
A block with mass m1 hangs from a rope that is extended over an ideal pulley and attached to a second block with mass m2 that sits on a ledge. The second block is also connected to a third block with mass m3 by a second rope that hangs over a second ideal pulley as shown in Figure P5.47. If the friction between the ledge and the second block is negligible, m1 = 3.00 kg, m2 = 5.00 kg, and m3 = 8.00 kg, find the magnitude of the tension in each rope and the acceleration of each block.
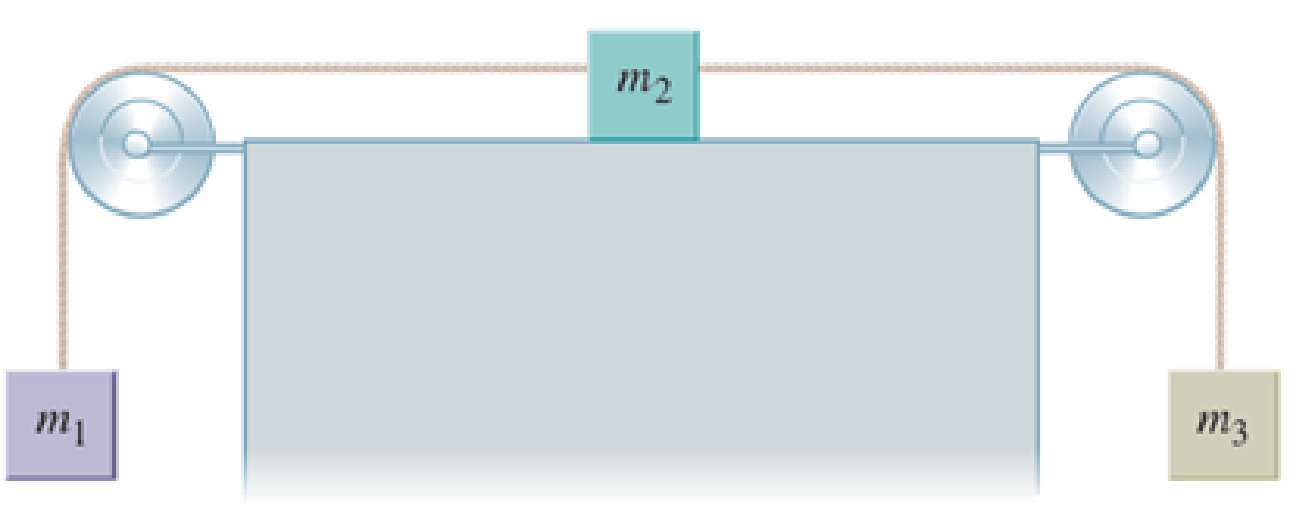
FIGURE P5.47
What is the magnitude of tension on each rope and the acceleration on each block?
Answer to Problem 47PQ
The magnitude of tension on each rope is
Explanation of Solution
From the given condition the
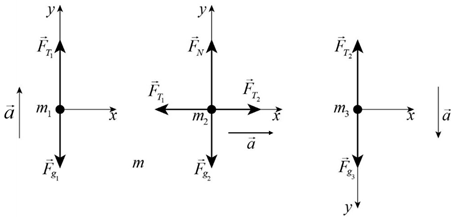
Applying Newton’s laws.
For
Here,
For
Here,
For
Here,
Write the equation for gravitational force.
Here,
Conclusion:
Using equation V find the gravitational force on each object.
Substitute the above values in equation I, II and IV to generate another three equation with unknown factors.
Solve the equation VI and VIII to get tension and substitute in equation VII.
Then equation VII becomes,
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude of tension on each rope is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- An object of mass M is held in place by an applied force F and a pulley system as shown in Figure P4.43. The pulleys are massless and frictionless. (a) Draw diagrams showing the forces on each pulley. Find (b) the tension in each section of rope, T1, T2, T3, T4, and T5 and (c) the magnitude of F. Figure P4.43 44. Any device that allows you to increase the force you exert is a kind of machine. Some machines, such as the prybar or the inclined plane, are very simple. Some machines do not even look like machines. For example, your car is stuck in the mud and you cant pull hard enough to get it out. You do, however, have a long cable that you connect taut between your front bumper and the trunk of a stout tree. You now pull sideways on the cable at its midpoint, exerting a force f. Each half of the cable is displaced through a small angle from the straight line between the ends of the cable. (a) Deduce an expression for the force acting on the car. (b) Evaluate the cable tension for the case where = 7.00 and f = 100 N.arrow_forwardTwo blocks of mass 3.50 kg and 8.00 kg are connected by a massless string that passes over a frictionless pulley (Fig. P4.47). The inclines are frictionless. Find (a) the magnitude of the acceleration of each block and (b) the tension in the string. Figure P4.47arrow_forwardTwo objects, m1 = 3.00 kg and m2 = 8.50 kg, are attached by a massless cord passing over a frictionless pulley as shown in Figure P5.51. Assume the horizontal surface is frictionless. a. Draw a free-body diagram for each of the two objects. b. What is the tension in the cord? c. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the two objects? FIGURE P5.51 Problems 51 and 65.arrow_forward
- Two blocks are connected by a rope that passes over a massless and frictionless pulley as shown in Figure P5.41. Given that m0 = 15.93 kg and m2 = 10.45 kg, determine the magnitudes of the tension in the rope and the blocks acceleration. FIGURE P5.41arrow_forwardAn object of mass m = 1.00 kg is observed to have an acceleration a with a magnitude of 10.0 m/s2 in a direction 60.0 east of north. Figure P4.29 shows a view of the object from above. The force F2 acting on the object has a magnitude of 5.00 N and is directed north. Determine the magnitude and direction of the one other horizontal force F1 acting on the object. Figure P4.29arrow_forwardAn object of mass m1 = 5.00 kg placed on a frictionless, horizontal table is connected to a string that passes over a pulley and then is fastened to a hanging object of mass m2 = 9.00 kg as shown in Figure P4.28. (a) Draw free-body diagrams of both objects. Find (b) the magnitude of the acceleration of the objects and (c) the tension in the string. Figure P4.28arrow_forward
- An object of mass m1 = 5.00 kg placed on a frictionless, horizontal table is connected to a string that passes over a pulley and then is fastened to a hanging object of mass m2 = 9.00 kg as shown in Figure P5.22. (a) Draw free-body diagrams of both objects. Find (b) the magnitude of the acceleration of the objects and (c) the tension in the string. Figure P5.22 Problems 22 and 29.arrow_forwardTwo objects are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley as shown in Figure P4.30. Assume the incline is frictionless and take m1 = 2.00 kg, m2 = 6.00 kg, and = 55.0. (a) Draw free-body diagrams of both objects. Find (b) the magnitude of the acceleration of the objects, (c) the tension in the string, and (d) the speed of each object 2.00 s after it is released from rest. Figure P4.30arrow_forwardA heavy chandelier with mass 125 kg is hung by chains in equilibrium from the ceiling of a concert hall as shown in Figure P5.77, with 1 = 37.0 and 2 = 64.0. Assuming the chains are massless, what are the tensions FT1, FT2, and FT3 in the three chains? FIGURE P5.77arrow_forward
- In Example 4.5, we pushed on two blocks on a table. Suppose three blocks are in contact with one another on a frictionless, horizontal surface as shown in Figure P4.49. A horizontal force F is applied to m1. Take m1 = 2.00 kg, m2 = 3.00 kg, m3 = 4.00 kg, and F = 18.0 N. (a) Draw a separate free-body diagram for each block. (b) Determine the acceleration of the blocks. (c) Find the resultant force on each block. (d) Find the magnitudes of the contact forces between the blocks. (e) You are working on a construction project. A coworker is nailing up plasterboard on one side of a light partition, and you are on the opposite side, providing backing by leaning against the wall with your back pushing on it. Every hammer blow makes your back sting. The supervisor helps you put a heavy block of wood between the wall and your back. Using the situation analyzed in parts (a) through (d) as a model, explain how this change works to make your job more comfortable. Figure P4.49arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 2.00 kg rests on the left edge of a block of mass M = 8.00 kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the two blocks is 0.300, and the surface on which the 8.00-kg block rests is frictionless. A constant horizontal force of magnitude F = 10.0 N is applied to the 2.00-kg block, setting it in motion as shown in Figure P5.103a. If the distance L that the leading edge of the smaller block, travels on the larger block is 3.00 m. (a) in what lime interval will the smaller block make it to the right side of the 8.00-kg block as shown in Figure P5.103b? (Note: Both blocks are set into motion when F is applied.) (b) How far does the 8.00-kg block move in the process?arrow_forwardInitially, the system of objects shown in Figure P5.49 is held motionless. The pulley and all surfaces and wheels are frictionless. Let the force F be zero and assume that m1 can move only vertically. At the instant after the system of objects is released, Find (a) the tension T in the string, (b) the acceleration of m2, (c) the acceleration of M, and (d) the acceleration of m1. (Note: The pulley accelerates along with the cart.) Figure P5.49 Problems 49 and 53arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





