
Long-term contract; revenue recognition over time vs. upon project completion
• LO5–9
On June 15, 2018, Sanderson Construction entered into a long-term construction contract to build a baseball stadium in Washington, D.C., for $220 million. The expected completion date is April 1, 2020, just in time for the 2020 baseball season. Costs incurred and estimated costs to complete at year-end for the life of the contract are as follows ($ in millions):
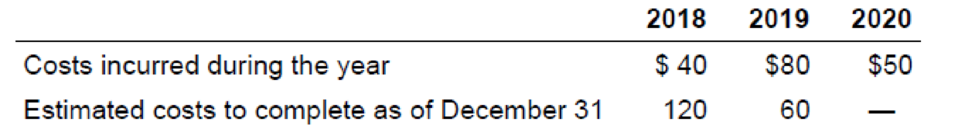
Required:
1. How much revenue and gross profit will Sanderson report in its 2018, 2019, and 2020 income statements related to this contract assuming Sanderson recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion?
2. How much revenue and gross profit will Sanderson report in its 2018, 2019, and 2020 income statements related to this contract assuming this project does not qualify for revenue recognition over time?
3. Suppose the estimated costs to complete at the end of 2019 are $80 million instead of $60 million. Determine the amount of revenue and gross profit or loss to be recognized in 2019 assuming Sanderson recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion.
Requirement – 1
Contract
Contract is a written document that creates legal enforcement for buying and selling the property. It is committed by the parties to performing their obligation and enforcing their rights.
Revenue recognized point of long term contract
A long-term contract qualifies for revenue recognition over time. The seller can recognize the revenue as per percentage of the completion of the project, which is recognized by revenue mines cost of completion until date.
A contract does not meet the performance obligation norm. The seller cannot recognize the revenue till the project complete.
The revenue recognition principle
The revenue recognition principle refers to the revenue that should be recognized in the time period, when the performance obligation (sales or services) of the company is completed.
The amount of revenue and gross profit or loss will report in 2018, 2019, and 2020 income statement of S Contraction, and assume revenue recognize over time according to percentage of completion.
Explanation of Solution
Recognized revenue
In the year 2018:
Given,
The contract price is $220,000,000
Actual cost to date is $4,000,000
Calculated total estimated cost is $160,000,000
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $55,000,000.
In the year 2019:
Given,
The contract price is $220,000,000
Actual cost to date is $120,000,000
Calculated total estimated cost is $180,000,000
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $91,670,000.
In the year 2020:
Given,
Contract price is $220,000,000
Calculated revenue recognition in 2018 is $55,000,000
Calculated revenue recognition in 2019 is $91,670,000
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $73,330,000.
Recognized gross profit
In the year 2018:
Given,
Estimated gross profit in 2018 is $60,000,000 (1)
Total estimated cost is $160,000,000
Actual cost to date is $40,000,000
Now, calculate the gross profit recognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $15,000,000.
In the year 2019:
Here,
Estimated gross profit in 2019 is $40,000,000 (1)
Total estimated cost is $180,000,000
Gross profit recognition in 2018 is $15,000,000
Actual cost to date is $120,000,000
Now, calculate the gross profit recognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $11,670,000.
In the year 2020:
Here,
Estimated gross profit in 2018 is $50,000,000 (1)
Gross profit recognition in 2016 is $15,000,000
Gross profit recognition in 2017 is $11,670,000
Now, calculate the gross profit recognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $11,670,000.
Working note:
Calculate the value of gross profit (in millions)
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |||
| Contract price | $220 | $220 | $220 | |||
| Actual costs to date | $40 | $120 | $170 | |||
| Estimated costs to complete | $120 | $60 | $0 | |||
| Less: Total estimated cost | $160 | $180 | $170 | |||
| Estimated gross profit | $60 | $40 | $50 | |||
Table (1)
(1)
Requirement – 2
To calculate: The amount of revenue and gross profit or loss to be recognized in 2018, 2019 and 2020 assuming the project does not qualify for revenue recognition over time.
Explanation of Solution
Revenue recognition:
In this case, there is no revenue recognition because the project does not qualify for revenue recognition overtime.
Recognized gross profit:
In the year 2018 and 2019:
In this case, there is no recognized profit, because the contract is not yet completed. Hence, the gross profit in the year 2018 and 2019 is $0.
In the year 2020:
Here,
The contract price is $220,000,000
Actual cost to date is $170,000,000
Now, calculate the gross profit recognition:
Hence, the calculated gross profit recognition is $50,000,000.
Requirement – 3
The amount of revenue and gross profit or loss to be recognized in 2019, and assume S Construction recognizes revenue over time according to percentage of completion.
Explanation of Solution
Revenue recognition in the year 2019:
Here,
Contract price is $220,000,000
Actual cost to date is $120,000,000
Total estimated cost is $200,000,000
Revenue recognition is $55,000,000
Profit recognizes is $15,000,000.
Now, calculate the revenue recognition:
Hence, the calculated revenue recognition is $77,000,000.
Recognized gross profit in the year 2019:
Here,
Revenue recognition in 2019 is $77,000,000
Actual cost to date is $80,000,000
Now, calculate the gross profit recognition:
Hence, the calculated gross loss recognition is $300,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting
- 56 On February 20, 2022, ABC Construction Company entered into a fixed-price contract to construct a commercial building for P9,000,000. ABC determined that the performance obligation is satisfied over time. Information relating to the contract is as follows: 2022 2023 Percentage of completion 25% 75% Estimated costs at completion P6,750,000 P7,200,000 How much is the contract costs charged to profit or loss in 2022? On February 20, 2022, ABC Construction Company entered into a fixed-price contract to construct a commercial building for P9,000,000. ABC determined that the performance obligation is satisfied over time. Information relating to the contract is as follows: 2022 2023 Percentage of completion 25% 75% Estimated costs at completion P6,750,000 P7,200,000 How much is the contract costs charged to profit or loss in 2022?arrow_forward43. On February 20, 2022, ABC Construction Company entered into a fixed-price contract to construct a commercial building for P9,000,000. ABC determined that the performance obligation is satisfied over time. Information relating to the contract is as follows: 2022 2023 Percentage of completion 25% 75% Estimated costs at completion P6,750,000 P7,200,000 How much is the contract costs charged to profit or loss in 2022?arrow_forwardTP5. LO 9.5 You own a construction company and have recently received a contract with the local school district to refurbish one of its elementary schools. You are given an up-front payment from the school district in the amount of $5 million. The contract terms extend from years 2018 to 2020. When would you recognize revenue for this payment? What method of accounting would you use for this construction project and why? What would be the benefits and challenges with your method selection? Give an example of your distribution selection and associated costs of the project (you may estimate based on other industry competitors). What might be some benefits and challenges associated with the other method of construction revenue recognition?arrow_forward
- 41. On February 20, 2022, ABC Construction Company entered into a fixed-price contract to construct a commercial building for P9,000,000. ABC determined that the performance obligation is satisfied over time. Information relating to the contract is as follows: 2022 2023 Percentage of completion 25% 75% Estimated costs at completion P6,750,000 P7,200,000 How much is the gross profit to be recognized in 2023?arrow_forward49. ABC Construction Company began work on a contract in 2022 and completed the contract in 2023. The total contact price was P8,500,000. Information related to the construction project are as follows: 2022 2023 Costs incurred during the year P1,200,000 P6,250,000 Estimated costs to complete 4,800,000 - Progress billings during the year 1,450,000 7,050,000 Collections during the year 800,000 6,000,000 How much is the receivable balance as of December 31, 2022?arrow_forwardE10.21 (LO3) (Government Grants) Rialto Group received a grant from the government of £100,000 to acquire £500,000 of delivery equipment on January 2, 2019. The delivery equipment has a useful life of 5 years. Rialto uses the straight-line method of depreciation. The delivery equipment has a zero residual value. Instructions A. If Rialto Group reports the grant as a reduction of the asset, answer the following questions. 1. What is the carrying amount of the delivery cquipment on the statement of financial position at December 31I, 2019? 2. What is the amount of depreciation expense related to the delivery equipment in 2020? 3. What is the amount of grant revenue reported in 2019 on the income statement? B. If Rialto Group reports the grant as deferred grant revenue, answer the following questions. 1. What is the balance in the deferred grant revenue account at December 31, 2019?…arrow_forward
- Hmm.211. blossom home inc, a real estate developing company was accounting for its long-term contracts using the completed contract method prior to 2024. in 2024 it changed to the percentage of completion method. The company decided to use the same for income tax purposes, rate enacted is 20%. Income before taxes under both the methods for the past three years appears below 2022 2023 2024 Completed Contract 440000 294000 148000 Percentage of completion 740000 367000 260000 Which of the following will be included in the journal entry made by Blossom Home to record the inco.me effect after taxes?arrow_forwardCH 21 POST-CLASS - SU21 Question 1 Ivanhoe Corporation enters into a 5-year lease of equipment on December 31, 2019, which requires 5 annual payments of $37,800 each, beginning December 31, 2019. In addition, Ivanhoe guarantees the lessor a residual value of $20,500 at the end of the lease. However, Ivanhoe believes it is probable that the expected residual value at the end of the lease term will be $10,250. The equipment has a useful life of 5 years.Prepare Ivanhoes' December 31, 2019, journal entries assuming the implicit rate of the lease is 10% and this is known to Ivanhoe. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually. For calculation purposes, use 5 decimal places as displayed in the factor table provided and round final answers to 0 decimal places e.g. 5,275.)Click here to view factor tables. Date Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit December 31, 2019 (To…arrow_forward2020 2019 Receivable from Construction contract Costs incurred each year. Construction in progress Partial billings on contract Collection each year P252,000 P240,000 460,800 292,800 873,600 240,000 720,000 2,167,000 8. The gross profit recognize from the long term construction contract is: 2019 2020 a. P52,800 P52,800 P547,200 b. P40,800 P240,000 C. d. P40,800 P307,200 P120,000arrow_forward
- Kw.113. Ch 12/14 A Three-year property type class equipment was bought for $35,000. The first year 40% bonus was claimed. What will be the tax amount in the first year, if the company is in the 34% combined tax bracket? The revenue and expenses for the first year are $15,000 and expense $2,000 respectively.arrow_forwardProblem 13-6 (Algo) Various contingencies [LO13-5, 13-6] Eastern Manufacturing is involved with several situations that possibly involve contingencies. Each is described below. Eastern's fiscal year ends December 31, and the 2021 financial statements are issued on March 15, 2022. a. Eastern is involved in a lawsuit resulting from a dispute with a supplier On February 3, 2022, judgment was rendered against Eastern in the amount of $111 million plus interest, a total of $126 million. Eastern plans to appeal the judgment and is unable to predict its outcome though it is not expected to have a material adverse effect on the company. b. In November 2020, the State of Nevada filed suit against Eastern, seeking civil penalties and injunctive relief for violations of environmental laws regulating hazardous waste. On January 12, 2022, Eastern reached a settlement with state authorities. Based upon discussions with legal counsel, the Company feels it is probable that $144 million will be…arrow_forwardHw.27. Entity A entered into a sale and repurchase agreement for its head office on 1 January 2022, selling the office to Bank B for $78,560,000. On the same date, the head office had a fair value of $97,800,000. Entity A will continue to use the head office for the next 2 years and has the option to buy back the property for $93,765,779, based on an effective interest rate of 9.25% per year over the next 2 years. Property prices are expected to increase over the next 2 years. REQUIRED: Measure the net amount to be shown in the Statement of Profit or Loss for the year ended 31 December 2022. 1. $7,938,979 Expense 2. $19,240,000 Expense 3. $0 4. $7,266,800 Expense 5. None of them.arrow_forward
