
Concept explainers
Allowance for Bad Accounts Installment Jewelry Company has been in business for 5 years but has never had its financial statements audited. Engaged to audit them for 2019, you find that the company’s
On your recommendation, the company agrees to revise its accounts for 2019 to give effect to bad account treatment on the allowance basis. The allowance is to be based on a percentage of credit sales that is derived from the experience of prior years. Statistics for the past 5 years are shown in the following table:
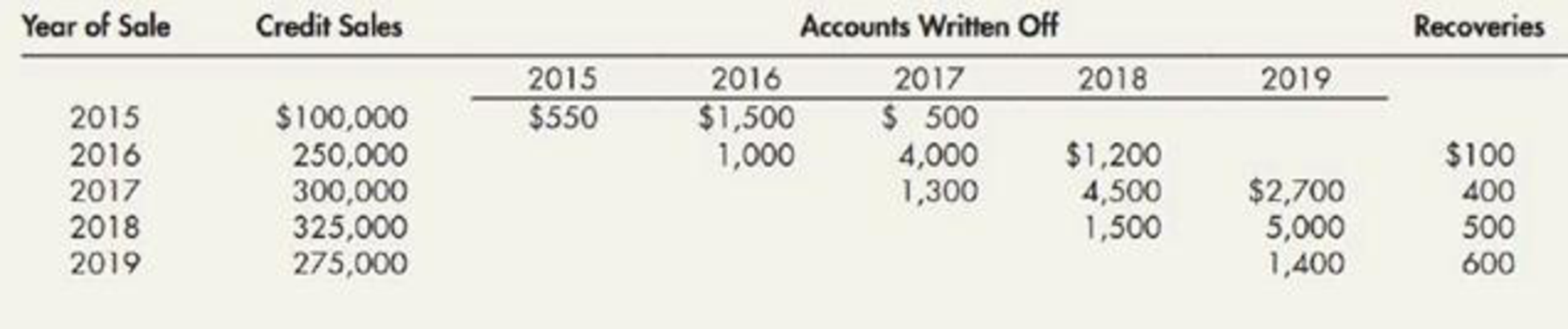
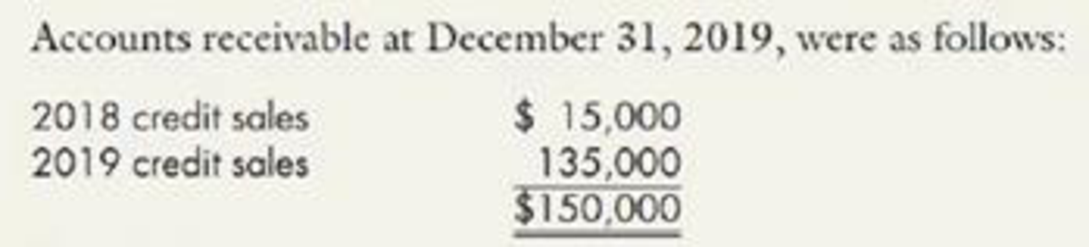
Required:
Prepare the
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 6 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
- Receivables Issues Magrath Company has an operating cycle of less than one year and provides credit terms for all of its customers. On April 3, 2019, the company factored, without recourse, some of its accounts receivable. Magrath does not normally factor its receivables. On August 1, 2019, Magrath sold special order merchandise and received an interest-bearing note due April 30, 2020. Magrath uses the allowance method to account for uncollectible accounts. During 2019, some accounts were written off as uncollectible, and other accounts previously written off as uncollectible were collected. Required: 1. Explain how Magrath should account for and report the accounts receivable factored on April 3, 2019. Why is this accounting treatment appropriate? 2. Explain how Magrath should report the effects of the interest-bearing note on its income statement for the year ended December 31, 2019, and its December 31, 2019, balance sheet. 3. Explain how Magrath should account for the collection of the accounts previously written off as uncollectible. 4. What are the two basic approaches to estimating uncollectible accounts under the allowance method? What is the rationale for each approach?arrow_forwardEstimation versus Direct Write-Off of Bad Debts Blunt Company makes credit sales of 21,000 during the month of February 2019. During 2019, collections are received on February sales of 20,400, accounts representing 600 of these sales are written off as uncollectible, and a 100 account previously written off is collected. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entries necessary to record the preceding information if (a) had debts are estimated as 3% of credit sales at the time of sale and (b) the bad debts are recorded as they actually occur. 2. Next Level Which methodrecording bad debts at the time of sale or when they actually occuris preferred? Why?arrow_forwardPrepare entries in general journal form to record the following: Aug. 6 Woodard Company failed to pay its 30-day, 5 percent note for 480, dated July 7. The note is thus dishonored at maturity.arrow_forward
- Non-Interest-Bearing Notes Payable On November 16, 2019, Clear Glass Company borrowed 20,000 from First American Bank by issuing a 90-day, non-interest-bearing note. The bank discounted this note at 12% and remitted the difference to Clear Glass. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entries of Clear Glass to record the preceding information, the related calendar year-end adjusting entry, and payment of the note at maturity. 2. Show how the preceding items Would be reported on the December 31, 2019, balance sheet. 3. Next Level What is Clear Glass Companys effective interest rate?arrow_forwardAccrued Interest On May 1, the Garnett Corporation wanted to purchase a $200,000 piece of equipment, but Garnett was only able to furnish $75,000 of its own cash to purchase the equipment. Garnett borrowed the remainder of the $200,000 from the Peoples National Bank on a 3-year, 4% note. Required: If the company keeps its records on a calendar year, what adjusting entry should Garnett make on December 31?arrow_forwardEstimating Bad Debts from Receivables Balances The following information is extracted from Shelton Corporations accounting records at the beginning of 2019: During 2019, sales on credit amounted to 575,000, 557,400 was collected on outstanding receivables and 2,600 of receivables were written off as uncollectible. On December 31, 2019, Shell on estimastes its bad debts to be 4% of the outstanding gross accounts receivable balance. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entry necessary to record Sheltons estimate of bad debt expense for 2019. 2. Prepare the Accounts Receivable section of Shelton's December 31, 2019, balance sheet. 3. Compute Shelton's receivables turnover. (Round to one decimal place.) 4. It Sheldon uses IFRS, what might be the heading for the accounts receivable section in Requirement 2?arrow_forward
- On January 1, 2019, Northfield Corporation becomes delinquent on a 100,000, 14% note to First National Bank, on which 16,651 of interest has accrued. On January 2, 2019, the bank agrees to restructure the note. It forgives the accrued interest, extends the repayment date to December 31, 2021, and reduces the interest rate to 10%. Required: Prepare a schedule for Northfield to compute the annual interest expense in regard to the preceding note for each year of the restructuring agreement.arrow_forwardWrite-Off of Uncollectible Accounts King Enterprises had 27 customers utilizing its financial planning services in 2019. Each customer paid King $25,000 for receiving Kings assistance. King estimates that 2% of its $675,000 credit sales in 2019 will be uncollectible. During 2020, King wrote off $2,700 related to services performed in 2019. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entry to record the defaulted balance. 2. Prepare the adjusting entry to record the bad debt expense for 2019.arrow_forwardReporting Liabilities Morton Electronics had the following obligations: a. A legally enforceable claim against the business to be paid in 3 months. b. A guarantee given by a seller to a purchaser to repair or replace defective goods during the first 6 months following a sale. c. An amount payable to Bank One in 10 years. d. An amount to be paid next year to Citibank on a long-term note payable. Required: CONCEPTIJAL CONNECTION Describe how each of these items should be reported in the balance sheet.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning





