
To calculate: The monthly savings of Person BB.
Introduction:
The series of payments that are made at equal intervals is an
Answer to Problem 57QP
The monthly savings of Person BB is $3,362.78.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Person BB wishes to save money to fulfill his three objectives. They are as follows:
- The first objective of Person BB is to retire at thirty years from now with a retirement amount of $20,000 for a month for every 25 years, the first payment will be expected at thirty years and a month from present
- The second objective of Person BB is to buy a cabin in the Place R within ten years at an projected cost of $375,000
- The third objective of Person B is to leave an inheritance of $2,000,000 to Person F after he passes on and at the last of the 25 years of withdrawal
Person BB can afford to save $25,000 for a month for the next ten years if he can earn the effective annual cost of 7% after his retirement and 10% before his retirement.
Time line of the cash flow:
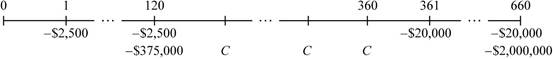
Note: The cash flows from the given information takes place monthly basis, the given interest rate is an effective annual rate. As the cash flows take place on a monthly basis, it is essential to compute the effective monthly rate by finding the annual percentage rate through monthly compounding, and then dividing it by 12. The preretirement annual percentage rate is calculated as follows:
Formula to calculate the effective annual rate:
Compute the effective annual rate:
Compute the annual percentage rate with the effective annual rate:
Hence, the annual percentage rate is 0.0957 or 9.57%.
The annual percentage rate for the post-retirement is calculated as follows:
Formula to calculate the effective annual rate:
Compute the effective annual rate:
Compute the annual percentage rate with the effective annual rate:
Hence, the annual percentage rate is 0.067 or 6.78%.
First, it is essential to compute the retirement needs of Person BB. The amount that is essential for the retirement is the present value of the monthly spending plus the inheritance’s present value. The present value of the two cash flows is as follows:
Formula to calculate the present value
Note: C denotes the payments, r denotes the rate of exchange, and t denotes the period.
Compute the present value annuity for without fee:
Formula to calculate the present value:
Compute the present value:
Hence, the present value is $368,498.36.
Person BB will be saving $2,500 per month for the upcoming ten years until he buys the cabin. The value of his savings after ten years is calculated as follows:
Formula to calculate the
Note: C denotes the annual cash flow or the annuity payment, r denotes the rate of interest, and t denotes the number of payments.
Compute the future value annuity of Person BB:
Hence, the future value of the annuity is $499,659.64.
The amount that remains in the hands of Person BB after the purchase of the cabin is as follows:
Note: The amount that remains in the hands of Person BB is calculated by subtracting the cost of the cabin from the calculated future value of the annuity.
Hence, the amount that Person BB has in his hands is $124,659.64.
Person BB still has twenty years until the retirement and at the time when he is ready to retire, the amount he would receive is as follows:
Formula to compute the future value:
Note: C denotes the annual cash flow or the annuity payment, r denotes the rate of interest, and t denotes the number of payments.
Compute the future value:
Hence, the future value is $838,647.73.
Thus, when Person BB is ready for the retirement based on his present savings, he will be short of the below amount:
Thus, the above calculated amount is the future value of the monthly savings that Person BB has to make between ten to thirty years.
Hence, the future value of an annuity of Person BB is $2,415,347.07.
Compute the monthly savings of Person BB using the Formula of the future value of an annuity:
Hence, the monthly savings of Person BB is $3,362.78.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals of Corporate Finance
- 5.3 Your parents will retire in 30 years. They currently have $230,000 saved, and they think they will need $1,650,000 at retirement. What annual interest rate must they earn to reach their goal, assuming they don't save any additional funds? Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardQ 24 Monica has decided that she wants to build enough retirement wealth that, if invested at 9 percent per year, will provide her with $3,600 of monthly income for 20 years. To date, she has saved nothing, but she still has 25 years until she retires. How much money does she need to contribute per month to reach her goal? First compute how much money she will need at retirement, then compute the monthly contribution to reach that goal. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your final answer to 2 decimal places.) CONTRIBUTION PER MONTH?arrow_forward1On the day you retire you have $500,000 saved. You expect to live another 30 years during which time you expect to earn 8% on your savings while inflation averages 3.5% annually. Assume you want to spend the same amount each year in real terms and die on the day you spend your last dime. What real amount will you be able to spend each year? a. $61,931.78 b. $79,211.09 c. $79,644.58 d. $30,695.77 2Now consider your financial objective is to save $500,000 for preparing your retirement, assuming 30 years from now. If you invest your RRSP savings in a mutual fund which can realize an average return of 10% per year. To achieve your goal, how much do you need to save at the end of each year over the 30-year period? a. 4,039.26 b. 3,039.62 c. 2,985.54 d. 10,988.32 3What is the FV of $100 deposited today into an account with an APR 12.6%, compounded semiannually for 10 years? a. 1478.96 b. 3460.06 c. 327.63 d. 339.36arrow_forward
- Q12: Suppose you are saving up to buy a holiday to Antarctica in five years that will cost you $10,000. If you are confident that your invested savings can earn 15% a year, how much would you need to invest today?arrow_forwardJUST NEED SUBPARTS D AND E You are trying to decide how much to save for retirement. Assume you plan to save $4,000 per year with the first investment made one year from now. You think you can earn 7.0% per year on your investments and you plan to retire in 29 years, immediately after making your last $4,000 investment. a. How much will you have in your retirement account on the day you retire? b. If, instead of investing $4,000 per year, you wanted to make one lump-sum investment today for your retirement that will result in the same retirement saving, how much would that lump sum need to be? c. If you hope to live for 28 years in retirement, how much can you withdraw every year in retirement (starting one year after retirement) so that you will just exhaust your savings with the 28th withdrawal (assume your savings will continue to earn 7.0% in retirement)? d. If, instead, you decide to withdraw $70,000 per year in retirement (again with the first withdrawal one…arrow_forward58. Modified True or False T means Correct and F means Wrong Scenario: CHUGS are considering two equally risky annuities, each of which pays $5,000 per year for 10 years. Investment ORD is an ordinary annuity, while Investment DUE is an annuity due. The present value of DUE exceeds the present value of ORD, while the future value of DUE is less than the future value of ORD. The present value of ORD exceeds the present value of DUE, and the future value of ORD also exceeds the future value of DUE. If the going rate of interest decreases from 10% to 0%, the difference between the present value of ORD and the present value of DUE would remain constant. A rational investor would be willing to pay more for DUE than for ORD, so their market prices should differ. Group of answer choices F,F,F,T F, F, F, F T,T,F,T T,T,T,T T,T,F,F F,T,F,Tarrow_forward
- 5.7 An investment will pay $150 at the end of each of the next 3 years, $200 at the end of Year 4, $350 at the end of Year 5, and $550 at the end of Year 6. If other investments of equal risk earn 5% annually, what is its present value? Its future value? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent. Present value: $ Future value: $arrow_forwardQuestion 8 Suppose a 65-year-old is contemplating retirement, expects to live for another 20 years, has a GHȼ1 million nest egg, expects the investments to earn a nominal annual rate of 6%, expects inflation to average 3% per year, and wants to withdraw a constant real amount annually over the next 20 years so as to maintain a constant standard of living. If the first withdrawal is to be made today, what is the amount of that initial withdrawal?arrow_forwardSHOW COMPLETE AND ORGANIZED SOLUTION1) A man wishes to bequeath to his son P100,000 ten years from now. What amount should he invest now if it will earn interest of 8% compounded annually during the first 5 years and 12% compounded quarterly during the next 5 years?2)If you are to invest your money, which is a better option: 12% compounded monthly, 12.20% compounded quarterly, 12.35% compounded semi-annually or 12.5% compounded annually?3) Determine the ordinary and exact simple interest on P60,000.00 for the period from January 16 to November 26, 2008 if the rate of interest is 14%arrow_forward
- 13–19. If you saved an average of $2,900 each year from your income tax return, $1,050 for not buying vendor coffee, and $2,400 (saving $200 each paycheck), how much would you have in your retirement account if you were able to invest these annual savings at the end of each year for 30 years at 5% interest compounded annually? PROVIDE THE FOLLOWING FOR EACH PROBLEM N= I= PV= PMT= FV= C/Y= P/Y =arrow_forwardQuestion 2B It is given that you need to save aside $320,000 for your retirement plan 10 years from now. You have a saving of $120,000 and is consider to put exactly an equal amount of money into Sustainable Investment Fund at the end of each month for 10 years to get 200 000 you still short of now. The fund is offering a rate of return 10.5 % per year, compounding monthly. Required: Calculate the monthly payment you need to contribute into Sustainable Investment Fund to get $200,000 after 10 years? If you change to contribute $1,000/month to that fund at the beginning of each month, how much money you would have in your account after 10 years? You are offered an investment that will pay $24 000 for the first year and then it will increase 4% each year. What is present value of this investment if the rate of return 13.5% applies?arrow_forward8 [Question text] You are considering to invest in a savings plan. The plan offers a rate of return of 8 percent per year. The plan requires you to save RM1,500, RM1,250, and RM6,400 at the end of each year for the next three years, respectively, how much do you need to save today? Select one: A. RM7,541 B. RM7,203 C. RM8,449 D. RM11,623arrow_forward
 PFIN (with PFIN Online, 1 term (6 months) Printed...FinanceISBN:9781337117005Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning
PFIN (with PFIN Online, 1 term (6 months) Printed...FinanceISBN:9781337117005Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning
