
(a)
Interpretation:
The equation for the calibration curve, standard deviations of the slope, intercept from the data of doxorubicin by LIF, its peak value and the R2 value needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The standard deviation is to tell how the measurements of group are spread out from average. In other words, it defines how far a set of numbers lie apart. If the value obtained is low, it means that most of the numbers are close to average, but if the value obtained is high, it means the number are spread out.
Answer to Problem 30.12QAP
The standard deviation of m is 0.015813, standard deviation of intercept is 0.374481. The value of R2 is 0.99821.
Explanation of Solution
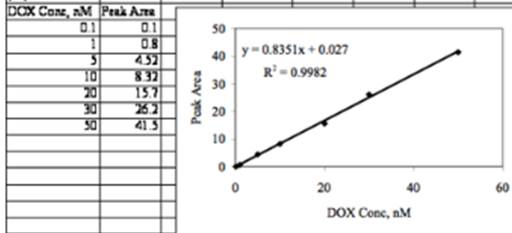
The graphical representation is as below:
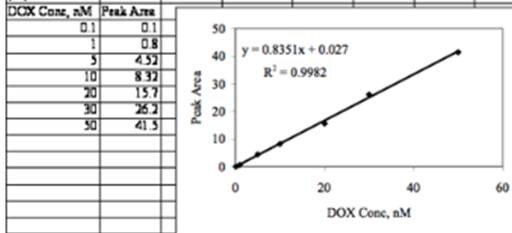
From the equation of straight line,
Slope m = 0.835066
Intercept, b = 0.026972
Standard deviation of m= 0.015813
Standard deviation of b = 0.374481
R2 = 0.99821
(b)
Interpretation:
The equation should be rearranged, and concentration should be expressed in terms of measured area.
Concept introduction:
For a straight-line curve, the equation is represented as follows:
Here, m is slope of the graph and c is intercept of the graph.
Answer to Problem 30.12QAP
The measured area
Explanation of Solution
The equation obtained from graph is
And the equation of the line is
Where,
y is represented as y − intercept and the x is represented as x- intercept
m = slope of line
c = constant value
The rearrangement is done to convert in terms of measured area which is represented by the x −intercept or by x, and it arrives as,
(c)
Interpretation:
The LOD in terms of moles needs to be determined, if the LOD for DOX is
Concept introduction:
Laser induced fluorescence is spectroscopic method in which a molecule is excited to higher energy level by absorbing light. It helps to study the structure of molecule.
Answer to Problem 30.12QAP
LOD in moles is
Explanation of Solution
LOD =
V (pL) = 100
V (L) =
The LOD in terms of moles is calculated by dividing the LOD value with injection volume in liter. This is given as-
Hence, LOD (in moles) =
(d)
Interpretation:
The concentrations and standard deviations of the unknown DOX injected needs to be determined, if the peaks of two DOX unknown samples injected is 11.3 and 6.97.
Concept introduction:
The laser induced fluorescence is method wherein atoms or molecules is excited by passing laser light that excites them to higher energy levels releasing light spontaneously. It is useful in studying the structure of molecules.
Answer to Problem 30.12QAP
Standard deviation of peak 1 is 0.91 and standard deviation of peak 2 is 0.92.
Explanation of Solution
The graphical representation is −
Peak 1 = 11.3
Peak 2 = 6.97
Concentration of peak 1 is 13.49956.
Standard deviation is 0.90802029.
Concentration of peak 2 is 8.314343.
Standard deviation is 0.92408899.
(e)
Interpretation:
The time required for applied voltage to be doubled needs to be determined, if the DOX concentration is 300s. Also, the time needs to be determined, if the capillary length is doubled.
Concept introduction:
The laser induced fluorescence is method wherein atoms or molecules is excited though passing a laser light that excites them to higher energy levels releasing light spontaneously. It is useful in studying the structure of molecules.
Answer to Problem 30.12QAP
The time is halved if voltage is doubled. Its value is 150s.
The time is doubled if capillary length is doubled. Its value is 600s.
Explanation of Solution
Consider the equation,
Where L=length of detector, Lt is total length,
From the equation, it is seen that time and voltage are inversely proportional. Hence, if the voltage is increased two times, then the time is halved.
Given, time is 300s, and then Voltage is 150s.
From the equation it is seen that time and lengths are directly proportional. Hence, if length is doubled, then time is also doubled.
Given 300 s and if it is doubled it becomes, 600s, therefore the time is 600s.
(f)
Interpretation:
The value of N if the capillary length is doubled at the same voltage and the value of N if the applied voltage is doubled with same capillary length.
Concept introduction:
The laser induced fluorescence involves excitation of molecules or atoms to higher energy levels releasing light spontaneously through passing of laser light. It is useful in studying the structure of molecules.
Answer to Problem 30.12QAP
The value of N is 50,000 if the capillary length is doubled at same voltage.
The value of N is 200,000 if the voltage is doubled at same capillary length.
Explanation of Solution
Consider equation,
Where
Given, plate count as 100,000.
From the given equation, the value of N is inversely proportional to total length. Hence, if the capillary length is doubled, the plate count is halved.
Therefore, N = 50,000.
Given plate count as 100,000.
From the given equation, the value of N is directly proportional to voltage; hence if voltage is doubled the value of N would also double. Hence, N =200,000.
(g)
Interpretation:
The plate height for capillary with N=100,000 for 40.6cm long capillary having diameter of 50µm needs to be determined.
Concept introduction:
The laser induced fluorescence involves excitation of molecules or atoms to higher energy levels releasing light spontaneously through passing of laser light. It is useful in studying the structure of molecules.
Answer to Problem 30.12QAP
The plate height is
Explanation of Solution
Consider equation,
Where Lt is total length and N is the number of theoretical plates.
Given value of Lt as 40.6 cm and N as 100,000. Substitute in equation above,
Hence, the value of H is
(h)
Interpretation:
The value of variance
Concept introduction:
The laser induced fluorescence involves excitation of molecules or atoms to higher energy levels releasing light spontaneously through passing a laser light. It is useful in studying the structure of molecules.
Answer to Problem 30.12QAP
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Consider equation,
Where Lt is total length, H is the plate height and
Given value of Lt as 40.6 cm and H is
Hence, the value of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- a. Calculate the Coulombic (ionic) interaction energy between atoms for the C=O ∙∙∙H-N hydrogen bond in a peptide at a distance of 1.5Å in units of kJ/mol. Assume that the partial charge on O is −0.434, the partial charge on H is +0.417 and the permittivity(Er) of the protein environment is 6. b. The dipole moment of an individual peptide group is approximately 3.46 D. Assuming that the dipoles line up linearly estimate the energy of interaction (in kJ.mol) of the hydrogen bond in Q1 using a dipole-dipole model. please help me! this is for an upper division physical chemistry course, so showing work would be appreciatedarrow_forwardAssume that for the reaction XTP <> XDP + Pi, the Keq =272024 (dimensionless). Calculate the standard free energy change (delta Go) for the synthesis of XTP from XDP and Pi at 41.4oC in J/mol to six significant figures. Thank you for your assistancearrow_forwardGive clear handwritten answer on the white paper please!arrow_forward
- plz asap give typed answer with step by step explanationarrow_forwardDiscuss the measurement and use of the terms pi and sigma in the study of quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSARs) for a range of substituted aromatic drug analogues.arrow_forwardAnswer Q 26, 27 & 28 explaining detailly your workingarrow_forward
 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning


