
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781337115773
Author: Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 40E
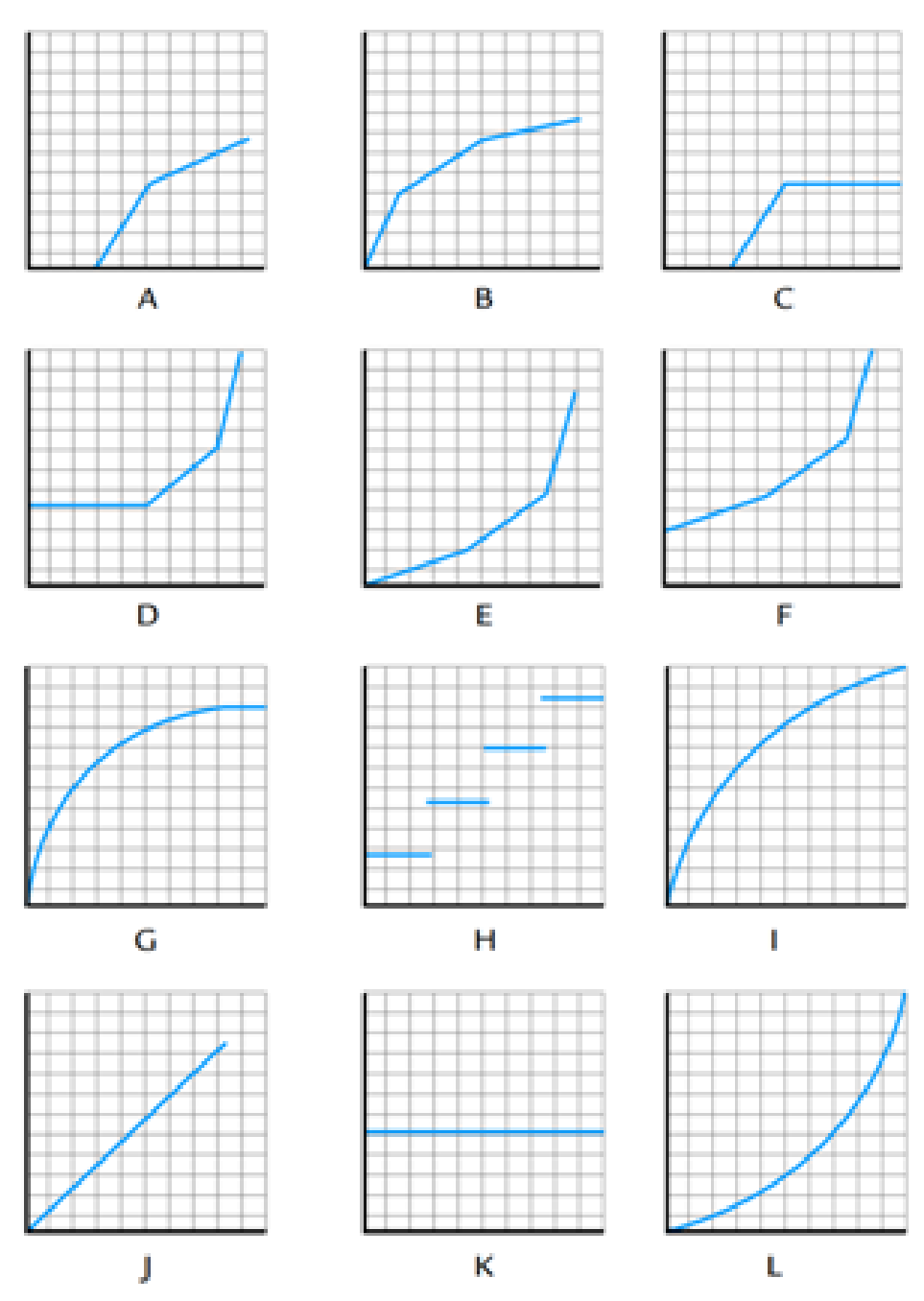
Matching Cost Behavior Descriptions to Cost Behavior Graphs
Select the graph (A through L) that best matches the numbered (1 through 7) italicized descriptions of various cost behavior. For each graph, the vertical (y) axis represents total dollars of cost, and the horizontal (x) axis represents output units during the period. The graphs may be used more than once.
- 1. The cost of depreciation. The asset being
depreciated is a large piece of production machinery equipment where thestraight-line depreciation method is used.letter _________
- 2. The cost of operating a forklift. The forklift is used to move work-in-process inventory in groups of 100 units across the factory floor.
letter _________
- 3. The cost of direct materials. The first 2,000 pounds of direct materials are free because they are donated by the local city government. After that, the direct materials cost consists of a per-unit amount that decreases after a threshold of 2,500 total pounds is reached.
letter _________
- 4. The cost of inspecting finished goods inventory. Each unit is inspected by a quality expert who is paid the same amount for each unit inspected.
letter _________
- 5. The cost of product shipping for all output shipped in the period. The shipping cost per unit decreases with each unit shipped up to a certain number of units, at which time the shipping cost per unit remains constant.
letter _________
- 6. The cost of compliance with Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations. An electric car plant manufactures car batteries. Part of the manufacturing process involves the emission of toxic chemicals into the environment, which is regulated by the EPA in the form of a fee assessed on a per-unit manufactured basis. The per-unit cost of complying with these regulations increases with every fifth battery produced.
letter ______
- 7. The cost of customer energy consumption. The local electric utility company uses a pricing system designed to encourage customers to conserve energy usage. Therefore, the rate per kilowatt-hour that is charged to customers increases with each hour the customer consumes.
letter _______
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Select the graph (A through L) that best matches the numbered (1 through 7) italicized descriptions of various cost behavior. For each graph, the vertical (y) axis represents total dollars of cost,and the horizontal (x) axis represents output units during the period. The graphs may be usedmore than once.1. The cost of depreciation. The asset being depreciated is a large piece of production machinery equipment where the straight-line depreciation method is used.letter ______2. The cost of operating a forklift. The forklift is used to move work-in-process inventory ingroups of 100 units across the factory floor.letter ______3. The cost of direct materials. The first 2,000 pounds of direct materials are free because theyare donated by the local city government. After that, the direct materials cost consists of aper-unit amount that decreases after a threshold of 2,500 total pounds is reached.letter ______4. The cost of inspecting finished goods inventory. Each unit is inspected by a…
Various cost-behavior patterns. (CPA, adapted).
The vertical axes of the graphs below represent total cost, and the horizontal axes represent units produced during a calendar year. In each case, the zero point of dollars and production is at the intersection of the two axes.
Select the graph that matches the numbered manufacturing cost data (requirements 1-9). Indicate by letter
which graph best fits the situation or item described. The graphs may be used more than once.
Annual depreciation of equipment, where the amount of depreciation charged is computed by the machine-hours method.
Electricity bill—a flat fixed charge, plus a variable cost after a certain number of kilowatt-hours are used, in which the quantity of kilowatt-hours used varies proportionately with quantity of units produced.
City water bill, which is computed as follows:
First 1,000,000 gallons or less $1,000 flat fee
Next 10,000 gallons $0.003 per gallon used
Next 10,000 gallons $0.006 per gallon used
Next 10,000…
Identify each of the following costs as either a product cost (PROD) or a period cost (PER). Depreciation—Office equipment.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making
Ch. 3 - Prob. 1DQCh. 3 - What is a driver? Give an example of a cost and...Ch. 3 - Suppose a company finds that shipping cost is...Ch. 3 - Some firms assign mixed costs to either the fixed...Ch. 3 - Explain the difference between committed and...Ch. 3 - Explain why the concept of relevant range is...Ch. 3 - Why do mixed costs pose a problem when it comes to...Ch. 3 - Describe the cost formula for a strictly fixed...Ch. 3 - Describe the cost formula for a strictly variable...Ch. 3 - What is the scattergraph method, and why is it...
Ch. 3 - Describe how the scattergraph method breaks out...Ch. 3 - What are the advantages of the scattergraph method...Ch. 3 - Prob. 13DQCh. 3 - What is meant by the best-fitting line?Ch. 3 - What is the difference between the unit cost of a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 16DQCh. 3 - (Appendix 3A) Explain the meaning of the...Ch. 3 - A factor that causes or leads to a change in a...Ch. 3 - Which of the following would probably be a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3MCQCh. 3 - In the cost formula, the term 128,000,000 a. is...Ch. 3 - In the cost formula, the term 12,000 a. is the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 6MCQCh. 3 - Prob. 7MCQCh. 3 - The following cost formula for total purchasing...Ch. 3 - An advantage of the high-low method is that it a....Ch. 3 - Prob. 10MCQCh. 3 - Prob. 11MCQCh. 3 - Prob. 12MCQCh. 3 - The total cost for monthly supervisory cost in a...Ch. 3 - Yates Company shows the following unit costs for...Ch. 3 - (Appendix 3A) In the method of least squares, the...Ch. 3 - Creating and Using a Cost Formula Big Thumbs...Ch. 3 - Using High-Low to Calculate Fixed Cost, Calculate...Ch. 3 - Using High-Low to Calculate Predicted Total...Ch. 3 - Using High-Low to Calculate Predicted Total...Ch. 3 - Using Regression to Calculate Fixed Cost,...Ch. 3 - Inventory Valuation under Absorption Costing Refer...Ch. 3 - Inventory Valuation under Variable Costing Refer...Ch. 3 - Absorption-Costing Income Statement Refer to the...Ch. 3 - Variable-Costing Income Statement Refer to the...Ch. 3 - Creating and Using a Cost Formula Kleenaire Motors...Ch. 3 - Using High-Low to Calculate Fixed Cost, Calculate...Ch. 3 - Using High-Low to Calculate Predicted Total...Ch. 3 - Brief Exercise 3-28 Using High-Low to Calculate...Ch. 3 - Using Regression to Calculate Fixed Cost,...Ch. 3 - Inventory Valuation under Absorption Costing Refer...Ch. 3 - Inventory Valuation under Variable Costing Refer...Ch. 3 - Brief Exercise 3-32 Absorption-Costing Income...Ch. 3 - Brief Exercise 3-33 Variable-Costing Income...Ch. 3 - Variable and Fixed Costs What follows are a number...Ch. 3 - Cost Behavior, Classification Smith Concrete...Ch. 3 - Prob. 36ECh. 3 - Prob. 37ECh. 3 - Prob. 38ECh. 3 - Step Costs, Relevant Range Bellati Inc. produces...Ch. 3 - Matching Cost Behavior Descriptions to Cost...Ch. 3 - Examine the graphs in Exercise 3-40. Required: As...Ch. 3 - Prob. 42ECh. 3 - Prob. 43ECh. 3 - High-Low Method Refer to the information for Luisa...Ch. 3 - Scattergraph Method Refer to the information for...Ch. 3 - Method of Least Squares Refer to the information...Ch. 3 - Use the following information for Exercises 3-47...Ch. 3 - Use the following information for Exercises 3-47...Ch. 3 - Method of Least Squares, Developing and Using the...Ch. 3 - The method of least squares was used to develop a...Ch. 3 - Identifying the Parts of the Cost Formula;...Ch. 3 - Inventory Valuation under Absorption Costing...Ch. 3 - Inventory Valuation under Variable Costing Lane...Ch. 3 - Income Statements under Absorption and Variable...Ch. 3 - (Appendix 3A) Method of Least Squares Using...Ch. 3 - (Appendix 3A) Method of Least Squares Using...Ch. 3 - Identifying Fixed, Variable, Mixed, and Step Costs...Ch. 3 - Identifying Use of the High-Low, Scattergraph, and...Ch. 3 - Identifying Variable Costs, Committed Fixed Costs,...Ch. 3 - Scattergraph, High-Low Method, and Predicting Cost...Ch. 3 - Method of Least Squares, Predicting Cost for...Ch. 3 - Cost Behavior, High-Low Method, Pricing Decision...Ch. 3 - Prob. 63PCh. 3 - Variable and Fixed Costs, Cost Formula, High-Low...Ch. 3 - Cost Separation About 8 years ago, Kicker faced...Ch. 3 - Variable-Costing and Absorption-Costing Income...Ch. 3 - Refer to the information for Farnsworth Company...Ch. 3 - (Appendix 3A) Scattergraph, High-Low Method,...Ch. 3 - (Appendix 3A) Separating Fixed and Variable Costs,...Ch. 3 - (Appendix 3A) Cost Formulas, Single and Multiple...Ch. 3 - Suspicious Acquisition of Data, Ethical Issues...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The cost behavior patterns below are lettered A through H. The vertical axes of the graphs represent total dollars of expense, and the horizontal axes represent production in units, machine hours, or direct labor hours. In each case, the zero point is at the intersection of the two axes. Each graph may be used no more than once. Required: Select the graph that matches the lettered cost described here. a. Depreciation of equipmentthe amount of depreciation charged is computed based on the number of machine hours that the equipment was operated. b. Electricity billflat fixed charge, plus a variable cost after a certain number of kilowatt hours are used. c. City water billcomputed as follows: d. Depreciation of equipmentthe amount is computed by the straight-line method. e. Rent on a factory building donated by the citythe agreement calls for a fixed fee payment, unless 200,000 labor hours are worked, in which case no rent need be paid. f. Salaries of repair workersone repair worker is needed for every 1,000 machine hours or less (i.e., 0 to 1,000 hours requires one repair worker, 1,001 to 2,000 hours requires two repair workers, etc.).arrow_forwardScattergraph method Using the data in P4-2 and a piece of graph paper: 1. Plot the data points on the graph and draw a line by visual inspection, indicating the trend shown by the data points. 2. Determine the variable cost per unit and the total fixed cost from the information on the graph. 3. Determine the variable cost to be charged to the product for the year. 4. Determine the fixed cost to be charged to factory overhead for the year. 5. Do these answers agree with the answers to P4-2? Why or why not?arrow_forwardUsing the data in P4-2 and Microsoft Excel: 1. Separate the variable and fixed elements. 2. Determine the cost to be charged to the product for the year. 3. Determine the cost to be charged to factory overhead for the year. 4. Determine the plotted data points using Chart Wizard. 5. Determine R2. 6. How do these solutions compare to the solutions in P4-2 and P4-3? 7. What does R2 tell you about this cost model?arrow_forward
- To determine the effect of different levels of production on the company’s income, move to cell B7 (Actual production). Change the number in B7 to the different production levels given in the table below. The first level, 100,000, is the current level. What happens to the operating income on both statements as production levels change? Enter the operating incomes in the following table. Does the level of production affect income under either costing method? Explain your findings.arrow_forwardIdentify each of the following costs as either a product cost (PROD) or a period cost (PER). Depreciation—Factory equipment.arrow_forwardClassify each of the following as direct or indirect with respect to traceability to product and as variable or fixed with respect to whether the costs fluctuate in total as volume of production changes over wide ranges. Explain your classifications. 1. The cost of components that are assembled into a final product. 2. The cost of supplies consumed when maintenance is performed on machines. 3. The wages of machine operators who work on only one product. 4. The cost of training mechanics who service processing machinery. Question content area bottom Part 1 1. The cost of components that are assembled into a final product. Classification Explanationarrow_forward
- Which one of the following accounts is an asset similar to work-in-process inventory? Group of answer choices Construction in Progress Cost of Construction Billings in Excess of Cost Revenue from Long-Term Contractsarrow_forward(a) Calculate the amount of direct materials purchased during the period. (b) Calculate the cost of goods manufactured during the period. (c) Calculate the total manufacturing overhead cost for the period. (d) Calculate the total manufacturing cost for the period.arrow_forwardCost classifications For each of the following costs, check the columns that most likely apply (both variable and fixed might apply for some costs).Product Costs Direct Indirect Period Variable FixedWages of assembly-line workersDepreciation of plant equipmentGlue and threadOutbound shipping costsRaw materials handling costsSalary of public relations managerProduction run setup costsPlant utilitiesElectricity cost of retail storesResearch and developmentexpensearrow_forward
- question is in image. Required: Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold. Prepare an income statement. Build a spreadsheet: Construct an Excel spreadsheet to solve all of the preceding requirements. Show how both cost schedules and the income statement will change if the following data change: direct labor is $390,000 and utilities cost $35,000.arrow_forwardWhich of the following is an example of a cost that varies in proportion to changes in the activity base? Depreciation on machinery Packaging cost Factory rent Insurance costarrow_forwardWhich of the following correctly describes the term cost driver? a.The primary factor which is correlated with the amount of cost incurred to produce a product b.The total material, labor, and overhead cost of a completed job c.The inflation rate which causes costs to rise d.The initial purchase price of direct materialsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...
Accounting
ISBN:9781337115773
Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:South-Western College Pub

Excel Applications for Accounting Principles
Accounting
ISBN:9781111581565
Author:Gaylord N. Smith
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Cost Classifications - Managerial Accounting- Fixed Costs Variable Costs Direct & Indirect Costs; Author: Accounting Instruction, Help, & How To;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QQd1_gEF1yM;License: Standard Youtube License