
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305251052
Author: Michael Cummings
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 24QP
Meiosis Explains Mendel’s Results: Genes Are on Chromosomes
The following diagram shows a hypothetical diploid cell. The recessive allele for albinism is represented by a, and d represents the recessive allele for deafness. The normal alleles for these conditions are represented by A and D, respectively.
- a. According to the principle of segregation, what is segregating in this cell?
- b. According to Mendel’s principle of independent assortment, what is independently assorting in this cell?
- c. How many chromatids are in this cell?
- d. Write the genotype of the individual from whom this cell was taken.
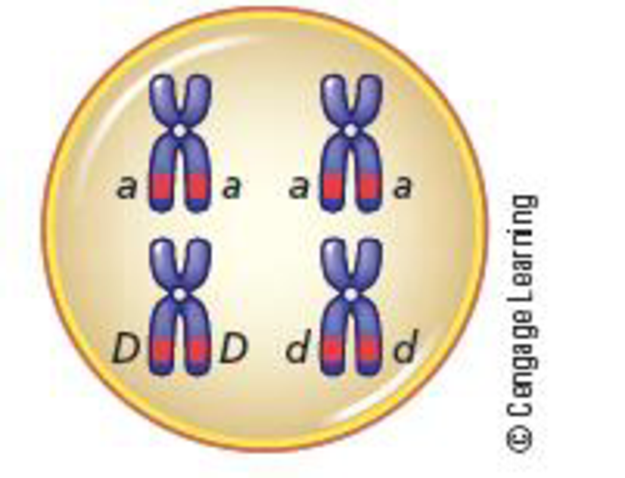
- e. What is the
phenotype of this individual? - f. What stage of cell division is represented by this cell (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, or telophase of meiosis I, meiosis II, or mitosis)?
- g. After meiosis is complete, how many chromatids and chromosomes will be present in one of the four progeny cells?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
When Gregor Mendel was working in the mid 1800s, scientists had not yet discovered chromosomes or meiosis. However, we now understand how Mendel's principles are rooted in the events of meiosis. As an example of this, state Mendel's principle of independent assortment and explain how it relates to independent assortment in meiosis.
Part 1: Make a three part process drawing (like a cartoon strip) to demonstrate Mendel’s Principle of Segregation. Use two parents with homologous chromosomes marked with alleles “A” and “a”.
Circle and label these three action parts of the Principle of Segregation: a) parents are diploid, b) alleles separate to form haploid gametes (indicate when this happens), and c) gametes from each parent combine at random to form diploid offspring
Part 2: Use the cross Aa x Aa and a Punnett square to demonstrate Mendel’s Principle of Segregation. Circle and label these three action parts of the Principle of Segregation: a) parents are diploid, b) alleles separate to form haploid gametes and c) gametes from each parent combine at random to form diploid offspring. Write the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios.
When does Mendel’s first law occur of equal segregation occur? Does it occur during mitosis, meiosis I, and/or meiosis II?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 3.4 - Why do scientists design experiments to disprove...Ch. 3.4 - Should Ockhams razor be considered an irrefutable...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 1EGCh. 3.7 - For most cases, a p value of 0.05 is used to...Ch. 3 - Prob. 1CSCh. 3 - Prob. 2CSCh. 3 - Prob. 3CSCh. 3 - Prob. 1QPCh. 3 - Crossing Pea Plants: Mendels Study of Single...Ch. 3 - Crossing Pea Plants: Mendels Study of Single...
Ch. 3 - Prob. 4QPCh. 3 - Crossing Pea Plants: Mendels Study of Single...Ch. 3 - Prob. 6QPCh. 3 - Crossing Pea Plants: Mendels Study of Single...Ch. 3 - Crossing Pea Plants: Mendels Study of Single...Ch. 3 - Crossing Pea Plants: Mendels Study of Single...Ch. 3 - Crossing Pea Plants: Mendels Study of Single...Ch. 3 - Crossing Pea Plants: Mendels Study of Single...Ch. 3 - More Crosses with Pea Plants: The Principle of...Ch. 3 - More Crosses with Pea Plants: The Principle of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 14QPCh. 3 - More Crosses with Pea Plants: The Principle of...Ch. 3 - More Crosses with Pea Plants: The Principle of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 17QPCh. 3 - More Crosses with Pea Plants: The Principle of...Ch. 3 - More Crosses with Pea Plants: The Principle of...Ch. 3 - More Crosses with Pea Plants: The Principle of...Ch. 3 - More Crosses with Pea Plants: The Principle of...Ch. 3 - More Crosses with Pea Plants: The Principle of...Ch. 3 - Meiosis Explains Mendels Results: Genes Are on...Ch. 3 - Meiosis Explains Mendels Results: Genes Are on...Ch. 3 - Meiosis Explains Mendels Results: Genes Are on...Ch. 3 - Prob. 26QPCh. 3 - Prob. 27QPCh. 3 - Variations on a Theme by Mendel A characteristic...Ch. 3 - Prob. 29QPCh. 3 - Variations on a Theme by Mendel Pea plants usually...Ch. 3 - Prob. 31QPCh. 3 - Prob. 32QPCh. 3 - Prob. 33QPCh. 3 - Prob. 34QPCh. 3 - Prob. 35QPCh. 3 - Prob. 36QP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Cystic fibrosis is a recessive human condition. A male with Cystic fibrosis and a woman with a dominant phenotype have sevral children, in which one displays Cystic fibrosis. What can you conclude about the genotype of the maternal parent and what is the probability that a child who does not display Cystic fibrosis is heterozygous?arrow_forwardA couple who are about to get married learn from studying their family histories that, in both their families, theirunaffected grandparents had siblings with cystic fibrosis(a rare autosomal recessive disease).a. If the couple marries and has a child, what is theprobability that the child will have cystic fibrosis?b. If they have four children, what is the chance that thechildren will have the precise Mendelian ratio of 3:1 fornormal:cystic fibrosis?c. If their first child has cystic fibrosis, what is theprobability that their next three children will be normal?arrow_forwardA karyotype shows that a child has Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY). If the child is also colorblind (due to a recessive X-linked allele), despite his parents having normal color vision, in which parent and stage of meiosis did nondisjunction occur? And explain why .arrow_forward
- . When Mendel crossed a large number of tall pea plants with short pea plants, all F1 plants were tall. The F2 generation was created by self-pollinating the F1 plants. Complete a genetic cross of F2 to show the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. State the ratio of phenotypes expected in the F2 offspring. Mendel’s First Law of inheritance states that, “…the alleles of a given locus segregate into separate gametes.” Explain how the genetic diagram above proves this law. (AC 2.1) can i get help please.arrow_forwardThe outcome of Mendel’s law of independent assortment is dependent on how chromosomes are arranged at which phase?arrow_forwardDescribe the Principles of Segregation and Independent Assortment in terms of Genetics. How do these Principles express during Meiosis?arrow_forward
- How did Mendel use evidence from monohybrid and dihybrid crosses to deduce his laws of segregation and independent assortment? How do these laws relate to meiosis?arrow_forwardHow can Mendel's postulates of segregation and independent assortment be explained by meiosis?arrow_forwardWhich of Mendels laws have their basis in separation of homologues in anaphase I?arrow_forward
- In humans, brown eyes (B) are dominant over blue. A brown eyed man marries a blue-eyed (b) woman and they have three children two of whom are brown-eyed and one of whom is blue-eyed. if the male has brown eyes but has a blue-eyed child, what must his genotype be?arrow_forwardHow do events in meiosis explain each of Mendels two laws?arrow_forwardIn cats, there is a gene that codes for fur colour on the X chromosome. One allele gives black fur, and the other gives orange fur. A cat that has one of each allele (heterozygous) has fur that has large patches of orange and large patches of black. This fur colour is called tortoiseshell (A) a) is this strict Mendelian, incomplete dominance, or co-dominance? (Choose only one and explain) b) is it possible for male cats to have the tortoiseshell fur colour? Explain. If a female fruit fly homozygous for white eyes is crossed with a red-eyed male, what percentage of the offspring would have white eyes? (eye colour is x-linked and white is recessive) a) 100% b) 0% c) 50%. d) 25%arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mitochondrial mutations; Author: Useful Genetics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvgXe-3RJeU;License: CC-BY