
Find the distance a.
Answer to Problem 7.148P
The distance a is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the cable AB is
The value of angle
The collar at A is slides freely and the collar at B is prevented from the moving.
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the cable assembly as in Figure 1.
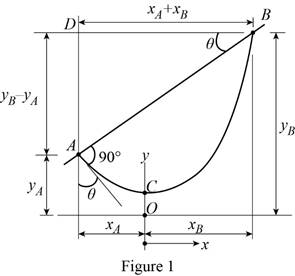
Refer Equation 7.16 in the textbook.
Write the equation of the catenary cable as follows;
Differentiate the equation with x;
The slope at point A is;
The length of the portion AC is;
The length of the portion CB is;
Find the distance
Substitute 10 ft for L,
Find the distance
Find the distance
Consider the triangle ABD;
Find the value of
Find the distance a using the relation.
Use the trial and error procedure to find the value of a.
Consider the value of c and for the given value of
Find the angle
Trial 1:
Consider a trial value of 1.60 ft for c.
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and 1.410 ft for
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and 1.410 ft for
Substitute 1.60 ft for c and 3.777 ft for
Substitute 1.410 ft for
The calculated value of
Trial 2:
Consider a trial value of 1.70 ft for c.
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and 1.498 ft for
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and 1.498 ft for
Substitute 1.70 ft for c and 3.891 ft for
Substitute 1.498 ft for
The calculated value of
Trial 3:
Consider a trial value of 1.8652 ft for c.
Substitute 1.8652 ft for c and
Substitute 1.8652 ft for c and 1.644 ft for
Substitute 1.8652 ft for c and 1.644 ft for
Substitute 1.8652 ft for c and 4.064 ft for
Substitute 1.644 ft for
The calculated value of
Therefore, the value of c is 1.8652 ft.
Substitute 2.638 ft for
Therefore, the distance a is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
- Show that the curve assumed by a cable that carries a distributed load w(x) is defined by the differential equation d2y/dx2 = w(x)/t0, ehere T0 is the tension at the lowest point.arrow_forwardA 500-ft-long aerial tramway cable having a weight per unit length of 2.8 lb/ft is suspended between two points at the same elevation. Knowing that the sag is 125 ft, find (a) the horizontal distance between the supports, (b) the maximum tension in the cable.arrow_forward(a) Determine the maximum allowable horizontal span for a uniform cable with a weight per unit length of w if the tension in the cable is not to exceed a given value Tm. (b) Using the result of part a , determine the maximum span of a steel wire for which w = 0.25 lb/ft and Tm = 8000 lb.arrow_forward
- A block with weight W is pulled up a plane forming an angle a with the horizontal by a force P directed along the plane. μ If is the coefficient of friction between the block and the plane, derive an expression for the mechanical efficiency of the system. Show that the mechanical efficiency cannot exceed 1/2 if the block is to remain in place when the force P is removed.arrow_forwardThree bars, two made of aluminum and one made of steel, support a rigid block. An object of weight W is dropped vertically from a distance h above the rigid block. Both steel and aluminum bars have cross-sectional area of 50 mm2 and length of 0.5 m. The elastic moduli for the aluminum and steel are 76 GPa and 184 GPa, respectively. a) If W=1000N and h=0.1m, determine whether the three bars are still safe to perform. b) If h=0.2m, determine the maximum weight that can be dropped without causing failure to the barsarrow_forwardA cable is placed around three parallel pipes. Two of the pipes are fixed and do not rotate; the third pipe is slowly rotated. Knowing that the coefficients of friction are μs= 0.25 and μk= 0.20, determine the largest weight W that can be raised (a) if only pipe A is rotated counterclockwise, (b) if only pipe C is rotated clockwise.arrow_forward
- Determine the value of w and P such that the resultant of the system is a downward force of magnitude 1200 N acting 3.6 m to the right of A. Determine the magnitude of the uniform load w. a.252 N/m b.646.1 N/m c.387.7 N/m d.553.8 N/marrow_forwardDetermine the maximum value of 'mass M' of the ball provided that the maximum load that each wire in the system can resist is 150N (g: 9.81 m/s^2)arrow_forwardThe frictional resistance of a thrust bearing decreases as the shaft and bearing surfaces wear out. It is generally assumed that the wear is directly proportional to the distance traveled by any given point of the shaft and thus to the distance r from the point to the axis of the shaft. Assuming then that the normal force per unit area is inversely proportional to r , show that the magnitude M of the couple required to overcome the frictional resistance of a worn-out end bearing (with contact over the full circular area) is equal to 75 percent of the value given by Eq. (8.9) for a new bearing.arrow_forward
- A thin circular rod is supported in a vertical plane by a bracket at A. Attached to the bracket and loosely wound around the rod is a spring of constant k= 3 lb/ft and undeformed length equal to the arc of circle AB. An 8-oz collar C , not attached to the spring, can slide without friction along the rod. Knowing that the collar is released from rest at an angle 0 with the vertical, determine (a) the smallest value of 0 for which the collar will pass through D and reach point A, (b) the velocity of the collar as it reaches point A.arrow_forwardThe uniform bar is at rest on a smooth half-sphere with radius R = b / 2. In A there is a ball joint and the bar rests at B against the vertical wall without friction. If the length of the bar AB is 4 m, and its weight is W = 200 N, at the midpoint of the bar. Take b = 1.6 m and d = 2.8 m, determine in Newtons: a) The magnitude of the normal force FN of the hemisphere on the bar. b) The magnitude of the normal force FB of the wall on the bar. c) The force AX of the patella on the bar in the X-axis. d) The force AY of the patella on the bar in the Y-axis. e) The force AZ of the patella on the bar in the Z-axis.arrow_forwardThree loads are applied as shown to a light beam supported by cables attached at B and D. Neglecting the weight of the beam, determine the range of values of Q for which neither cable becomes slack when P=0.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





