
Interpretation:
The meaning of electroosmotic flow and the reason for itsoccurrence needs to be explained.
Concept introduction:
When electric field is applied in a liquid, the ions present in the liquid moves under the influence of potential gradient. This flow of liquid is termed as electroosmotic flow. It is most obvious is those having small channels. It occurs in buffered solutions and natural water.
Answer to Problem 30.1QAP
Electroosmotic flow of liquid is caused by gradient in potential across the capillary tube on the flowing liquid that has dissolved ions. This is caused when the capillary walls get electrically charged.
Explanation of Solution
When a capillary tube is filled with fluid having dissolved ions, and electrical field is applied, the buffer ions move to respond to the electrical charges. As the solvent which is water is neutral, it remains stationary and the fluid ions move towards its electrodes with respect to the charges applied. Below is depiction of movement of electrons:
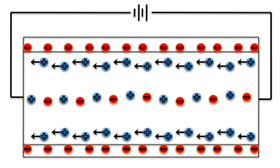
There is coulombic force induced by charges of ions in the solution wherein its net mobile charge causes electroosmotic flow. During this process of maintaining
Electroosmotic flow of liquid is caused due to a potential gradient across the capillary tube on the flowing liquid containing dissolved ions. This is caused when the capillary walls get electrically charged due to the application of electric field from outside.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- For weak electrolytes, how can molar conductance be used to determine the degree of dissociation?arrow_forwardA solution of common salt in water is prepared by adding 50kg of salt to 200kg of water tomake a liquid density of 1250kg/m3. Calculate the concentration of salt in this solution as a: i) Weight(w/w)fraction (Ans: weight fraction 20%)arrow_forwardThe molar conductivity of a 1.5 M solution of an electrolyte is found to be 138.9 S cm2mol-1. Calculate the conductivity of the solution.arrow_forward
- The osmotic pressure of a solution of polystyrene in toluene (methylbenzene} was measured at 25 °C with the following results:c/(g dm-3) 2.042 6.613 9.521 12.602∏/Pa 58.3 188.2 270.8 354.6Determine the molar mass of the polymer.arrow_forwardYou are asked to calculate molar conductivity of a NaCl solution with a concentration of 0.03125 mol/L according to the following equation, where χ is the conductivity and is 1.41x10-3 (±0.02) ohm^-1 cm^-1 and C is the concentration of the solution. The uncertainty of the volume measurement in determining concentration is given as ±0.02 and the mole value is given with no significant error. Calculate molar conductivity in ohm^-1 cm2mol^-1 and give your result with necessary significant figures.arrow_forwardWhat is the kinetic property observed in suspension? What is the optical property observed in solutions?arrow_forward
- draw and sketch a group for action poyential polarization phases with membrane potential vm in milivoltsarrow_forwardSuppose the concentration of a solute varies along the length of a container according to c(x) = c0 - βc0x2, where c0 is the concentration at x = 0. Calculate the thermodynamic force on the solute at 25 °C and x = 8 cm and 16 cm given that the concentration falls to 1/2c0 when x = 15 cm. Hint: Start by finding the value of β.arrow_forwardThe diffusion coefficient of water molecules in hydrogen (the carrier gas) at 307 k and 1 atm is 1 cm2/sec. What is the average time that the water molecules to travel a distance of 1 mm in the gas chromatographic system? Assuming there no interactions between water and the system.arrow_forward
- 1. A hypothetical three component system has a composition of 24% A, 40% B and 36% C. Plot this composition in a Roozeboom diagram.arrow_forwardCalculate the gravimetric factor of: FeO in Fe2O3 Bi2S3 in BaSO4 BaSO4 in (NH4)2SO4 Mn2O3 in Mn3O4 NOTE: Present complete solution and include the detailed computation of the molecular weight. Express your final answers up to FOUR decimal places.arrow_forwardThe molar conductivity at infinite dilution of hydrobromic acid, sodium acetate, & sodium bromide at 298 K are 520.1 Scm2mol-1, 105.9 Scm2mol-1, and 186.3 Scm2mol-1, respectively. Determine the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of acetic acid.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





