
A particle moves according to a law of motion s = f(t), t ≥ 0, where t is measured in seconds and s in feet.
(a) Find the velocity at time t.
(b) What is the velocity after 1 second?
(c) When is the particle at rest?
(d) When is the particle moving in the positive direction?
(e) Find the total distance traveled during the first 6 seconds.
(f) Draw a diagram like Figure 2 to illustrate the motion of the particle.
(g) Find the acceleration at time t and after 1 second.
(h) Graph the position, velocity, and acceleration functions for 0 ≤ t ≤ 6.
(i) When is the particle speeding up? When is it slowing down?
FIGURE 2
f(t) = sin(πt/2)
(a)
To find: The velocity at time t.
Answer to Problem 3E
The velocity at time is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The given equation is as below.
Calculation:
Calculate the velocity at time
Differentiate the equation (1) with respect to time.
Therefore, the velocity at time
(b)
To find: The velocity after 1 second.
Answer to Problem 3E
The velocity after 1 second is
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the velocity after 1 second.
Substitute 1 for
Therefore, the velocity after 1 second is
(c)
To find: The time when particle at rest.
Answer to Problem 3E
The particle never is at rest when
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the time when particle will be at rest.
The velocity will be zero, when the particle is at rest.
Substitute 0 for
Here,
(d)
To find: The particle moving in the positive direction.
Answer to Problem 3E
The velocity of particle always moves in positive direction when
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the time at which the particle will be moving in the positive direction.
The particle will move in positive direction when
(e)
To find: The total distance traveled during the first 6 seconds.
Answer to Problem 3E
The total distance travelled during first 6 second is
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the total distance traveled during first 6 seconds.
Here, the velocity changes from 1, 3 and 5 which appears in the interval of [0,6].
Substitute 1 and 0 for
The total distance travelled is as below.
Therefore, the total distance travelled during first 6 seconds is
(f)
To find: The diagram to illustrate the motion of the particle.
Answer to Problem 3E
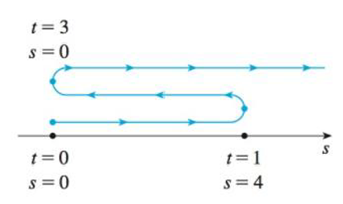
The diagram to illustrate the motion of particle is shown in the figure (1).
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the distance s using the expression.
Substitute 0 for
Calculate the value of t and s as shown in the table (1).
| t | s |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 3 | -1 |
| 5 | 1 |
| 6 | 0 |
Show the diagram to illustrate the motion of the particle as shown below in figure (1).
(g)
To find: The acceleration at time t and after 1 second.
Answer to Problem 3E
The acceleration at time is
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the acceleration at any time t.
Differentiate the equation (2) with respect to t.
Therefore, the acceleration at any time is
Calculate the acceleration after 1 second.
Substitute 1 for
Therefore, the acceleration after 1 second is
(h)
To sketch: The graph the position, velocity, and acceleration function for
Answer to Problem 3E
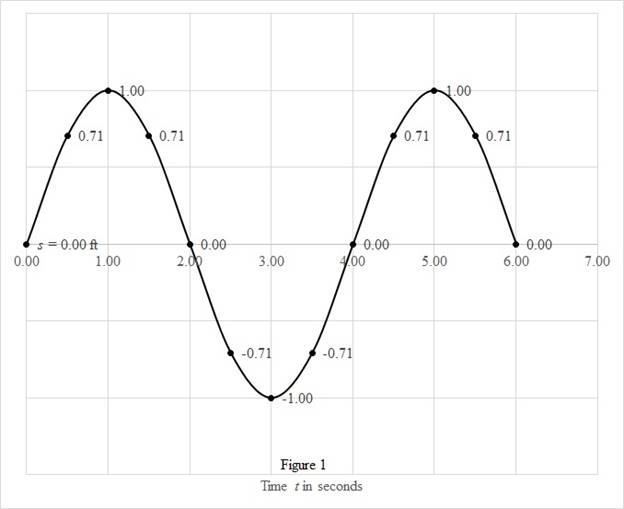
The position, velocity, and acceleration functions are plotted for time limits
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the position with respect to time using the formula.
Substitute 0 for
Similarly, calculate the remaining values.
Calculate the value of
| 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 0.50 | 0.71 |
| 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 1.50 | 0.71 |
| 2.00 | 0.00 |
| 2.50 | -0.71 |
| 3.00 | -1.00 |
| 3.50 | -0.71 |
| 4.00 | 0.00 |
| 4.50 | 0.71 |
| 5.00 | 1.00 |
| 5.50 | 0.71 |
| 6.00 | 0.00 |
Calculate the velocity using the expression.
Substitute 0 for
Similarly, calculate the remaining values.
Calculate the value of
| 0.00 | 1.57 |
| 0.50 | 1.11 |
| 1.00 | 0.00 |
| 1.50 | -1.11 |
| 2.00 | -1.57 |
| 2.50 | -1.11 |
| 3.00 | 0.00 |
| 3.50 | 1.11 |
| 4.00 | 1.57 |
| 4.50 | 1.11 |
| 5.00 | 0.00 |
| 5.50 | -1.11 |
| 6.00 | -1.57 |
Calculate the acceleration using the formula.
Substitute 0 for
Similarly, calculate the remaining values.
Calculate the value of
| 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 0.50 | -1.74 |
| 1.00 | -2.47 |
| 1.50 | -1.74 |
| 2.00 | 0.00 |
| 2.50 | 1.74 |
| 3.00 | 2.47 |
| 3.50 | 1.74 |
| 4.00 | 0.00 |
| 4.50 | -1.74 |
| 5.00 | -2.47 |
| 5.50 | -1.74 |
| 6.00 | 0.00 |
Draw the position as a function of time curve as shown in the Figure (2).

Draw the speed as a function of time curve as shown in the figure (3).

Draw the acceleration as a function of time curve as shown in the figure (4).

(i)
To find: The time when the particle is speeding up and slowing down.
Answer to Problem 3E
The acceleration is negative when the value of time is
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the time when particle speeding up and slowing down.
Substitute 0 for
Here, variable
Therefore, the acceleration is negative when the value of time is
Chapter 3 Solutions
Single Variable Calculus: Concepts and Contexts, Enhanced Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Calculus Early Transcendentals, Binder Ready Version
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals, Single Variable (3rd Edition)
Calculus, Single Variable: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Thomas' Calculus: Early Transcendentals (14th Edition)
Precalculus: A Unit Circle Approach
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





