
Concept explainers
This problem concerns the m. o module from Figure 7.5 and the following version of the swap, c function that counts the number of times it has been called:

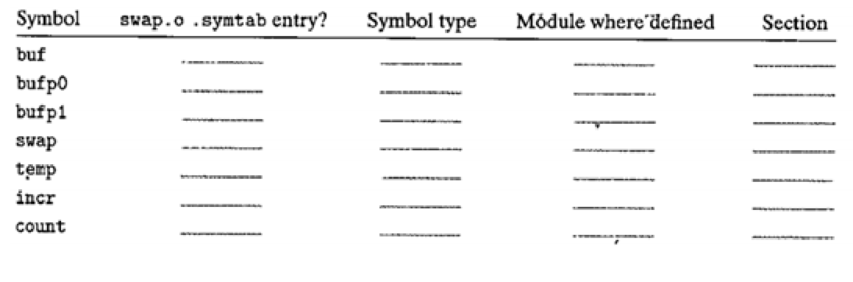
For each symbol that is defined and referenced in swap. o, indicate if it will have a symbol table entry in the symbol section in module swap. o. If so, indicate the module that defines the symbol (swap .o or m. o), the symbol type (local, global, or extern), and the section (.text, .data, or bss) it occupies in that module.
Sections in relocatable object files:
There are many sections in a relocatable object file. They are given below:
- “.text”:
- It is the machine code of the compiled program.
- “.rodata”:
- This section is used to read only the data in the format such as
- Strings in “printf” statements.
- Jump tables for switch statements.
- This section is used to read only the data in the format such as
- “.data”:
- This section is used in the initialized “C” variables of global variable and static “C” variables.
- Local “C” variables are initialized at execution time on the stack.
- It does not show in either the “.data” or “.bss” sections.
- “.bss”:
- It is used in the uninitialized global and static “C” variables, along with any global or static variables that are assigned to zero.
- “.symtab”:
- It is a symbol table.
- It contains the information about functions and global variables that are defined and referenced in the program.
- “.rel.text”:
- This section contains a list of locations in the “.text” section.
- It will require to be changed once the linker merges this object file with others.
- This section contains a list of locations in the “.text” section.
- “.rel.data”:
- This section contains relocation information for any global variables that are referenced or defined by the module.
- “.debug”:
- It is a symbol table for debugging
- It contains entries for following
- Definition of Local variables, global variables and typedefs variables and original “C” source file.
- “.line”:
- It is a mapping between line numbers in the given program
- That is in original “C” source program and machine code instructions in the “.text” section.
- It is a mapping between line numbers in the given program
- “.strtab”:
- It is a string table.
- It contains symbol tables in the “.symtab” and “.debug” sections.
- It is the table for section names in the section headers.
- It is a string table.
Explanation of Solution
For symbol “buf”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is an “extern” type. Because, the variable “buf” is declared in “extern” type which is present in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “buf” type is defined in “m.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “buf” are defined in “m.c” file”.
- When converting source file “m.c” to a relocatable object file, the given file becomes “m.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “buf” is defined in “.data” section. It is the initialized global variable of “m.c” file.
For symbol “bufp0”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “global” symbol type. Because, the variable “bufp0” is declared outside the function in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “bufp0” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “bufp0” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable object file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “bufp0” is defined in “.data” section. It is the initialized global variable of “swap.c” file
For symbol “bufp1”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “local” type. Because, the variable “bufp1” with “static” type in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “bufp1” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “bufp1” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable object file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “bufp1” is defined in “.bss” section. It is the uninitialized static “C” variable of “swap.c” file
For symbol “swap”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “global” type. Because, the symbol “swap” is used in the entire program.
- Module defined position:
- The “swap” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “swap” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “swap” is present in “.text” section. It is the machine code of the compiled program.
For symbol “temp”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- The local variable “temp” does not a have a symbol table entry.
- So, it does not have a symbol type, module defined position and section.
- The local variable “temp” does not a have a symbol table entry.
For symbol “incr”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “local” type. Because, the function “incr” uses return type of “static” in “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “swap” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “swap” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “swap” is present in “.text” section. It is the machine code of the compiled program.
For symbol “count”:
- “.symtab” entry:
- It is occurs in the symbol table.
- Symbol type:
- It is a “local” type. Because, the variable “count” declared in “static” type in the “swap.c” file.
- Module defined position:
- The “swap” type is defined in “swap.o” module.
- Because, the symbol “swap” are defined in “swap.c” file”.
- When converting source file “swap.c” to a relocatable file, the given file becomes “swap.o”.
- Section:
- The symbol “swap” is present in “.bss” section. Here, the static variables “count” are initialized to “0” in “swap.c” file.
The final table is
| Symbol | .symtab entry? | Symbol type | Module where defined | Section |
| buf | Yes | extern | m.o | .data |
| bufp0 | Yes | global | swap.o | .data |
| bufp1 | Yes | local | swap.o | .bss |
| swap | Yes | global | swap.o | .text |
| temp | No | - | - | - |
| incr | Yes | local | swap.o | .text |
| count | Yes | local | swap.o | .bss |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective Plus Mastering Engineering With Pearson Etext -- Access Card Package (3rd Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Concepts of Programming Languages (11th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (3rd Edition)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach
Software Engineering (10th Edition)
- Using a C language, write a C program that will display the menu as shown below and will ask the user to pick a choice that will perfom its function. For example, the user choice 1] which is to get the CARDINAL NUMBER OF A SET, the program must ask the user to input any set of numbers before getting its cardinality. Same goes to the other choices. Make the descriptions below as the reference for each choices in the MENU. It is an algebra and I don't have any idea how to code the above mention. M E N U 1] CARDINAL NUMBER OF A SET 2] UNION OF SETS 3] INTERSECTION OF SETS 4] DIFFERENCE OF 2 SETS 5] COMPLEMENT OF A SET 6] QUIT Enter choice: Description in every choices: 1] Cardinal Number of a Set Example: Set A ={1, 4, 0, -3, -1, 3, 17} Cardinal Number of Set A = 7 2] Union of Sets Example: Set A ={1, 4, 0, -3, -1, 3, 17} Set B = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10} A Ս B = {0, 1, -1, 2, 3, -3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 17} 3] Intersection of Sets Example: Set A ={1, 4, 0, -3, -1, 3, 17} Set B = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10} A Ո B…arrow_forwardWrite a function in C language to swap two numbers passed by reference. In main function test the function swap using values a= 2, b= 3.arrow_forwardWrite in c language please, The Fibonacci sequence begins with 0 and then 1 follows. All subsequent values are the sum of the previous two, for example: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13. Complete the Fibonacci() function, which has an index n as a parameter and returns the nth value in the sequence. Any negative index values should return -1. Ex: If the input is: 7 the output is: Fibonacci(7) is 13 Note: Use a for loop and DO NOT use recursion.arrow_forward
- Given the code segment below, what is the value that is passed to func() given the function call? Assume that func() is defined. If it is an invalid access, write INVALID (in all capital letters) as your answer. Assume that the array aData[] is associated to the memory address 1010 (in decimal). If the value is an address, then indicate the memory address in decimal. double aData[15] = {0.0, 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5, 6.6, 7.7, 8.8, 9.9};func(aData + 2);arrow_forward1. Given a global list of users and password like the following, write a function (called login) that takes a user name and password and logs in the user if login is successful:- the user exists in the list- and the password is correct The function should return a True/False users = {'Jane': 'Password123@', 'John': 'Password123!'} 2. Write a function called register that takes a user name and password and adds the user to the list if the user does not already exist in the listThe function should return a True/False Put it all together: 3. Write a showmenu function that shows the following options and reads the choice from user and returns it: 1: register 2: login 0: logout 3. In the main section, based on the user's selected option, ask the required input (user name, passwords) and perform the requested operation. 4. Repeat the above until the user enters 0. (keep showing the menu that asks for another option)arrow_forwardIn case of pass by reference The values of those variables are passed to the function so that it can manipulate O them The location of variable in memory is passed to the function so that it can use Q the same memory area for its processing Both of above O None of above O narrow_forward
- Write a C program to swap two integers you should write a function named as swap_intand it should accept arguments as pointers then it should swap integers bydereferencing those pointers.arrow_forwardWrite a program to count Non-Armstrong numbers from m and n (including m and n also) using the concept of passing pointers to function. Pass addresses of m, n and count integers from the main () function to the user defined function: calculate () [Function is not returning any value], and display the count in the main () function. Answer should be in C language.arrow_forwardWrite a C program that uses the following: a main() to read two integer values from the user, val1 and val2, and prints the returned value from swap().a swap() that uses call by reference (takes the addresses into pointers) to swap values, and prints their values after the swap "num1 = # and num2 = #". This function returns the largest of the two values. If these are equal, it returns their sum.arrow_forward
- Develop a basic calculator with arithmetic operations like +, -, *, / and % using switch case by reading values from user in form of integer pointers and performing the operation basing on user's choicearrow_forwardWrite the definition of a function called swap(), which is used to swap two integervariables. The function is used as follows:swap(&x, &y); // x and y are now swapped In C programming pleasearrow_forwardMatch the following function with a possible asymptotic notation. I've tried to start it, but I need a little help. Thank youarrow_forward
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr

