The diatomic molecule can rotate about the x and z axes. Rotational J energy 6 - 21 E 15 E The energies of allowed states can CM 4 10E be calculated using Figure 42.5 Rotation of a Equation 42.6. diatomic molecule around its cen- - 6 Ej ter of mass. (a) A diatomic mole- cule oriented along the y axis. (b) Allowed rotational energies of a diatomic molecule expressed as multiples of E, = h²/I. 3E E E, = 0 b ENERGY
The diatomic molecule can rotate about the x and z axes. Rotational J energy 6 - 21 E 15 E The energies of allowed states can CM 4 10E be calculated using Figure 42.5 Rotation of a Equation 42.6. diatomic molecule around its cen- - 6 Ej ter of mass. (a) A diatomic mole- cule oriented along the y axis. (b) Allowed rotational energies of a diatomic molecule expressed as multiples of E, = h²/I. 3E E E, = 0 b ENERGY
Modern Physics
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781111794378
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Chapter11: Molecular Structure
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 11P
Related questions
Question
Most of the mass of an atom is in its nucleus. Model the mass distribution in a diatomic molecule as two spheres of uniform density, each of radius 2.00 x 10-15 m and mass 1.00 x 10-26 kg, located at points along the y axis as in 42.5a, and separated by 2.00 x 10-10 m. Rotation about the axis joining the nuclei in the diatomic molecule is ordinarily ignored because the first excited state would have an energy that is too high to access. To see why, calculate the ratio of the energy of the first excited state for rotation about the y axis to the energy of the first excited state for rotation about the x axis.
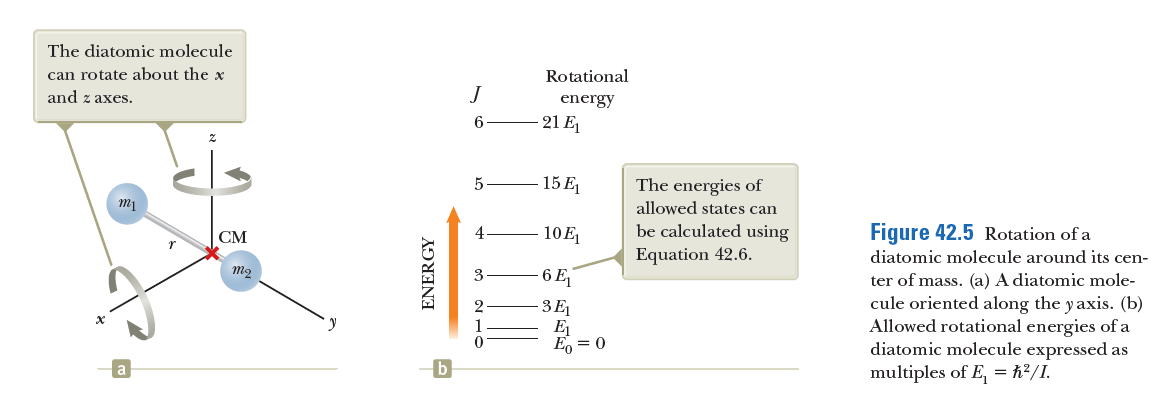
Transcribed Image Text:The diatomic molecule
can rotate about the x
and z axes.
Rotational
J
energy
6
- 21 E
15 E
The energies of
allowed states can
CM
4
10E
be calculated using
Figure 42.5 Rotation of a
Equation 42.6.
diatomic molecule around its cen-
- 6 Ej
ter of mass. (a) A diatomic mole-
cule oriented along the y axis. (b)
Allowed rotational energies of a
diatomic molecule expressed as
multiples of E, = h²/I.
3E
E
E, = 0
b
ENERGY
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781111794378
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax


Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781111794378
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax


Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning