
Concept explainers
Sketch the budget constraint.
Explanation of Solution
Maximum unit of good Y (0 unit of good X is purchased) that a person can purchase with the given income and price can be calculated by using the following formula:
Substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to calculate the maximum unit of Y that can be purchased.
The maximum unit of Y is 200 units.
Maximum unit of good X (0 unit of good Y is purchased) that a person can purchase with the given income and price can be calculated by using the following formula:
Substitute the respective values in Equation (2) to calculate the maximum unit of X that can be purchased.
The maximum unit of X is 50 units.
Option (a):
Figure 1 shows the budget constraint of case “a”.
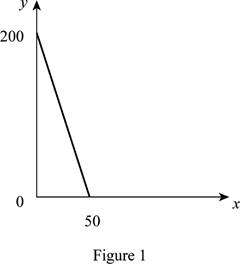
In Figure 1, the vertical axis measures the price of good Y and horizontal axis measures the price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Option (b):
The maximum quantity of good X and Y is 25 and 40 respectively that is obtained by using Equation (1) and (2).
Figure 2 shows the budget constraint of case “b”.
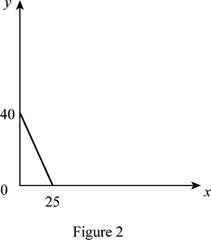
In Figure 2, the vertical axis measure price of good Y and horizontal axis measures price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Option (c):
The maximum quantity of good X and Y is 40 and 5, respectively that is obtained by using Equation (1) and (2).
Figure 3 shows the budget constraint of case “c”.
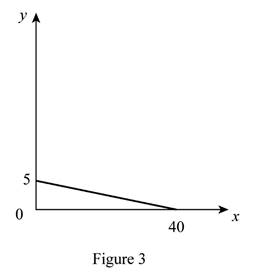
In Figure 3, the vertical axis measures the price of good Y and horizontal axis measures the price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Option (d):
The maximum quantity of good X and Y is 20 and 50, respectively that is obtained by using Equation (1) and (2).
Figure 4 shows the budget constraint of case “d”.
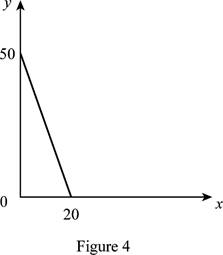
In Figure 4, the vertical axis measures the price of good Y and horizontal axis measures the price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Option (e):
The maximum quantity of good X and Y is 4 and 6, respectively that is obtained by using Equation (1) and (2).
Figure 5 shows the budget constraint of case “e”.
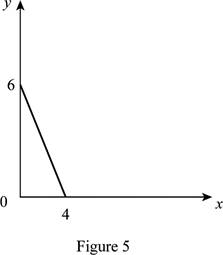
In Figure 5, the vertical axis measures the price of good Y and horizontal axis measures the price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Option (f):
The maximum quantity of good X and Y is 24 and 4, respectively that is obtained by using Equation (1) and (2).
Figure 6 shows the budget constraint of case “f”.
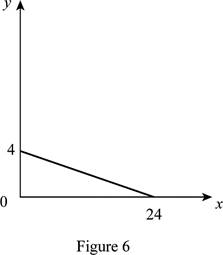
In Figure 6, the vertical axis measures the price of good Y and horizontal axis measures the price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Option (g)
The maximum quantity of good X and Y is 4 and 24, respectively that is obtained by using Equation (1) and (2).
Figure 7 shows the budget constraint of case “g”.
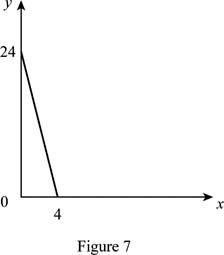
In Figure 7, the vertical axis measures the price of good Y and horizontal axis measures the price of good X. The downward sloping cure is the budget constrain of the household.
Budget constraints: Restrictions imposed on household’s choices by the factors like wealth, income and price of product are termed as the budget constraint.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
- Suppose Raymond decides to cut his monthly budget in half. Coincidentally, the next time he shops, he learns that meatloaves and pineapples are on sale for half price. Show what happens to Raymond’s budget line?arrow_forwardJody has $360 to spend on her summer vacation. She decided to use the moneyon trips to the zoo and on tickets to the movies. Her original budget constraintis shown below. Let X represent movie tickets and Y represent trips to the zoo.i. What is the equation of the original budget constraintarrow_forwardJody has $360 to spend on her summer vacation. She decided to use the moneyon trips to the zoo and on tickets to the movies. Her original budget constraintis shown below. Let X represent movie tickets and Y represent trips to the zoo.i. What is the equation of the original budget constraint? ii. What is the price of a movie ticket? a trip to the zoo? iii. Assume a price change occurs and Jody now face the new budgetconstraint. What is the equation of the new budget constraint? iv. With the new budget constraint, what is the price of an amusement parkticket? a baseball ticketarrow_forward
- Jody has $360 to spend on her summer vacation. She decided to use the moneyon trips to the zoo and on tickets to the movies. Her original budget constraintis shown below. Let X represent movie tickets and Y represent trips to the zoo.i. What is the equation of the original budget constraint? ii. What is the price of a movie ticket? a trip to the zoo? iii. Assume a price change occurs and Jody now face the new budgetconstraint. What is the equation of the new budget constraint? iv. With the new budget constraint, what is the price of a movie ticket? atrip to the zoo?arrow_forwardJody has $360 to spend on her summer vacation. She decided to use the moneyon trips to the zoo and on tickets to the movies. Her original budget constraintis shown below. Let X represent movie tickets and Y represent trips to the zoo.i. What is the equation of the original budget constraint? ii. What is the price of a movie ticket? a trip to the zoo? iii. Assume a price change occurs and Jody now faces the new budgetconstraint. What is the equation of the new budget constraint? iv. With the new budget constraint, what is the price of an amusement parkticket? a baseball ticket?arrow_forwardMary allocates $50 per month to spend on coffee and cookies. The price of coffee is $3 and the price of a cookie is $2. a. Create Mary’s budget constraint for coffee and cookies. b. Show the change in the budget constraint if the price of coffee increased to $4. c. Show the change in the budget constraint if the price of cookies decreased to $1.5. d. Suppose Mary received a bonus and allocated extra $20 for coffee and cookies. Show the change in her budget constraint. e. Can you determine the point in her budget constraint Mary would choose to consume? Why?arrow_forward
- Raymond consumes meatloaves and pineapples. He has decided that hismonthly budget will be $1500. Suppose that one meatloaf costs $375, while one pineapple costs $150. Suppose Raymond decides to cut his monthly budget in half. Coincidentally, the next time he shops, he learns that meatloaves and pineapples are on sale for half price. Show what happens to Raymond’s budget line?arrow_forwardI have to create a budget constraint for two cars with the median income. However, the income is smaller than the price of the cars. How can I approach this question?arrow_forwardSuppose Alphonso’s town raises the price of bus tickets from $0.50 to $1 and the price of burgers rises from $2 to $4. Why is the opportunity cost of bus tickets unchanged? Suppose Alphonso’s weekly spending money increases from $10 to $20. How is his budget constraint affected from all three changes? Explainarrow_forward
 Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning




