
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Two most stable Lewis structures for thiocyanate ion are to be written and the atom in each of them that bears a formal charge
Concept introduction:
The formal charge of an atom is calculated by the following formula:
Thiocyanate ion is a good nucleophile and reacts with a primary
Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula but differ in the connectivity of atoms in their structure.
Answer to Problem 23P
Solution:
a) The stable Lewis structures for thiocyanate ion are:
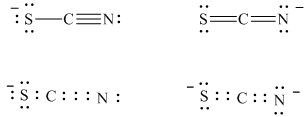
In structure I, the sulfur atom has a formal charge of
b) The structures of the two constitutional isomers of

Explanation of Solution
a) Thiocyanate ion,
The total number of valence electrons in
The two stable Lewis structures of the thiocyanate ion are shown below:
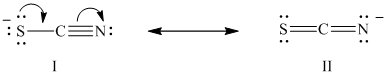
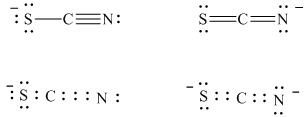
Carbon belongs to Group
In structure I, the electron counts and formal charge for each atom are as follows:
Hence, in structure I, the sulfur atom has a formal charge of
In structure
Hence, in structure
b)
In the reaction given, the alkyl halide is a primary alkyl bromide. The nucleophile is thiocyanate ion, formed by the dissociation of
Thiocyanate ion has two nucleophilic centers, which means it can attack through either sulfur or nitrogen atom. Because of this, when thiocyanate is used as a nucleophile, two possible products are obtained. In one product, the nucleophile attacks through the sulfur atom and gets attached to the carbon atom in the alkyl halide. In the other product, the nucleophile attacks through the nitrogen atom and gets attached to the carbon atom in the alkyl halide. The molecular formula of both the products remains the same; only the connectivity of atoms is different. Hence, they form constitutional isomers as follows:
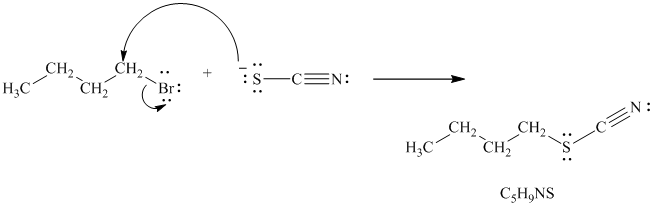
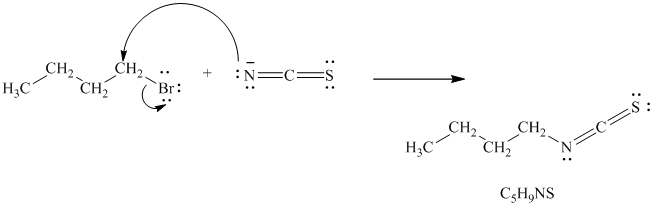
Thus, the structures of the two constitutionally isomeric products of the molecular formula

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- Compound A(C10H12O)gives off oxygen on treatment with sodium metal and also decolorizes Br2 in CCl4 to give organic compound B. Compound A on treatment with I2 in NaOH gives iodoform and salt C which after acidification gives a white solid D(C7H6O2). Using knowledge of organic chemistry identify structures A,B,C and Darrow_forwardCompound A, C5H10O, is one of the basic building blocks of nature. All steroids ans many other naturally occurring compounds are built from compound A. Spectroscopic analysis of A yields the following information. a) how many double bonds and/or rings does A have? b) From the IR spectrum, what is the identity of the oxygen-conataining functional group? c) what kinds of protons are responsible for the NMR absorptions listed d) propose a structure for Aarrow_forward1,2,3,4,5-Pentafluoro-6-nitrobenzene reacts readily with sodium methoxide in methanol at room temperature to yield two major products, each having the molecular formula C7H3F4NO3. Suggest reasonable structures for these two compounds.arrow_forward
- Compound A whose molecular formula is C9H11ClO, is found to be aromatic, and on vigorous oxidation with hot, concentrated, basic potassium permanganate followed by acidification, a new aromatic, compound B with the molecular formula of C7H5ClO2 is formed. On treatment with bromine and a ferric bromide catalyst, compound B produces ONLY 2 monobrominated derivatives, compounds C and D, each having the molecular formula C7H4BrClO2. On treatment with sodium metal, compound A produces bubbles of hydrogen gas. Controlled oxidation of compound A with PCC first gives compound E, with formula C9H9ClO. Compound E produces a silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent. Mild oxidation of compound E by chromic acid produces compound F, with the molecular formula C9H9ClO2 which turns blue litmus red. When compound A is heated with concentrated sulfuric acid, a single compound G, whose molecular formula is C9H9Cl, is produced. On ozonolysis followed by reaction with dimethyl sulfide, compound G gives…arrow_forwardNicotine is a diamino compound isolated from dried tobacco leaves. Nicotine has two rings and M+=162.1157 by high-resolution mass spectrometry. Give a molecular formula for nicotine, and calculate the number of double bonds.arrow_forwardFrom the following 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra, assign a structure for a compound with a formula of C4H9Br. Give reasons (explanations) for the choosen structure.arrow_forward
- Birch reduction of 2-methoxynaphthalene gave a mixture of two isomeric compounds, each having the molecular formula C11H14O. Suggest reasonable structures for these compounds.arrow_forwardA) Considering compounds 2a through 2l, identify: 1)one pair of geometric isomers 2)two pairs of enantiomers and 3)three pairs of identical molecules B) Give the names, including the configurations, of each of the geometric isomers and of each of the enantiomers identified in 1A and 1B. Draw the relevant structures. C) Sort compounds 2a, 2b, 2c, 2f and 2k in order of increasing solubility in water and briefly justify.arrow_forwardCompound EE, C5H10O gives a positive result (formation of silver mirror) when reacted with Tollen’s reagent. Reduction of EE with sodiumborohydride, NaBH4 followed by acidified water, H3O+ produces compound FF. Dehydration of compound FF uses concentrated sulphuric acid, H2SO4 at a temperature of 180°C produces compound GG. Compound FF also reacts with hot acidified potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7 to produce 2-methylbutanoic acid, C4H9COOH. Esterification between 2-methylbutanoic acid and methanol, CH3OH produces compound HH. Draw the structural formula of compounds EE, FF, GG, and HH.arrow_forward
- On being heated with a solution of sodium ethoxide in ethanol, compound A (C7H15Br) produced a mixture of two alkenes B and C, each of which had the molecular formula C7H14. Catalytic hydrogenation of major isomer B or minor isomer C gave only 3-ethylpentane. Suggest structures and mechanisms for compounds A, B, and C consistent with these observations.arrow_forwardGive a proposal on the synthesis methods of CoSO4.7H2Oarrow_forwardUsing the normal/primary isomer of C4H10O, treat it with conc.H2SO4 and heat to produce A. Treatment of A with HCl/H2O gives B and with cold KMnO4/ OH- gives C . Give the name and structures of A, B and C Treatment of A with Hot KMnO4/OH- gives D followed by acidification of the mixture to give E. What is D and E ?arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

