
Concept explainers
To label: The indicated structures on the given diagram of a neuron.
Introduction: Neurons are the cells within the nervous system that communicate with each other in unique ways.
Answer to Problem 1IQ
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 represents the labeled structures of the neuron.
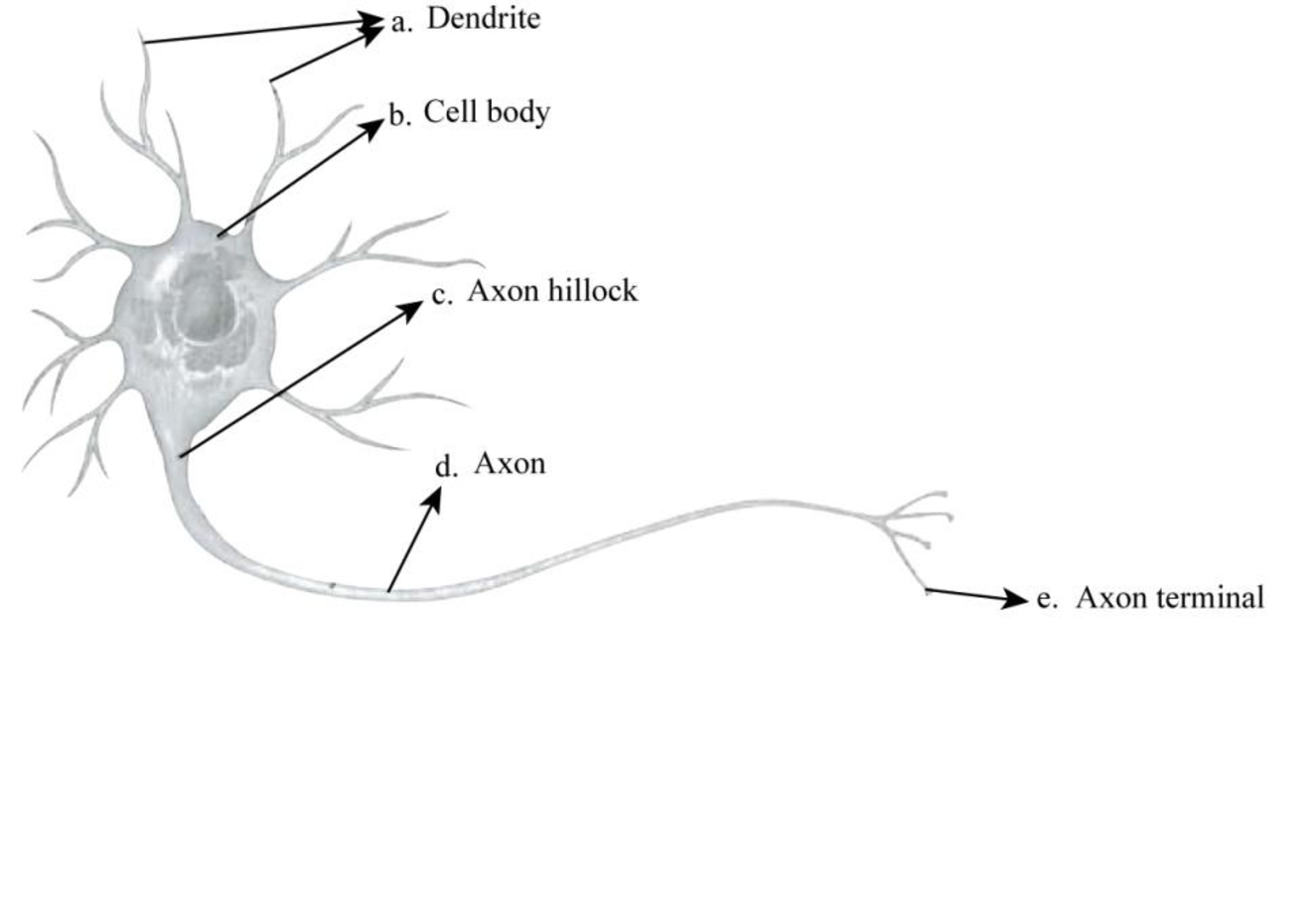
Fig.1: Structure of a neuron
Explanation of Solution
A neuron consists of a cell body, axon, dendrites, and terminal branches. The cell body is the largest part of the neuron; dendrites receive the signals, and then transmit them to axons, which further transfer them to the terminal branches. These signals originate from a region of cell body known as axon hillock. The synaptic terminals are present at the branching ends of the axons, which generally release neurotransmitters.
To determine: The direction of impulse transmission.
Introduction: An impulse refers to a signal transmitted along a nerve fiber. It is the way nerve cells communicate with each other.
Explanation of Solution
The direction of impulse transmission in a typical neuron is one direction. The dendrite receives the nerve impulse from other neurons, and a single axon transmits signals to other cells. The information is transmitted to another cell at the synapse. The synaptic terminals present at the ends of axons release neurotransmitters that relay signals to another neuron.
To determine: The event that occurs at Part e.
Introduction: The basic working unit of the brain is known as a neuron. It transmits information to other nerve cells, gland, or muscle cells.
Explanation of Solution
The branching ends of the axons are known as synaptic terminals. These terminals usually release neurotransmitters that relay signals to another neuron, a gland cell, or a muscle cell.
Synaptic terminals release neurotransmitters that transmit signals to another nerve cell, muscle cell, or gland cell.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 48 Solutions
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
- Explain where free nerve endings are located in the body and note some functions of the various kinds.arrow_forwardName the process through which injured axons are repaired, and describe the process.arrow_forwardDamage to neurons from Alzheimer's disease may prevent neurons from receiving signals from other neurons. Which of the following structures of a neuron is first affected by the damage? Select one: a. Axon b. Cell Body c. Axon Terminal d. Dendritesarrow_forward
- Neurofibromatosis type 1 is a condition where tumours can grow in the nerves near the skin. The growth of tumours prevents the action potentials from quickly travelling through the neurons. Identify the nerve structure from the image below and the division of the nervous system affected by neurofibromatosis type 1. CNS = Central Nervous System PNS = Peripheral Nervous System Select one: a. Nerve Structure Division of Nervous System 3 PNS b. Nerve Structure Division of Nervous System 4 CNS c. Nerve Structure Division of Nervous System 5 PNS d. Nerve Structure Division of Nervous System 1 CNSarrow_forwardDescribe the smaller and largest living unit of nerve cellsarrow_forwardA) The neuron labelled "D" in the figure is what class of functional neuron?: 3rd-order? lower motor neurone? upper motor neurone? 2nd-order? bipolar? unipolar? B) The message in the pleural pathway in figure 3 comes from the: occipital lobe? skeletal muscle? somatosensoty cortex? temporal lobe? receptors? parietal lobe? frontal lobe? C) Damage to this structure in the figure would affect the ability to move your RIGHT leg: A, B, C, D, E, F, Garrow_forward
- View an electron micrograph of a cross-section of a myelinated nerve fiber image below. The axon contains microtubules and neurofilaments, bounded by a plasma membrane known as the axolemma. Outside the plasma membrane of the axon is the myelin sheath, which is composed of the tightly wrapped plasma membrane of a Schwann cell. What aspects of the cells in this image react with the stain that makes them the deep, dark, black color, such as the multiple layers that are the myelin sheath?arrow_forwardMake a table (containing the summary) of the stages of emrbyonic development in nervous system with the following: 1. Neural tube 2. Primary and secondary vesicles 3. Ventriclesarrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning


