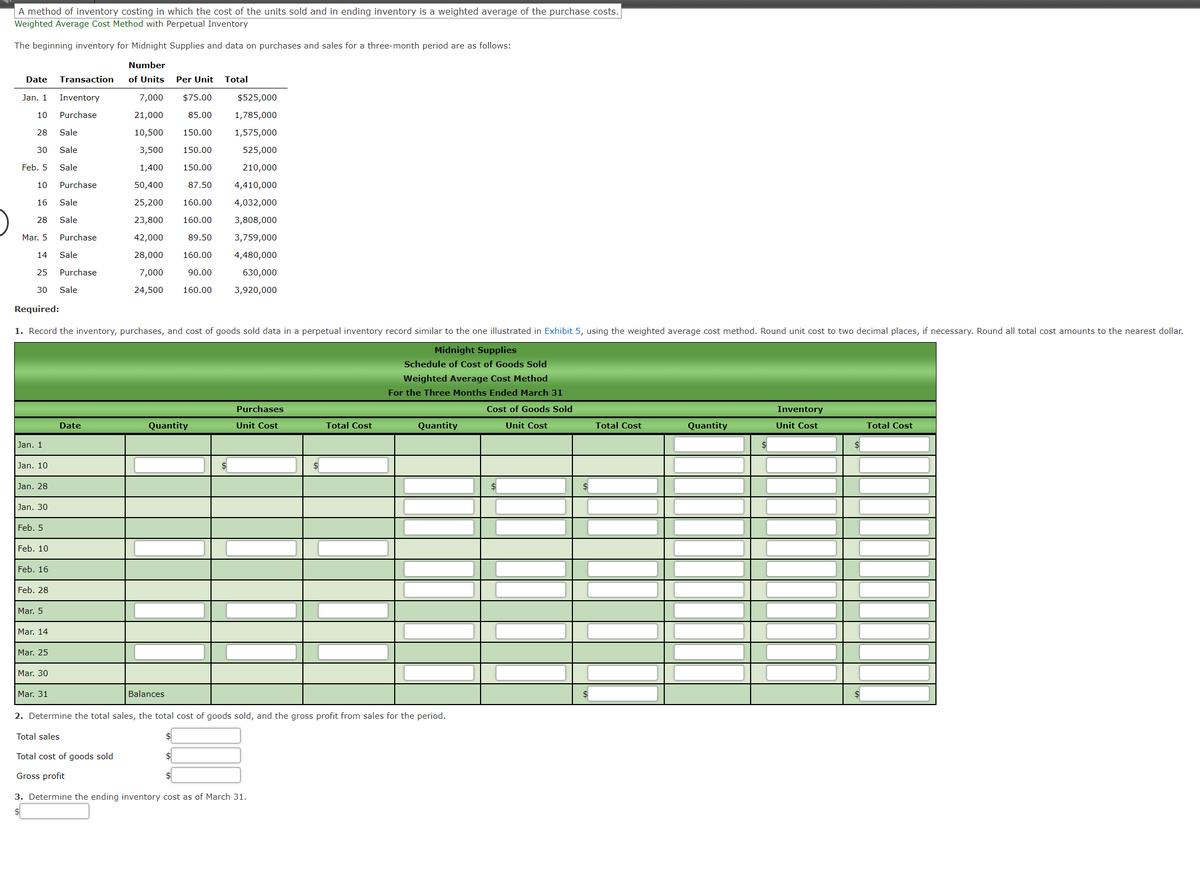
A method of inventory costing in which the cost of the units sold and in ending inventory is a weighted average of the purchase costs. Weighted Average Cost Method with Perpetual Inventory The beginning inventory for Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are as follows: Number Date Transaction of Units Per Unit Total Jan. 1 Inventory 7,000 $75.00 $525,000 10 Purchase 21,000 85.00 1,785,000 28 Sale 10,500 150.00 1,575,000 30 Sale 3,500 150.00 525,000 Feb. 5 Sale 1,400 150.00 210,000 10 Purchase 50,400 87.50 4,410,000 16 Sale 25,200 160.00 4,032,000 28 Sale 23,800 160.00 3,808,000 Mar. 5 Purchase 42,000 89.50 3,759,000 14 Sale 28,000 160.00 4,480,000 25 Purchase 7,000 90.00 630,000 30 Sale 24,500 160.00 3,920,000 Required: 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 5, using the weighted average cost method. Round unit cost to two decimal places, if necessary. Round all total cost amounts to the nearest dollar. Midnight Supplies Schedule of Cost of Goods Sold Weighted Average Cost Method For the Three Months Ended March 31 Purchases Cost of Goods Sold Inventory Date Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost Quantity Unit Cost Total Cost Jan. 1 Jan. 10 Jan. 28 Jan. 30 Feb. 5 Feb. 10 Feb. 16 Feb. 28 Mar. 5 Mar. 14 Mar. 25 Mar. 30 Mar. 31 Balances 2. Determine the total sales, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profit from sales for the period. Total sales Total cost of goods sold Gross profit 3. Determine the ending inventory cost as of March 31.
The beginning inventory for Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are as follows.
Required:
1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 5, using the weighted average cost method. Round unit cost to two decimal places, if necessary. Round all total cost amounts to the nearest dollar.
2. Determine the total sales, the total cost of goods sold, and the gross profit from sales for the period.
| Total sales | $_______________ |
| Total cost of goods sold | $_______________ |
| Gross profit | $_______________ |
3. Determine the ending inventory cost as of March 31.
$___________
The inventory valuation can be done using different systems like perpetual inventory system or periodic inventory system. Under the perpetual inventory system, the cost of goods sold is recorded at the time of sale transaction while under the periodic inventory system, the change in inventory is recorded at the end of the period.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images









