
Balance Sheet and Notes Listed here in random order are Wicks Construction Limited’s balance sheet accounts and related ending balances as of December 31, 2019:
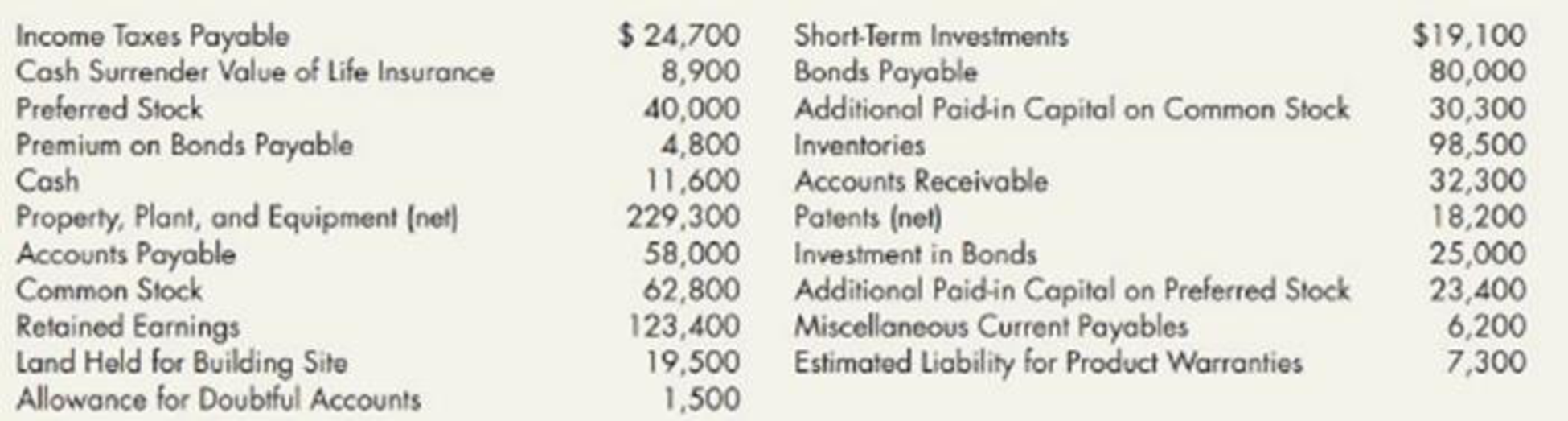
Additional information:
- 1. The company reports on the balance sheet the total amount for inventories and the net book value of property, plant, and equipment, with the related details for each account disclosed in notes.
- 2. The
straight line method is used todepreciate buildings, machinery, and equipment, based upon their cost and estimated residual value’s and lives. A breakdown of property, plant, and equipment shows the following: land at a cost of $32,000, buildings at a cost of $182,400 and a net book value of $120,200, machinery at a cost of $63,900, and relatedaccumulated depreciation of $18,600, and equipment (40% depreciated) at a cost of $53,000. - 3. Patents are amortized on a straight line basis directly to the Patent account.
- 4. Inventories are listed at the lower of cost or market value using an average cost. The inventories include raw-materials, $22,200; work in process, $34,700; and finished goods, $41,600.
- 5. Common stock has a $10 par value per share, 12,000 shares are authorized, and 6,280 shares have been issued.
- 6.
Preferred stock has a $100 par value per share, 1,000 shares are authorized, and 400 shares have been issued. - 7. The investment in bonds is carried at the original cost, which is the face value, and is being held to maturity.
- 8. Short-term investments in marketable securities were purchased at year-end.
- 9. The bonds payable mature on December 31, 2024.
- 10. The company attaches a 1-year warranty on all the products it sells.
Required:
- 1. Prepare Wicks Construction’s December 31, 2019, balance sheet (including appropriate parenthetical notations).
- 2. Prepare notes to accompany the balance sheet that itemize company accounting policies; inventories; and property, plant, and equipment.
- 3. Next Level Compute the
current ratio and the quick ratio. How do these two ratios provide different information about the company’s liquidity? Why are these ratios useful?
1.
Prepare the balance sheet of Company W for December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity.
The balance sheet of company W is prepared as follows:
| Company W | |||
| Balance Sheet | |||
| December 31,2019 | |||
| Current Assets: | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | $11,600 | ||
| Short-term investments in marketable securities [Refer to subpart 2 (note 1)] | $19,100 | ||
| Accounts receivable | $32,300 | ||
| Less: Allowance for doubtful accounts | ($1,500) | $30,800 | |
| Inventories [Refer to subpart 2 (Notes 1 and 2) ] | $98,500 | ||
| Total current assets | $160,000 | ||
| Long-Term Investments: | |||
| Investment in bonds [Refer to subpart 2 (note 1)] | $25,000 | ||
| Land held for building site | $19,500 | ||
| Cash surrender value of life insurance | $8,900 | ||
| Total long-term investments | $53,400 | ||
| Property, plant, and equipment [Refer to subpart 2 (Notes 1 and 3) ] | $229,300 | ||
| Intangible Assets: | |||
| Patents (net) [Refer to subpart 2 (Notes 1 and 2) ] | $18,200 | ||
| Total Assets | $460,900 | ||
| Liabilities | |||
| Current Liabilities: | |||
| Accounts payable | $58,000 | ||
| Income taxes payable | $24,700 | ||
| Miscellaneous current payables | $6,200 | ||
| Estimated liability for product warranties | $7,300 | ||
| Total current liabilities | $96,200 | ||
| Long-Term Liabilities: | |||
| Bonds payable (mature on 12/31/2024) | $80,000 | ||
| Premium on bonds payable | $4,800 | ||
| Total long-term liabilities | $84,800 | ||
| Total Liabilities | $181,000 | ||
| Shareholders’ Equity | |||
| Contributed Capital: | |||
| Preferred stock, $100 par, 1,000 shares authorized, 400 shares issued | $40,000 | ||
| Common stock, $10 par, 12,000 shares authorized, 6,280 shares issued | $62,800 | ||
| Additional paid-in capital on: | |||
| Preferred stock | $23,400 | ||
| Common stock | $30,300 | ||
| Total contributed capital | $156,500 | ||
| Retained earnings | $123,400 | ||
| Total Shareholders’ Equity | $279,900 | ||
| Total Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity | $460,900 | ||
Table (1)
Therefore, the amount of total assets and total liabilities and stockholders’ equity equals $460,900.
2.
Prepare notes to accompany the balance sheet that itemize company accounting policies, inventories, and property, plant and equipment.
Explanation of Solution
Accompanying Notes to the balance sheet:
Note (1):
Summary of important accounting policies:
- Inventories are valued at the lower of average cost or market.”.
- Property, plant, and equipment are recorded at cost less accumulated depreciation. The straight-line method is used to depreciate all property, plant, and equipment, except land”.
- Patents are amortized on a straight-line basis directly to the Patent account”.
- Temporary investments in marketable securities are stated at their market value”.
- Investment in bonds is carried at original cost (face value) and is being held to maturity”.
Note (2):
Composition of inventories:
The inventories of the company as of December 31, 2019, are composed of the following components:
| Particulars | Amount |
| Raw materials | $22,200 |
| Work in process | $34,700 |
| Finished goods | $41,600 |
| Total | $98,500 |
Table (2)
Note (3)
Composition of property, plant, and equipment:
The property, plant, and equipment of the company as of December 31, 2019, comprise the following:
| Item | Cost | Accumulated Depreciation | Book value |
| Land | $32,000 | $32,000 | |
| Buildings | $182,400 | $62,200 | $120,000 |
| Machinery | $63,900 | $18,600 | $45,300 |
| Equipment | $53,000 | $21,200 | $31,800 |
| Total | $331,300 | $102,000 | $229,300 |
Table (3)
3.
