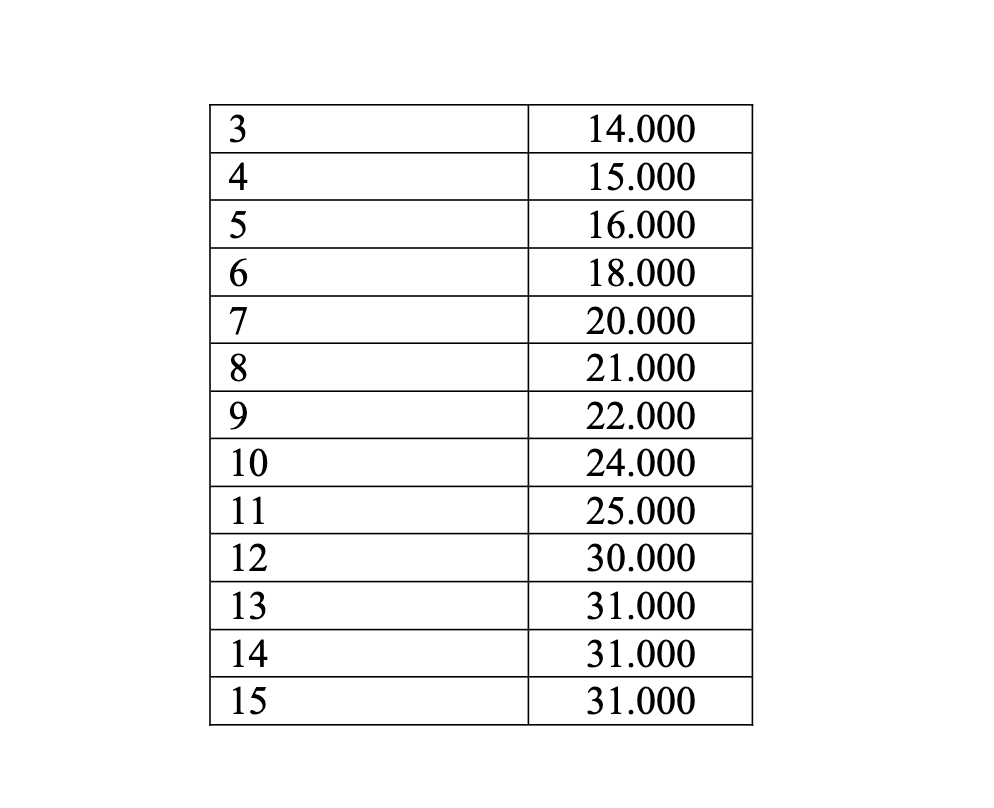
JJ is the financial manager in charge of the company pension fund at Arm Inc. JJ knows that the fund must be sufficient to make the payments listed in Table. Each payment must be made on the first day of each year. JJ is going to finance these payments by purchasing bonds. It is currently January 1 of year 1, and three bonds are available for immediate purchase. The prices and coupons for the bonds are as follows. (We assume that all coupon payments are received on January 1 and arrive in time to meet cash demands for the year on which they arrive.) ▪ Bond 1 costs $980 and yields a $60 coupon in the years 2 through 5 and a $1060 payment on maturity in the year 6. ▪ Bond 2 costs $970 and yields a $65 coupon in the years 2 through 11 and a $1065 payment on maturity in the year 12. 1 Bond 3 costs $1050 and yields a $75 coupon in the years 2 through 14 and a $1075 payment on maturity in the year 15. JJ must decide how much cash to allocate (from company coffers) to meet the initial $11,000 payment and buy enough bonds to make future payments. He knows that any excess cash on hand can earn an annual rate of 4% in a fixed-rate account. How should he proceed? Ano Pagamento $ 1 11.000 2 12.000
JJ is the
■ Bond 1 costs $980 and yields a $60 coupon in the years 2 through 5 and a $1060 payment on maturity in the year 6.
■ Bond 2 costs $970 and yields a $65 coupon in the years 2 through 11 and a $1065
payment on maturity in the year 12.
■ Bond 3 costs $1050 and yields a $75 coupon in the years 2 through 14 and a $1075
payment on maturity in the year 15.
JJ must decide how much cash to allocate (from company coffers) to meet the initial $11,000 payment and buy enough bonds to make future payments. He knows that any excess cash on hand can earn an annual rate of 4% in a fixed-rate account. How should he proceed?

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps


