
Concept explainers
( Appendix 6B) Inventory Costing Methods
Jet Black Products uses a periodic inventory system. For 2018 and 2019, Jet Black has the following data:
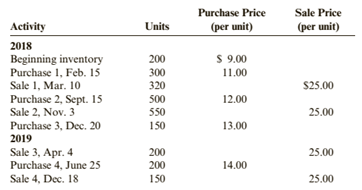
All purchases and sales are for cash.
Required:
1. Compute cost of goods sold, the cost of ending inventory, and gross margin for each year using FIFO.
2. Compute cost of goods sold, the cost of ending inventory, and gross margin for each year using LIFO.
3. Compute cost of goods sold, the cost of ending inventory, and gross margin for each year using the average cost method. ( Note: Use four decimal places for per unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest dollar.)
4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which method would result in the lowest amount paid for taxes?
5. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which method produces the most realistic amount for income? For inventory? Explain your answer.
6. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION What is the effect of purchases made later in the year on the gross margin when LIFO is employed? When FIFO is employed? Be sure to explain why any differences occur.
7. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION If you worked Problem 6-68A, compare your answers. What are the differences? Be sure to explain why any differences occurred.
(a)
Inventory costing methods:
FIFO, LIFO and average cost method, are those method which used for calculation of closing inventory and cost of goods sold.
The cost of ending inventory, the cost of goods sold and gross margin using the FIFO.
Answer to Problem 73APSA
| Particular | ||
| Cost of goods sold | ||
| Closing inventory value |
Explanation of Solution
The given information for the year
Total available units are:
The given information for the year
Total available units are:
Calculation of Closing Inventory as per FIFO Method:
Under this method, which material purchased first, issued first for production. However closing inventory includes last purchased materials in stock. Due to latest purchase in closing inventory, higher value of latest purchase effects cost of goods sold as lower and profit margin will be high.
As in the periodic system, no updated records are available. So, the cost of goods sold will be computed by subtracting the cost of goods available for sale and cost of ending inventory.
The method followed here is FIFO in which the closing inventory of
In the year
Hence, the closing inventory is
The cost of goods sold is as follows:
In the year
Hence, the closing inventory is
The cost of goods sold is as follows:
Computation of Gross Margin for the year
| Particulars | Amount |
Amount |
| Sales | ||
| Less: Cost of goods sold | ||
| Gross Margin |
(b)
Inventory costing methods:
FIFO, LIFO and average cost method, are those method which used for calculation of closing inventory and cost of goods sold.
The cost of ending inventory, the cost of goods sold and gross margin using the LIFO.
Answer to Problem 73APSA
| Particular | ||
| Cost of goods sold | ||
| Closing inventory value |
Explanation of Solution
The given information for the year
Total available units are:
The given information for the year
Total available units are:
Calculation of closing inventory as per LIFO Method:
Under this method, which material purchased last, issued first for production. However closing inventory includes earliest purchased material in stock. Due to earliest purchase material in stock, lower value of earliest purchased effects cost of goods sold as high and profit margin will be lower.
As in the periodic system, no updated records are available. So, the cost of goods sold will be computed by subtracting the cost of goods available for sale and cost of ending inventory.
The method followed here is LIFO in which the closing inventory of
In the year
Hence, the closing inventory is
The cost of goods sold is as follows:
In the year
Hence, the closing inventory is
The cost of goods sold is as follows:
Computation of Gross Margin for the year
| Particulars | Amount |
Amount |
| Sales | ||
| Less: Cost of goods sold | ||
| Gross Margin |
(c)
Inventory costing methods:
FIFO, LIFO and average cost method, are those method which used for calculation of closing inventory and cost of goods sold.
The cost of ending inventory, the cost of goods sold and gross margin using the average cost method.
Answer to Problem 73APSA
| Particular | ||
| Cost of goods sold | ||
| Closing inventory value |
Explanation of Solution
The given information for the year
Total available units are:
The given information for the year
Total available units are:
Calculation of closing inventory as per weighted average method:
Under this method, average cost per unit of inventory is calculated and closing inventory value is to be calculated on that basis. Average cost of inventory is changed on purchase high or low. However we follow indirect method of average cost to calculate closing inventory.
As in the periodic system, no updated records are available. So, the cost of goods sold will be computed by subtracting the cost of goods available for sale and cost of ending inventory.
The method followed here is average cost method in which the closing inventory of
In the year
Hence, the closing inventory is
The cost of goods sold is as follows:
In the year
Hence, the closing inventory is
The cost of goods sold is as follows:
As all the three sales are done after purchases some units and beginning inventory. Hence, there will requirement of various average cost for computing the cost of goods sold.
Computation of Gross Margin for the year
| Particulars | Amount |
Amount |
| Sales | ||
| Less: Cost of goods sold | ||
| Gross Margin |
(d)
Inventory costing methods:
FIFO, LIFO and average cost method, are those method which used for calculation of closing inventory and cost of goods sold.
The method for determining the lowest amount paid for tax.
Answer to Problem 73APSA
The cost of goods sold of LIFO method is higher in both the years and value of closing inventory is lower than other methods in both the years which mean LIFO method provides lowest tax expenses in all methods.
Explanation of Solution
Comparison of closing inventory and Cost of goods sold as per above three methods:
| Particulars | FIFO | LIFO | Average Cost | |||
| Cost of goods sold | ||||||
| Closing inventory value | ||||||
According the evaluation of the above table, it can be concluded that the lowest tax paid is provided by the LIFO method as the expense of cost of goods sold is highest in both the years which makes the income low and lower closing value of inventory in both the years also makes the income lower. Thus, the LIFO is the required method.
(e)
Inventory costing methods:
FIFO, LIFO and average cost method, are those method which used for calculation of closing inventory and cost of goods sold.
The method for determining the most realistic amount for inventory.
Answer to Problem 73APSA
FIFO method describes most realistic amount of closing inventory. It is not so high or not so less value.
Explanation of Solution
Comparison of closing inventory and Cost of goods sold as per above three methods:
| Particulars | FIFO | LIFO | Average Cost | |||
| Cost of goods sold | ||||||
| Closing inventory value | ||||||
According the evaluation of the above table, it can be concluded that the most realistic amount for the inventory is getting from the method named FIFO method as it provides a medium value i.e. not very high and not very low to affect the income.
(f)
Gross profit margin ratio:
The gross margin ratio is a type of profitability ratio which is used to measure the returns and earning after direct expenses and compute the ratio in respect to the sales of the business.
Inventory Turnover ratio:
The ratio which measures the efficiency of the company in managing their inventory by diving the cost of goods sold by the average inventory.
The effect of purchases made later in the year on the gross margin when LIFO and FIFO is employed.
Answer to Problem 73APSA
The effect of purchases when LIFO employed is that due to increase in price the cost of goods sold goes to the highest and closing inventory lowest which gives lower gross margin. On using FIFO, the effect is that the prices earlier lowest and then in later increased which makes the cost of goods sold lower and closing inventory value higher which gives higher gross margin.
Explanation of Solution
| Particulars | FIFO | LIFO | Average Cost | |||
| Sales |
||||||
| Less: Cost of goods sold |
||||||
| Gross Profit |
||||||
| Opening Inventory |
||||||
| Closing Inventory |
||||||
By analyzing the above table, it can be said that the purchases of later time affects the cost of goods sold and closing inventory valuation as they are increasing. In FIFO method, the purchases of earlier period is used for computing cost of goods sold which results in lower value and the inventory left is of later purchases of high value which results in higher value of closing inventory. This results in higher gross margin.
Likewise, opposite scenario is in LIFO method. The purchases of later with increased prices used for computing cost of goods sold which leads to higher cost of goods sold and the inventory left is of earlier period in which purchases of lower value which leads to lower closing inventory value. This results in lower gross margin.
(g)
Inventory costing methods:
FIFO, LIFO and average cost method, are those method which used for calculation of closing inventory and cost of goods sold.
The difference of the results in two same answers.
Answer to Problem 73APSA
The reason of difference in two same answers is due to the difference in the method followed in both the answers to record the transactions.
Explanation of Solution
On comparison the answer with that of problem
In this problem, the method used is the periodic inventory method in which businesses does not maintain up to date records and transactions of every sale and purchase. This method does not affect the answer of FIFO and LIFO method but affect the average cost method and its reason is its difference in timings.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
- ( Appendix 6B) Inventory Costing Methods Grencia Company uses a periodic inventory system. For 2018 and 2019, Grencia has the following data (assume all purchases and sales are for cash): Required: 1. Compute cost of goods sold, the cost of ending inventory, and gross margin for each year using FIFO. 2. Compute cost of goods sold, the cost of ending inventory, and gross margin for each year using LIFO. 3. Compute cost of goods sold, the cost of ending inventory, and gross margin for each year using the average cost method. ( Note: Use four decimal places for per unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest dollar.) 4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which method would result in the lowest amount paid for taxes? 5. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which method produces the most realistic amount for income? For inventory? Explain your answer. 6. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION What is the effect of purchases made later in the year on the gross margin when LIFO is employed? When FIFO is employed? Be sure to explain why any differences occur. 7. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION If you worked Problem 6-68B, compare your answers. What are the differences? Be sure to explain why any differences occurred.arrow_forwardThe following data were extracted from the accounting records of Harkins Company for the year ended April 30, 2019: a. Prepare the cost of merchandise sold section of the income statement for the year ended April 30, 2019, using the periodic inventory system. b. Determine the gross profit to be reported on the income statement for the year ended April 30, 2019. c. Would gross profit be different if the perpetual inventory system was used instead of the periodic inventory system?arrow_forward( Appendices 6A and 6B) Inventory Costing Methods Edwards Company began operations in February 2019. Edwards accounting records provide the following data for the remainder of 2019 for one of the items the company sells: Â Edwards uses a periodic inventory system. All purchases and sales were for cash. Required: 1. Compute cost of goods sold and the cost of ending inventory using FIFO. 2. Compute cost of goods sold and the cost of ending inventory using LIFO. 3. Compute cost of goods sold and the cost of ending inventory using the average cost method. ( Note: Use four decimal places for per-unit calculations and round all other numbers to the nearest dollar.) 4. Prepare the journal entries to record these transactions assuming Edwards chooses to use the FIFO method. 5. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which method would result in the lowest amount paid for taxes? 6. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Refer to Problem 6-67B and compare your results. What are the differences? Be sure to explain why the differences occurred.arrow_forward
- Under the periodic inventory system, what account is debited when an estimate is made for the cost of merchandise inventory sold this year, but expected to be returned next year? (a) Estimated Returns Inventory (b) Sales Returns and Allowances (c) Merchandise Inventory (d) Customer Refunds Payablearrow_forwardCompany Elmira reported the following cost of goods sold but later realized that an error had been made in ending inventory for year 2021. The correct inventory amount for 2021 was 32,000. Once the error is corrected, (a) how much is the restated cost of goods sold for 2021? and (b) how much is the restated cost of goods sold for 2022?arrow_forwardRefer to the information provided in RE8-4. If Paul Corporations inventory at January 1, 2019, had a cost and net realizable value of 300,000, prepare the journal entry to record the reductions to NRV for Paul Corporation assuming that Paul uses a periodic inventory system and the allowance method. Paul Corporation uses FIFO and reports the following inventory information: Assuming Paul uses a perpetual inventory system and the direct method, prepare the journal entry to record the write-down of inventory.arrow_forward
- Refer to the information provided in RE8-4. If Paul Corporations inventory at January 1, 2019, had a cost and net realizable value of 300,000, prepare the journal entry to record the reductions to NRV for Paul Corporation assuming that Paul uses a periodic inventory system and the direct method. Paul Corporation uses FIFO and reports the following inventory information: Assuming Paul uses a perpetual inventory system and the direct method, prepare the journal entry to record the write-down of inventory.arrow_forwardThe moving average inventory cost flow assumption is applicable to which of the following inventory systems? Questions M7-6 and M7-7 are based on the following data: City Stationers Inc. had 200 calculators on hand on January 1, 2019, costing 18 each. Purchases and sales of calculators during the month of January were as follows: City uses a periodic inventory system. According to a physical count, 150 calculators were on hand at January 31, 2019.arrow_forwardOn December 31, 2019, the balances of the accounts appearing in the ledger of Wyman Company are as follows: Instructions 1. Does Wyman Company use a periodic or perpetual inventory system? Explain. 2. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for Wyman Company for the year ended December 31, 2019. The merchandise inventory as of December 31, 2019, was 305,000. The adjustment for estimated returns inventory for sales for the year ending December 31, 2019, was 30,000. 3. Prepare the closing entries for Wyman Company as of December 31, 2019. 4. What would the net income have been if the perpetual inventory system had been used?arrow_forward
- Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for WCS12 are as follows: Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, determine (a) the weighted average unit cost after the October 22 purchase, (b) the cost of goods sold on October 29, and (c) the inventory on October 31.arrow_forwardUse the last-in, first-out (LIFO) cost allocation method, with perpetual inventory updating, to calculate (a) sales revenue, (b) cost of goods sold, and c) gross margin for A75 Company, considering the following transactions.arrow_forwardRefer to the information for Morgan Inc. above. If Morgan uses a perpetual inventory system, what is the cost of ending inventory under FIFO at April 30? a. $32,500 b. $38,400 c. $63,600 d. $69,500arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





