
Concept explainers
One of the steps in the pentose phosphate pathway for glucose catabolism is the reaction of xylulose 5-phosphate with ribose 5-phosphate in the presence of a transketolase to give glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and sedoheptulose 7-phosphate.
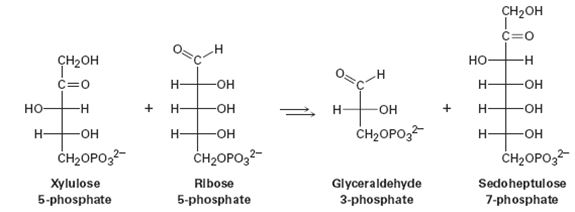
(a) The first part of the reaction is nucleophilic addition of thiamin diphosphate (TPP) ylide to xylulose 5-phosphate, followed by a retro-aldol cleavage to give glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and a TPPcontaining enamine. Show the structure of the enamine and the mechanism by which it is formed.
(b) The second part of the reaction is addition of the enamine to ribose 5-phosphate followed by loss of TPP ylide to give sedoheptulose 7-phosphate. Show the mechanism.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 29 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Chemistry: Atoms First
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry
- One of the steps in the pentose phosphate pathway for glucose catabolism is the reaction of sedoheptulose 7-phosphate with glyceraldehydes 3-phosphate in the presence of a transaldolase to yield erythrose 4-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate. (a) The first part of the reaction is the formation of a protonated Schiff base of sedoheptulose 7-phosphate with a lysine residue in the enzyme followed by a retro-aldol cleavage to give an enamine plus erythrose 4-phosphate. Show the structure of the enamine and the mechanism by which it is formed. (b) The second part of the reaction is a nucleophilic addition of the enamine to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate followed by hydrolysis of the Schiff base to give fructose 6-phosphate. Show the mechanism.arrow_forwardThe dehydration of citrate to yield cis-aconitate, a step in the citric acid cycle, involves the pro-R “arm’’ of citrate rather than the pro-S arm. Which of the following two products is formed?arrow_forwardOne of the steps in the biosynthesis of uridine monophosphate is the reaction of aspartate with carbamoyl phosphate to give carbamoyl aspartate followed by cyclization to form dihydroorotate. Propose mechanisms for both steps.arrow_forward
- The C2-epimer of D-xylose is called (blank 1). The enediol rearrangementconverts an aldose into a (blank 2). The aldopentose embedded in RNA is(blank 3). An aldopentose would have (blank 4) possible stereoisomers,of whichBlankwould be D-sugars. An ketopentose would have (blank 4) possiblestereoisomers, of which (blank 5) would be D-sugarsarrow_forwardAldolase catalyzes the glycolytic reaction The standard free-energy change for this reaction in the direction written is +23.8 kJ/mol. The concentrations of the three intermediates in the hepatocyte of a mammal are: fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, 1.4 × 10−5 M; glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, 3 × 10−6 M; and dihydroxyacetone phosphate, 1.6 ×10−5 M. At body temperature (37 °C), what is the actual free-energy change for the reaction?arrow_forwardThe tartaness of some wines is high concentration of l malate.write a consequence of reactions showing how yeast cells synthesize l malate from glucose under anaerobic conditions in the presence of co2arrow_forward
- When some sugars dissolve in water they spontaneously undergo changes in optical rotation called mutarrotation. The Mutarrotation of D-glucopyranose is catalyzed by acid and bases. 2-Hydroxypyridine is a more effective catalyst than phenol and pyridine for this reaction because: a.Both oxygen and N in 2-hydroxypyridine act as bases increasing the rapid interconversion of sugar b. The OH of 2-hydroxypyridine serves as the base while the current N as the acid. c. 2-hydroxypyridine acts both as a base to remove the proton from the hydroxyl group in the hemiacetal and as an acid to provide a proton to the oxygen in the hemiacetal. d.Phenol and pyridine are very expensive.arrow_forwardThe carbonyl group in d-galactose may be isomerized from C1 to C2 by brief treatmentwith dilute base (by the enediol rearrangement, Section 23-7). The product is the C4epimer of fructose. Draw the furanose structure of the product.arrow_forwardOne step in glycolysis is the conversion of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. The direct reaction of fructose-6-phosphate with inorganic phosphate fructose-6-phosphate + Pi ⇌ fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + H₂O is very unfavorable, with ∆G'°= 16.3 kJ/mol and K'eq = 1.39×10⁻³. However, in glycolysis the reaction is coupled to ATP hydrolysis: fructose-6-phosphate + ATP ⇌ fructose-1,6-phosphate + ADP and the reaction if favorable. What is the equilibrium [fructose-1,6-bisphosphate]/[fructose-6-phosphate] ratio in the coupled reaction when [ATP] = [ADP]? For ATP hydrolysis ∆G'°= -30.5 kJ/mol at 25°C.arrow_forward
- Identify the sugar in each description. a. An aldopentose that is not d-arabinose forms d-arabinitol when it is reduced with NaBH4. b. A sugar that is not D-altrose forms d-altraric acid when it is oxidized with nitric acid. c. A ketose that, when reduced with NaBH4, forms d-altritol and d-allitol.arrow_forwardDeduce the structure of the disaccharide isomaltose from the following data.a. Hydrolysis yields D-glucose exclusively. b. Isomaltose is cleaved with α-glycosidase enzymes. c. Isomaltose is a reducing sugar. d. Methylation with excess CH3I, Ag2O and then hydrolysis with H3O+ forms two products:arrow_forwardChorismate mutase is an enzyme that promotes a pericyclic reaction by forcing the substrate to assume the conformation needed for the reaction. The product of the pericyclic reaction is prephenate that is subsequently converted into the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. What kind of a pericyclic reaction does chorismate mutase catalyze?arrow_forward