Compute the current ratio and the quick ratio, state the way in which the two ratios provide different information about the liquidity of the company and explain the way in which these ratios are useful.
Explanation of Solution
Current ratio: The financial ratio which evaluates the ability of a company to pay off the debt obligations which mature within one year or within completion of operating cycle is referred to as current ratio. This ratio assesses the liquidity of a company.
Quick ratio: The financial ratio which evaluates the ability of a company to pay off the instant debt obligations is referred to as quick ratio. Quick assets are cash, marketable securities, and accounts receivables. This ratio assesses the short-term liquidity of a company from its most liquid (quick) assets.
Calculate the current ratio:
Therefore, the current ratio is 1.66:4.
Compute quick ratio:
Therefore, the quick ratio is 0.64:1.
- Current ratio evaluates the liquidity
- Quick ratio analyzes a company’s potential working capital.
- Comparison of these two ratios states the amount of liquidity that comes from the inventory, which is not as liquid as the quick assets.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
- Comprehensive: Balance Sheet, Schedules, and Notes The following is an alphabetical listing of Stone Boat Companys balances sheet accounts and account balances on December 31, 2019: Additional information: 1. The company reports on the balance sheet the net book value of property and equipment and long-term liabilities (known as control accounts). The related details are disclosed in the notes. 2. The straight-line method is used to depreciate property and equipment based upon cost, estimated residual value, and estimated life. The costs of the assets in this account are: land, 29,500; buildings, 164,600; store fixtures, 72,600; and office equipment, 30,000. 3. The accumulated depreciation breakdown is as follows: buildings, 54,600; store fixtures, 37,400; and office equipment, 17,300. 4. The long term debt includes 12%, 36,000 face value bonds that mature on December 31, 2024, and have an unamortized bond discount of 1,000; 11%, 48,000 face value bonds that mature on December 31, 2025, have a premium on bonds payable of 1,800, and whose retirement is being funded by a bond sinking fund; and a 13% note payable that has a face value of 6,200 and matures on January 1, 2022. 5. The non-interest-bearing note receivable matures on June 1, 2023. 6. Inventory is listed at lower of cost or market; cost is determined on the basis of average cost. 7. The investment in affiliate is carried at cost. The company has guaranteed the interest on 12%, 50,000, 15-year bonds issued by this affiliate, Jay Company. 8. Common stock has a 10 par value per share, 10,000 shares are authorized, and 1,000 shares were issued during 2019 at a price of 13 per share, resulting in 8,000 shares issued at year-end. 9. Preferred stock has a 50 par value per share, 2,000 shares are authorized, and 140 shares were issued during 2019 at a price of 55 per share, resulting in 640 shares issued at year-end. 10. On January 15, 2020, before the December 31, 2019, balance sheet was issued, a building with a cost of 20,000 and a book value of 7,000 was totally destroyed. Insurance proceeds will amount to only 5,000. 11. Net income and dividends declared and paid during the year were 50,500 and 21,000, respectively. Required: 1. Prepare Stone Boats December 31, 2019, balance sheet (including appropriate parenthetical notations). 2. Prepare a statement of shareholders equity for 2019. (Hint: Work back from the ending account balances.) 3. Prepare notes that itemize the balance sheet control accounts and those necessary to disclose any company accounting policies, contingent liabilities, and subsequent events. 4. Next Level Compute the debt-to-assets ratio at the cud of 2019. What is your evaluation of this ratio if it was 39% at the end of 2018? Use the following information for P415 and P416: McCormick Company, Inc. is one of the worlds leading producers of spices, herbs, seasonings, condiments, and other flavorings for foods. Its products are sold to consumers, with sonic of the leading brands of spices and seasonings, as well as to industrial producers of foods. McCormicks consolidated balance sheets for 20X2 and 20X3 follow.arrow_forwardOn December 31, 2019, Vail Company owned the following assets: Vail computes depreciation and amortization expense to the nearest whole year. During 2020, Vail engaged in the following transactions: Required: 1. Check the accuracy of the accumulated depreciation balances at December 31, 2019. Round to the nearest whole dollar in all requirements. 2. Prepare journal entries to record the preceding events in 2020, as well as the year-end recording of depreciation expense. 3. Prepare an Accumulated Depreciation account for each category of assets, enter the beginning balance, post the journal entries from Requirement 2, and compute the ending balance.arrow_forwardSoon after December 31, 2019, the auditor requested a depreciation schedule for trucks of Jarrett Trucking Company, showing the additions, retirements, depreciation, and other data affecting the income of the company in the 4-year period 2016 to 2019, inclusive. The following data were in the Trucks account as of January 1, 2016: The Accumulated DepreciationTrucks account, previously adjusted to January 1,2016, and duly entered in the ledger, had a balance on that date of 16,460. This amount represented the straight-line depreciation on the four trucks from the respective dates of purchase, based on a 5-year life and no residual value. No debits had been made to this account prior to January 1, 2016. Transactions between January 1,2017, and December 31, 2019, and their record in the ledger were as follows: 1. July 1, 2016: Truck no. 1 was sold for 1,000 cash. The entry was a debit to Cash and a credit to Trucks, 1,000. 2. January 1, 2017: Truck no. 3 was traded for a larger one (no. 5) with a 5-year life. The agreed purchase price was 12,000. Jarrett paid the other company 1,780 cash on the transaction. The entry was a debit to Trucks, 1,780, and a credit to Cash, 1,780. 3. July 1, 2018: Truck no. 4 was damaged in a wreck to such an extent that it was sold as junk for 50 cash. Jarrett received 950 from the insurance company. The entry made by the bookkeeper was a debit to Cash, 1,000, and credits to Miscellaneous Revenue, 50, and Trucks, 950, 4. July 1, 2018: A new truck (no. 6) was acquired for 20,000 cash and debited at that amount to the Trucks account. The truck has a 5-year life. Entries for depreciation had been made at the close of each year as follows: 2016, 8,840; 2017, 5,436; 2018, 4,896; 2019, 4,356. Required: 1. Next Level For each of the 4 years, calculate separately the increase or decrease in earnings arising from the companys errors in determining or entering depreciation or in recording transactions affecting trucks. 2. Prove your work by one compound journal entry as of December 31, 2019; the adjustment of the Trucks account is to reflect the correct balances, assuming that the books have not been closed for 2019.arrow_forward
- Investing Activities and Depreciable Assets Verlando Company had the following account balances and information available for 2019: During 2019, Verlando recorded the following transactions affecting these accounts: a. Land with a carrying value of 35,000 was sold at a loss of 6,000. b. Land and equipment were purchased with cash during the period. c. Equipment with an original cost of 20,000 that had a book value of 4,000 was written off as obsolete. d. A building with an original cost of 60,000 and accumulated depreciation of 25,000 was sold at a 23,000 gain. e. Depreciation expense and amortization expense were recorded. f. Net income for the year was 60,000. g. A patent was acquired during the year in exchange for 1,200 shares of common stock with a par value of 1 per share and a market value of 26 per share. h. Additional marketable securities wefe purchased during the year. i. Verlando Company has no notes payable in the liabilities section of its balance sheet. Required: 1. Next Level Assuming that Verlando uses the indirect method to determine operating cash flows, what is the amount of depreciation expense and amortization expense that would be added back to net income: 2. Prepare the investing activities section of the statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2019. 3. Prepare the disclosure for significant noncash transactions for the statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2019.arrow_forwardBalance Sheet Presentation The following information relates to the assets of Westfield Semiconductors as of December 31, 2019. Westfield uses the straight-line method for depreciation and amortization. Required: Use the information above to prepare the property, plant, and equipment and intangible assets portions of a classified balance sheet for Westfield.arrow_forwardDinnell Company owns the following assets: In the year of acquisition and retirement of an asset, Dinnell records depreciation expense for one-half year. During 2020, Asset A was sold for 7,000. Required: Prepare the journal entries to record depreciation on each asset for 2017 through 2020 and the sale of Asset A. Round all answers to the nearest dollar.arrow_forward
- Refer to the information for Cox Inc. above. What amount would Cox record as depreciation expense for 2019 if the units-of-production method were used ( Note: Round your answer to the nearest dollar)? a. $179,400 b. $184,000 c. $218,400 d. $224,000arrow_forwardSpreadsheet The following 2019 information is available for Payne Company: Partial additional information: The net income for 2019 totaled 1,600. During 2019, the company sold, for 390, equipment that cost 390 and had a book value of 300. The company sold land for 200, resulting in a loss of 40. The remaining change in the Land account resulted from the purchase of land through the issuance of common stock. Required: Making whatever additional assumptions that are necessary, prepare a spreadsheet to support the 2019 statement of cash flows for Payne.arrow_forwardShannon Corporation began operations on January 1, 2019. Financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2020, contained the following errors: In addition, on December 31, 2020, fully depreciated machinery was sold for 10,800 cash, but the sale was not recorded until 2021. There were no other errors during 2019 or 2020, and no corrections have been made for any of the errors. Refer to the information for Shannon Corporation above. Ignoring income taxes, what is the total effect of the errors on the amount of working capital (current assets minus current liabilities) at December 31, 2020? a. working capital overstated by 4,200 b. working capital understated by 5,800 c. working capital understated by 6,000 d. working capital understated by 9,800arrow_forward
- At the end of 2020, while auditing Sandlin Companys books, before the books have been closed, you find the following items: a. A building with a 30-year life (no residual value, depreciated using the straight-line method) was purchased on January 1, 2020, by issuing a 90,000 non-interest-bearing, 4-year note. The entry made to record the purchase was a debit to Building and a credit to Notes Payable for 90,000; 12% is a fair rate of interest on the note. b. The inventory at the end of 2020 was found to be overstated by 15,000. At the same time, it was discovered that the inventory at the end of 2019 had been overstated by 35,000. The company uses the perpetual inventory system. c. For the last 3 years, the company has failed to accrue salaries and w-ages. The correct amounts at the end of each year were: 2018, 12,000; 2019, 18,000; and 2020, 10,000. Required: 1. Prepare journal entries to correct the errors. Ignore income taxes. 2. Assume, instead, that the company discovered the errors after it had closed the books. Prepare journal entries to correct the errors. Ignore income taxes.arrow_forwardDuring 2019, Ryel Companys controller asked you to prepare correcting journal entries for the following three situations: 1. Machine A was purchased for 50,000 on January 1, 2014. Straight-line depreciation has been recorded for 5 years, and the Accumulated Depreciation account has a balance of 25,000. The estimated residual value remains at 5,000, but the service life is now estimated to be 1 year longer than estimated originally. 2. Machine B was purchased for 40,000 on January 1, 2017. It had an estimated residual value of 5,000 and an estimated service life of 10 years. it has been depreciated under the double-declining-balance method for 2 years. Now, at the beginning of the third year, Ryel has decided to change to the straight-line method. 3. Machine C was purchased for 20,000 on January 1, 2018, Double-declining-balance depreciation has been recorded for 1 year. The estimated residual value of the machine is 2,000 and the estimated service life is 5 years. The computation of the depreciation erroneously included the estimated residual value. Required: Prepare any necessary correcting journal entries for each situation. Also prepare the journal entry necessary for each situation to record depreciation expense for 2019.arrow_forwardKoolman Construction Company began work on a contract in 2019. The contract price is 3,000,000, and the company determined that its performance obligation was satisfied over time. Other information relating to the contract is as follows: Required: 1. Compute the gross profit or loss recognized in 2019 and 2020. 2. Prepare the appropriate sections of the income statement and ending balance sheet for each year.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning


