
1.
Prepare the worksheet to develop Company S’s financial statements for the first 6 months of 2019.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Worksheet: A worksheet is a tool that is used while preparing a financial statement. It is a type of form, having multiple columns and it is used in the adjustment process.
Prepare the worksheet to develop Company S’s financial statements for the first 6 months of 2019:
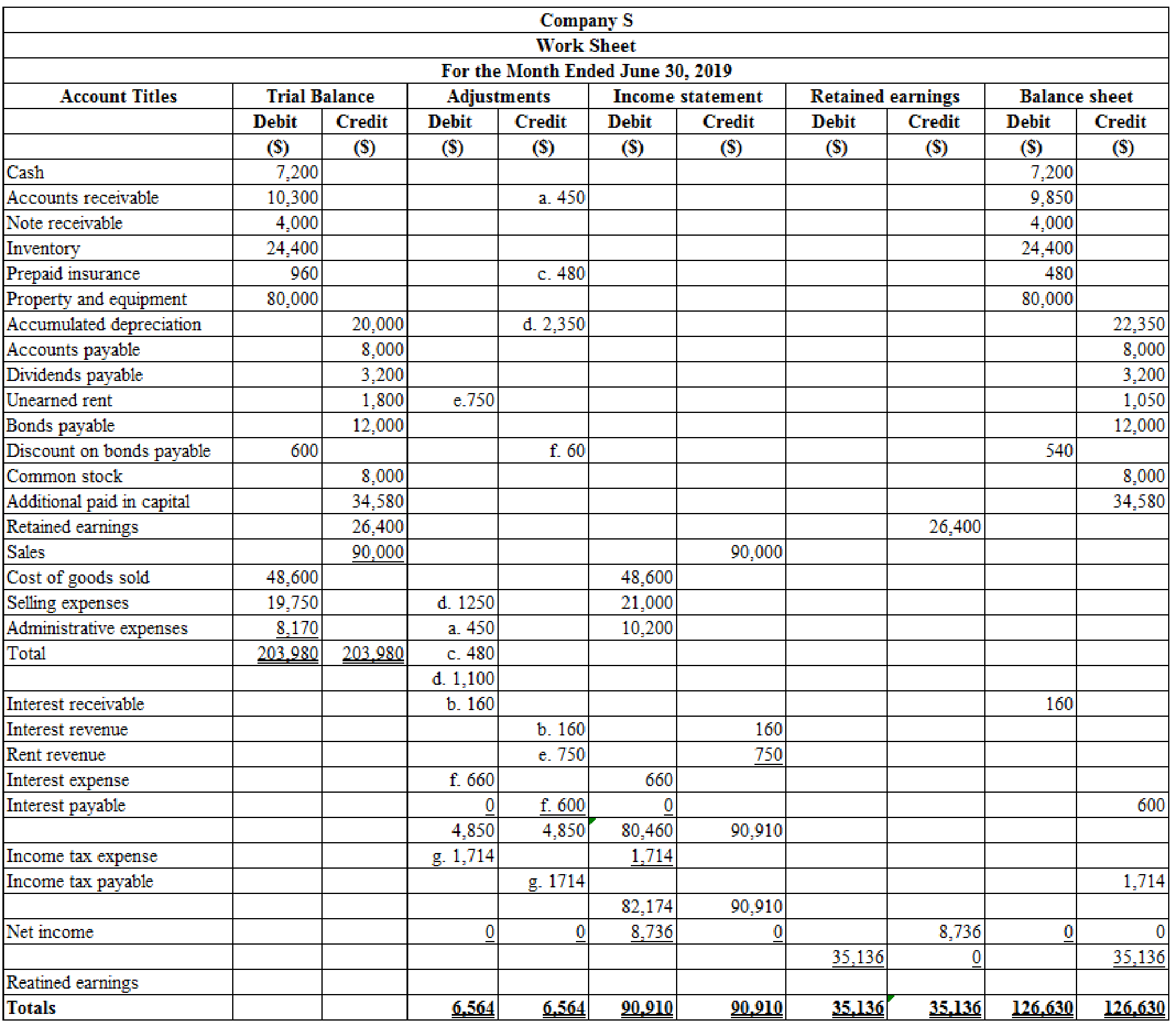
Table (1)
Working notes:
a. Calculate the amount of
b. Calculate the amount of interest revenue:
c. Calculate the amount of insurance expense:
d. Calculate the amount of
e. Calculate the amount of rent revenue:
f. Calculate the amount of interest expense:
g. Calculate the amount of income tax expense for first 6 months:
Calculate estimated annual pre-tax income:
Calculate estimated effective income tax rate:
Calculate the amount of income tax expense for first 6 months:
2 (a)
Prepare the income statement for the first 6 months of 2019.
2 (a)
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare the income statement for the first 6 months of 2019:
| Company S | ||
| Interim Income statement | ||
| For the period ended June 30, 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Sales | 90,000 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | (48,600) | |
| Gross profit | 41,400 | |
| Operating expenses: | ||
| Selling expenses | 21,000 | |
| Administrative expenses | 10,200 | |
| Total operating expenses | (31,200) | |
| Pre-tax operating income | 10,200 | |
| Other items: | ||
| Interest revenue | 160 | |
| Rent revenue | 750 | |
| Interest expense | (660) | |
| Total other revenues and expenses | 250 | |
| Income before income taxes | 10,450 | |
| Less: Income tax expense | (1,714) | |
| Net income | $8,736 | |
| Earnings per share | $1.09 | |
Table (2)
Working notes:
h. Calculate earnings per share for 6 months:
2 (b)
Prepare the income statement for the second quarter of 2019.
2 (b)
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare the income statement for the second quarter of 2019:
| Company S | ||
| Interim Income statement | ||
| For the period ended June 30, 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Sales | 50,000 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | (25,600) | |
| Gross profit | 24,400 | |
| Operating expenses: | ||
| Selling expenses | 12,200 | |
| Administrative expenses | 5,990 | |
| Total operating expenses | (18,190) | |
| Pre-tax operating income | 6,210 | |
| Other items: | ||
| Interest revenue | 120 | |
| Rent revenue | 450 | |
| Interest expense | (330) | |
| Total other revenues and expenses | 240 | |
| Income before income taxes | 6,450 | |
| Less: Income tax expense | (1,014) | |
| Net income | $5,436 | |
| Earnings per share | $0.68 | |
Table (3)
Working notes:
i. Calculate the amount of sales for second quarter:
j. Calculate the amount of cost of goods sold for 3 months:
k. Calculate the amount of selling expenses for second quarter:
l. Calculate the amount of administrative expenses for second quarter:
m. Calculate the amount of interest revenue for second quarter:
n. Calculate the amount of rent revenue for second quarter:
o. Calculate the amount of interest expense for second quarter:
p. Calculate the amount of income tax expenses for second quarter:
q. Calculate earnings per share for second quarter:
3.
Prepare the statement of
3.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of Retained Earnings: Statement of retained earnings shows, the changes in the retained earnings, and the income left in the company after payment of the dividends, for the accounting period.
Prepare the statement of retained earnings for the first 6 months:
| Company S | ||
| Statement of Retained Earnings | ||
| For First 6 Months Ended June 30, 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Retained earnings, January 1, 2019 | 29,600 | |
| Add: Net income | 8,736 | |
| Subtotal | 38,336 | |
| Less: Dividends | (3,200) | |
| Retained earnings at June 30, 2019 | $35,136 | |
Table (4)
Working note:
r. Calculate the amount of retained earnings, January 1, 2019:
4.
Prepare the balance sheet as on June 30, 2019 of Company S.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Balance Sheet: Balance Sheet is one of the financial statements which summarize the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Interim financial reports: these are the financial reports prepared by the company between the two annual reports.
Prepare the balance sheet as on June 30, 2019 of Company S:
| Company S | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| As on June 30, 2019 | ||
| Assets | ||
| Current assets: | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | 7,200 | |
| Accounts receivable | 9,850 | |
| Note receivable | 4,000 | |
| Interest receivable | 160 | |
| Inventory | 24,400 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 480 | |
| Total current assets | 46,090 | |
| Property and equipment | 80,000 | |
| (22,350) | ||
| Net property, plant and equipment | 57,650 | |
| Total assets | $103,740 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities: | ||
| Accounts payable | 8,000 | |
| Interest payable | 600 | |
| Dividends payable | 3,200 | |
| Income tax payable | 1,714 | |
| Unearned rent | 1,050 | |
| Bonds payable | 12,000 | |
| Less: Discount on bonds payable | (540) | 11,460 |
| Total liabilities | 26,024 | |
| Shareholders’ Equity | ||
| Contributed Capital: | ||
| Common stock | 8,000 | |
| Additional paid in capital on common stock | 34,580 | |
| Retained earnings | 35,136 | |
| Total shareholders’ equity | 77,716 | |
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $103,740 | |
Table (5)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
- On June 30, 2019, the balances of the accounts appearing in the ledger of Simkins Company are as follows: Instructions 1. Does Simkins Company use a periodic or perpetual inventory system? Explain. 2. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for Simkins Company for the year ended June 30, 2019. The merchandise inventory as of June 30, 2019, was 508,000. The adjustment for estimated returns inventory for sales for the year ending December 31, 2019, was 33,000. 3. Prepare the closing entries for Simkins Company as of June 30, 2019. 4. What would the net income have been if the perpetual inventory system had been used?arrow_forwardOn December 31, 2019, the balances of the accounts appearing in the ledger of Wyman Company are as follows: Instructions 1. Does Wyman Company use a periodic or perpetual inventory system? Explain. 2. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for Wyman Company for the year ended December 31, 2019. The merchandise inventory as of December 31, 2019, was 305,000. The adjustment for estimated returns inventory for sales for the year ending December 31, 2019, was 30,000. 3. Prepare the closing entries for Wyman Company as of December 31, 2019. 4. What would the net income have been if the perpetual inventory system had been used?arrow_forwardCost of Goods Sold, Income Statement. and Statement of Comprehensive Income Gaskin Company derives the following items from its adjusted trial balance as of December 31, 2019: The following; additional information is also available. The December 31, 2019, ending inventory is 14,700. During 2019, 4,200 shares of'common stock were outstanding the entire year. The income tax rate 30% on all items of income. Required: 1. As a supporting document for Requirements 2 and 3, prepare a separate schedule for Gaskins cost of goods sold. 2. Prepare a 2019 single-step income statement. 3. Prepare a 2019 multiple-step income statement. 4. Prepare a 2019 statement of comprehensive income.arrow_forward
- Inventory Pools Stone Shoe Company adopted dollar-value LIFO on January 1, 2019. The company produces four products and uses a single inventory pool. The companys beginning inventory consists of the following: During 2019, the company has the following purchases and sales: Required: 1. Compute the dollar-value LIFO cost of the ending inventory. Round the cost index to 4 decimal places and all other amounts to the nearest dollar. 2. Next Level By how much would the companys gross profit differ if it had used four pools instead of a single pool?arrow_forwardEffects of an Inventory Error The income statements for Graul Corporation for the 3 years ending in 2019 appear below. During 2019, Graul discovered that the 2017 ending inventory had been misstated due to the following two transactions being recorded incorrectly. a. A purchase return of inventory costing $42,000 was recorded twice. b. A credit purchase of inventory' made on December 20 for $28,500 was not recorded. The goods were shipped F.O.B. shipping point and were shipped on December 22, 2017. Required: 1. Was ending inventory for 2017 overstated or understated? By how much? 2. Prepare correct income statements for all 3 years. 3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Did the error in 2017 affect cumulative net income for the 3-year period? Explain your response. 4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Why was the 2019 net income unaffected?arrow_forwardSALES RETURNS AND ALLOWANCES ADJUSTMENT At the end of year 1, MCs estimates that 2,400 of the current years sales will be returned in year 2. Prepare the adjusting entry at the end of year 1 to record the estimated sales returns and allowances and customer refunds payable for this 2,400. Use accounts as illustrated in the chapter.arrow_forward
- Under the periodic inventory system, what account is debited when an estimate is made for sales made this year, but expected to be returned next year? (a) Sales Returns and Allowances (b) Merchandise Inventory (c) Customer Refunds Payable (d) Salesarrow_forwardInventory Valuation You are engaged in an audit of Roche Mfg. Company for the year ended December 31, 2019. To reduce the workload at year-end, Roche took its annual physical inventory under your observation on November 30, 2019. Roches inventory account, which includes raw materials and work in process, is on a perpetual basis, and it uses the first-in, first-out method of pricing. It has no finished goods inventory. The companys physical inventory revealed that the book inventory of 60,570 was understated by 3,000. To avoid distorting the interim financial statements, Roche decided not to adjust the book inventory until year-end except for obsolete inventory items. Your audit revealed this information about the November 30 inventory: Pricing tests showed that the physical inventory was overpriced by 2,200. Footing and extension errors resulted in a 150 understatement of the physical inventory. Direct labor included in the physical inventory amounted to 10,000. Overhead was included at the rate of 200% of direct labor. You determined that the amount of direct labor was correct and the overhead rate was proper. The physical inventory included obsolete materials recorded at 250. During December, these materials were removed from the inventory account by a charge to cost of sales. Your audit also disclosed the following information about the December 31, 2019, inventory. Total debits to certain accounts during December are: The cost of sales of 68,600 included direct labor of 13,800. Normal scrap loss on established product lines is negligible. However, a special order started and completed during December had excessive scrap loss of 800 which was charged to Manufacturing Overhead Expense. Required: 1. Compute the correct amount of the physical inventory at November 30, 2019. 2. Without prejudice to your solution to Requirement 1, assume that the correct amount of the inventory at November 30, 2019, was 57,700. Compute the amount of the inventory at December 31,2019.arrow_forwardUnder the periodic inventory system, what account is credited when an estimate is made for sales made this year, but expected to be returned next year? (a) Merchandise Inventory (b) Customer Refunds Payable (c) Sales (d) Sales Returns and Allowancesarrow_forward
- Borys Companys periodic inventory at December 31, 2019, is understated by 10,000, but purchases are correct. Johnson correctly values its 2020 ending inventory. What is the effect of this error on Boryss 2019 and 2020 financial statements?arrow_forwardUnder the periodic inventory system, what account is debited when an estimate is made for the cost of merchandise inventory sold this year, but expected to be returned next year? (a) Estimated Returns Inventory (b) Sales Returns and Allowances (c) Merchandise Inventory (d) Customer Refunds Payablearrow_forwardPalisade Creek Co. is a merchandising business that uses the perpetual inventory system. The account balances for Palisade Creek Co. as of May 1, 2019 (unless otherwise indicated), are as follows: During May, the last month of the fiscal year, the following transactions were completed: Instructions 1. Enter the balances of each of the accounts in the appropriate balance column of a four-column account. Write Balance in the item section and place a check mark () in the Posting Reference column. Journalize the transactions for May, starting on Page 20 of the journal. 2. Post the journal to the general ledger, extending the month-end balances to the appropriate balance columns after all posting is completed. In this problem, you are not required to update or post to the accounts receivable and accounts payable subsidiary ledgers. 3. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance. 4. At the end of May, the following adjustment data were assembled. Analyze and use these data to complete (5) and (6). 5. (Optional) Enter the unadjusted trial balance on a 10-column end-of-period spreadsheet (work sheet), and complete the spreadsheet. 6. Journalize and post the adjusting entries. Record the adjusting entries on Page 22 of the journal. 7. Prepare an adjusted trial balance. 8. Prepare an income statement, a statement of owners equity, and a balance sheet. 9. Prepare and post the closing entries. Record the closing entries on Page 23 of the journal. Indicate closed accounts by inserting a line in both Balance columns opposite the closing entry. Insert the new balance in the owners capital account. 10. Prepare a post-closing trial balance.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





