attached to an ideal battery with an emf of Ɛ = 450 V by means of a switch S that is closed at time t = 0, then answer the following questions. (a) What is the time constant of this circuit? (b) How long will it take for the capacitor to reach 75% of its final charge? (c) What is the final charge on the capacitor?arrow_forwardA 42 Ω resistor and a 20 Ω resistor are connected in parallel, and the combination is connected across a 240 V dc line. (a) What is the resistance of the parallel combination? (b) What is the total current through the parallel combination? (c) What is the current through each resistor?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning



