
Concept explainers
A heavy chandelier with mass 125 kg is hung by chains in equilibrium from the ceiling of a concert hall as shown in Figure P5.77, with θ1 = 37.0° and θ 2 = 64.0°. Assuming the chains are massless, what are the tensions FT1, FT2, and FT3 in the three chains?
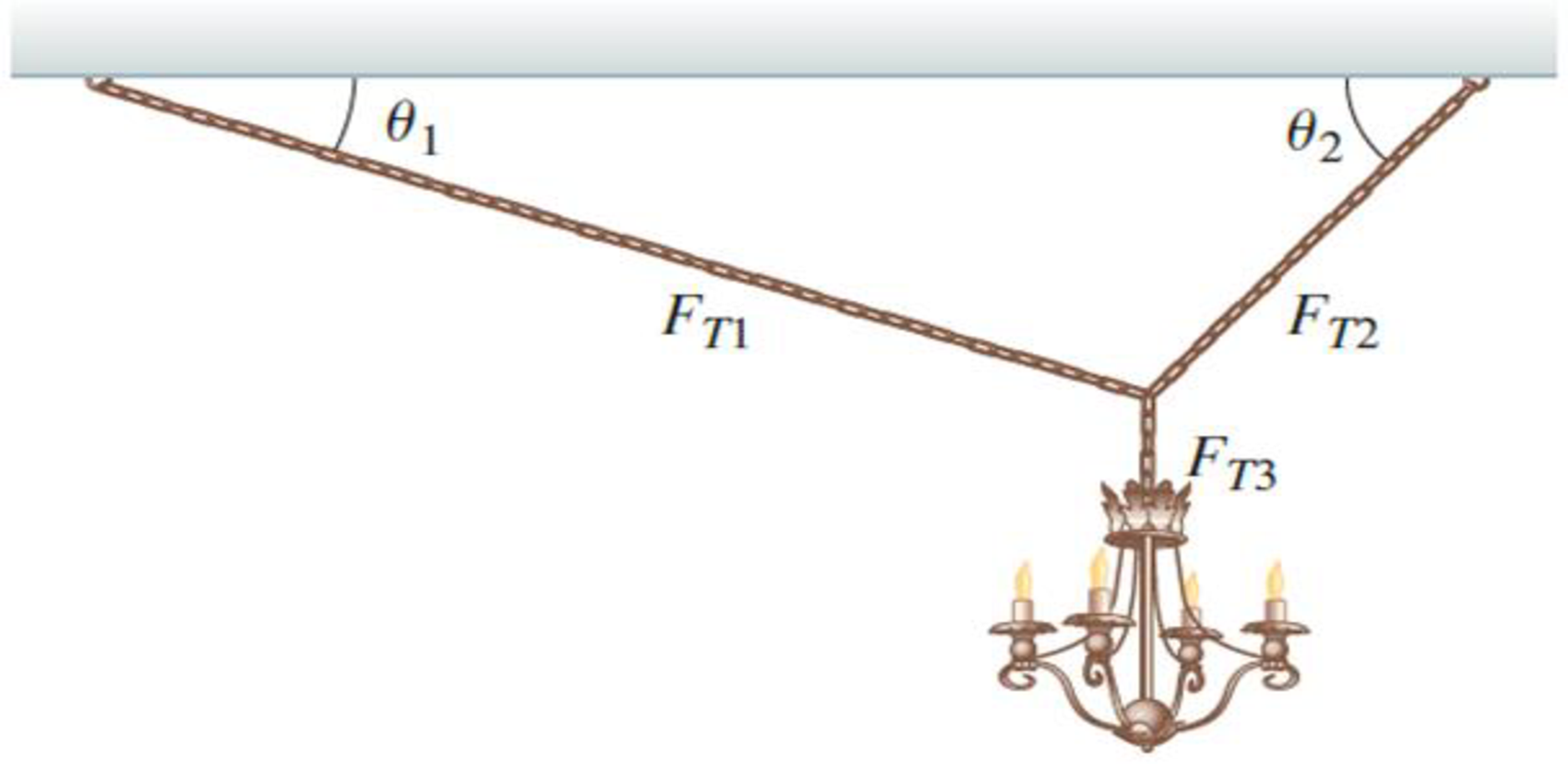
FIGURE P5.77
Find the values of tensions
Answer to Problem 77PQ
The values of tensions
Explanation of Solution
The free body diagram is given below.
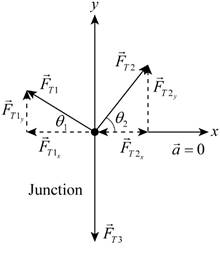
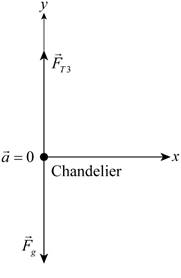
Applying Newton’s laws.
Here,
Here,
Rewrite the equation I to find
Since the chandelier is at equilibrium then the gravitational force is the tension force.
Here,
Substitute equation III in equation II.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the values of tensions
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- Two objects, m1 = 3.00 kg and m2 = 8.50 kg, are attached by a massless cord passing over a frictionless pulley as shown in Figure P5.51. Assume the horizontal surface is frictionless. a. Draw a free-body diagram for each of the two objects. b. What is the tension in the cord? c. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the two objects? FIGURE P5.51 Problems 51 and 65.arrow_forwardTwo blocks, each of mass m = 3.50 kg, are hung from the ceiling of an elevator as in Figure P4.33. (a) If the elevator moves with an upward acceleration a of magnitude 1.60 m/s2, find the tensions T1 and T2 in the upper and lower strings. (b) If the strings can withstand a maximum tension of 85.0 N, what maximum acceleration can the elevator have before a string breaks? Figure P4.33 Problems 33 and 34.arrow_forwardTwo blocks are connected by a rope that passes over a massless and frictionless pulley as shown in Figure P5.41. Given that m0 = 15.93 kg and m2 = 10.45 kg, determine the magnitudes of the tension in the rope and the blocks acceleration. FIGURE P5.41arrow_forward
- Four blocks, with masses m1 = 5.20 kg, m2 = 5.40 kg, m3 = 7.10 kg, and m4 = 7.10 kg, are pulled on a horizontal frictionless surface by a 34.0 N force that makes an angle of 25 degrees with the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the tension between the m2 and m3 blocks?arrow_forwardA box of mass m1 = 10.0 kg rests on a smooth, horizontal floor in contact with a box of mass m2 = 5.00 kg. You nowpush on box 1 with a horizontal force of magnitude F = 30.0 N. (a) What is the acceleration of the boxes? (b) What isthe force of contact between the boxes?arrow_forwardCassie is sitting on a frictionless playground slide that makes an angle θ with the horizontal. Maddy, who is on the top of the slide, is holding Cassie's belt parallel to the slide. If Cassie weighs 55.0 [kg] and feels a normal force of 403 [N], what should the tension be to prevent Cassie from sliding? Set the direction down the slide as the positive direction. 339 N 346 N 359 N 326 Narrow_forward
- An object of mass M is held in place by an applied force F and a pulley system as shown in Figure P4.43. The pulleys are massless and frictionless. (a) Draw diagrams showing the forces on each pulley. Find (b) the tension in each section of rope, T1, T2, T3, T4, and T5 and (c) the magnitude of F. Figure P4.43 44. Any device that allows you to increase the force you exert is a kind of machine. Some machines, such as the prybar or the inclined plane, are very simple. Some machines do not even look like machines. For example, your car is stuck in the mud and you cant pull hard enough to get it out. You do, however, have a long cable that you connect taut between your front bumper and the trunk of a stout tree. You now pull sideways on the cable at its midpoint, exerting a force f. Each half of the cable is displaced through a small angle from the straight line between the ends of the cable. (a) Deduce an expression for the force acting on the car. (b) Evaluate the cable tension for the case where = 7.00 and f = 100 N.arrow_forwardTwo blocks, each of mass m, are hung from the ceiling of an elevator as in Figure P4.33. The elevator has an upward acceleration a. The strings have negligible mass. (a) Find the tensions T1 and T2 in the upper and lower strings in terms of m, a, and g. (b) Compare the two tensions and determine which string would break first if a is made sufficiently large. (c) What are the tensions if the cable supporting the elevator breaks? Figure P4.33 Problems 33 and 34.arrow_forward(a) What is the resultant force exerted by the two cables supporting the traffic light in Figure P4.75? (b) What is the weight of the light? Figure P4.75arrow_forward
- Two blocks connected by a rope of negligible mass are being dragged by a horizontal force (Fig. P5.13). Suppose F = 68.0 N, m1 = 12.0 kg, m2 = 18.0 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between each block and the surface is 0.100. (a) Draw a free-body diagram for each block. Determine (b) the acceleration of the system and (c) the tension T in the rope. Figure P5.13arrow_forwardA 276-kg glider is being pulled by a 1 950-kg jet along a horizontal runway with an acceleration of a = 2.20 m/s2 to the right as in Figure P4.41. Find (a) the thrust provided by the jets engines and (b) the magnitude of the tension in the cable connecting the jet and glider. Figure P4.41arrow_forwardA bag of cement weighing 325 N hangs in equilibrium from three wires as suggested in Figure P4.23. Two of the wires make angles 1 = 60.0 and 2 = 40.0 with the horizontal. Assuming the system is in equilibrium, find the tensions T1, T2, and T3 in the wires. Figure P4.23 Problems 23 and 24.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





