
Concept explainers
a)
To determine: The break-even point quantity for the manual process.
Introduction:
Break-even point (BEP):
The break-even point is measured in units or in sales term to identify the point in a business which is required to cover the total investment costs. The total profit at break-even point is zero.
a)
Answer to Problem 25P
The break-even point quantity for the manual process is 50,000 bags.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual
Fixed costs= $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formula to calculate Break-even point (BEP) in units:
Calculation of Break-even point (BEP) in units:
The Break-even point is calculated by dividing the fixed cost with the difference of selling price and variable cost.
Hence, the Break-even point (BEP) in units is 50,000 bags.
b)
To determine: The revenue for the manual process at break-even point quantity.
Introduction:
Break-even point (BEP):
The break-even point is measured in units or in sales term to identify the point in a business which is required to cover the total investment costs. The total profit at break-even point is zero.
b)
Answer to Problem 25P
The revenue for the manual process at break-even point quantity is $125,000.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formula to calculate Revenue for the manual process:
Calculation of Revenue
The revenue is calculated by dividing the fixed cost with the value obtained by dividing the resultant value obtained from dividing the difference between the selling price and variable cost divided by the selling price.
Hence, the revenue for the manual process at break-even point quantity is $125,000.
c)
To determine: The break-even point quantity for the mechanized process.
c)
Answer to Problem 25P
The break-even point quantity for the mechanized process is 60,000 bags.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formula to calculate Break-even point (BEP) in units:
Calculation of Break-even point (BEP) in units:
The Break-even point is calculated by dividing the fixed cost with the difference of selling price and variable cost.
Hence, the Break-even point (BEP) in units is 60,000 bags.
d)
To determine: The revenue for the mechanized process at break-even point quantity.
d)
Answer to Problem 25P
The revenue for the mechanized process at break-even point quantity is $150,000.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formula to calculate Revenue for the manual process:
Calculation of Revenue
The revenue is calculated by dividing the fixed cost with the value obtained by dividing the resultant value obtained from dividing the difference between the selling price and variable cost divided by the selling price.
Hence, the revenue for the manual process at break-even point quantity is $150,000.
e)
To determine: The monthly profit or loss for the manual process for the sale of 60,000 bags of lettuce per month.
e)
Answer to Problem 25P
The monthly profit for the manual process for the sale of 60,000 bags of lettuce per month is $7,500.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formula to calculate Profit or loss:
Calculation of profit or loss for manual process:
The profit is calculated by multiplying number of bags of lettuce with selling price and the resultant value is subtracted from the fixed cost and the value obtained by multiplying number of bags of lettuce and variable cost.
The monthly profit for the manual process for the sale of 60,000 bags of lettuce per month is $7,500.
f)
To determine: The monthly profit or loss for the mechanized process for the sale of 60,000 bags of lettuce per month.
f)
Answer to Problem 25P
The monthly profit or lossfor the mechanized process for the sale of 60,000 bags of lettuce per month is $0which is the break-even point.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formula to calculate Profit or loss:
Calculation of profit or loss for mechanized process:
The profit is calculated by multiplying number of bags of lettuce with selling price and the resultant value is subtracted from the fixed cost and the value obtained by multiplying number of bags of lettuce and variable cost.
Hence, the monthly profit or loss for the mechanized process for the sale of 60,000 bags of lettuce per month is $0 which is the break-even point.
g)
To determine: The point at which both the process will yield the same amount.
g)
Answer to Problem 25P
The point at which both the process will yield the same amount is 75,000 bags.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formation of equation 1 for manual process:
Formation of equation 2 for mechanized process:
Calculation of the point at which both process yields the same amount:
The point is calculated by substituting all the known values in equation (1) and (2) and equating each other.
Hence, the point at which both the process will yield the same amount is 75,000 bags.
h)
To determine: The range of demand at which the manual process will be preferred over the mechanized process and the range of demand at which the mechanized will be preferred over the manual process.
Introduction:
Indifference point:
The indifference point in a business is a point where two different types of alternatives will not have any difference in the output they yield.
h)
Answer to Problem 25P
The manual process will be preferred over the mechanized process for the volume below 75,000 bags. The mechanized process will be preferred over the manual process for the volume above 75,000 bags.
Figure for showing the range at which one process will be better than the other:
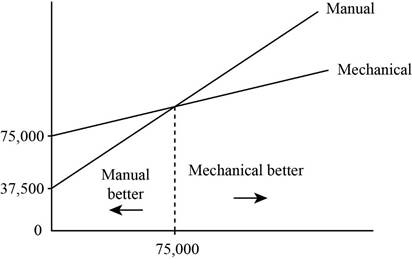
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Manual process:
Fixed costs = $37,500 / month
Variable costs = $1.75 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Mechanized process:
Fixed cost = $75,000 / month
Variable cost = $1.25 / bag
Selling price = $2.50 / bag
Formation of equation 1 for manual process:
Formation of equation 2 for mechanized process:
Calculation of the point at which both process yields the same amount:
The point is calculated by substituting all the known values in equation (1) and (2) and equating each other.
The fixed costs of both the processes are plotted as shown in the graph. The intersection point in the graph is the point where both process will have no advantage over the other. It is also known as the indifference point. The indifference point is 75, 000 bags.
Hence, the manual process will be preferred over the mechanized process for the volume below 75,000 bags. The mechanized process will be preferred over the manual process for the volume above 75,000 bags.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Principles Of Operations Management
- Zan Azlett and Angela Zesiger have joined forces to start A&Z Lettuce Products, a processor of packaged shredded lettuce for institutional use. Zan has years of food processing experience, and Angela has extensive commercial food preparation experience. The process will consist of opening crates of lettuce and then sorting, washing, slicing, preserving, and finally packaging the prepared lettuce. Together, with help from vendors, they think they can adequately estimate demand, fixed costs, revenues, and variable cost per bag of lettuce. They think a largely manual process will have monthly fixed costs of $40,000 and variable costs of $2.00 per bag. A more mechanized process will have fixed costs of $72,000 per month with variable costs of $1.25 per bag. They expect to sell the shredded lettuce for $3.00 per bag. a) The break-even quantity in units for the manual process = enter your response here bags (round your response to the nearest whole number). b) The revenue…arrow_forwardMary Jones and Jack Smart have joined forces to start M&J Food Products, a processor of packaged shredded lettuce for institutional use. Jack has years of food processing experience, and Mary has extensive commercial food preparation experience. The process will consist of opening crates of lettuce and then sorting, washing, slicing, preserving, and finally packaging the prepared lettuce. Together, with help from vendors, they think they can adequately estimate demand, fixed costs, revenues, and variable cost per 5-pound bag of lettuce. They think a largely manual process will have monthly fixed cost of $50,000 and a variable cost of $2.50 per bag. They expect to sell 75,000 bags of lettuce per month. They expect to sell the shredded lettuce for $3.25 per 5-pound bag. Jack and Mary has been contacted by a vendor to consider a more mechanized process. This new process will have monthly fixed cost of $125,000 per month with a variable cost of $1.75 per bag. Based on the above…arrow_forwardSuppose the newsvendor model describes a firm’s operations decision. Is it possible to havepositive stockout probability and positive expected leftover inventory? Choose the best answer. a. No. If there is leftover inventory, then a stockout doesn’t occur.b. No. If the stockout probability is positive, then expected inventory must be negative.c. No. Actual demand can differ from sales.d. Yes. A firm does not stock out and have leftover inventory at the same time, but the stockout probability can be positive even though there is positive expected leftover inventory.e. Yes, as long as the underage cost is greater than the overage cost.arrow_forward
- Willie Lohmann travels from city to city for business. Every other year he buys a used car for about $15,000. The dealer allows about $8000 as a trade-in allowance, so Willie spends $7000 every other year for a car. Willie keeps accurate records of his expenses, which total 32.3¢ per mile. Willie's employer has two plans to reimburse car expenses: (A)Actual expenses: Willie will receive all his oper-ating expenses, and $3500 each year for the car's decline in value. (B) Standard mileage rate: Willie will receive 56.5 ¢per mile but no operating expenses and no depre-ciation allowance. If Willie travels 18,000 miles per year, which method gives him the larger reimbursement? At what annual mileage do the two methods give the same reimbursement?arrow_forwardEmarpy Appliance is a company that produces allkinds of major appliances. Bud Banis, the president of Emarpy,is concerned about the production policy for the company’s bestsellingrefrigerator. The annual demand has been about 8,000units each year, and this demand has been constant throughoutthe year. The production capacity is 200 units per day. Each timeproduction starts, it costs the company $120 to move materialsinto place, reset the assembly line, and clean the equipment. Theholding cost of a refrigerator is $50 per year. The current productionplan calls for 400 refrigerators to be produced in each productionrun. Assume there are 250 working days per year.a) What is the daily demand of this product?b) If the company were to continue to produce 400 units each timeproduction starts, how many days would production continue?c) Under the current policy, how many production runs per yearwould be required? What would the annual setup cost be?d) If the current policy continues, how many…arrow_forward1. Foxie Owl’s Besty Bagel shop makes fresh bagels. She has to buy raw materials fresh every day for selling on that day. She wants to know exactly how much should she spend on raw materials. Foxie did some analysis over the past month and came back with the following numbers: Daily demand was equally likely to be 200, 225, 250, 275, or 300 bagels. What should be the number of bagels on hand to satisfy a Fill Rate requirement of 96%, rounded to next integer value? Group of answer choices 300 275 286 263 2. Suppose that instead of a discrete demand distribution, Foxie’s shop determines that the daily demand for bagels is normally distributed, with a mean of 250 and a standard deviation of 35. Foxie still wants a Fill Rate of 98%. What is the appropriate level of on-hand inventory for Foxie’s shop? Group of answer choices 263 274 257 270arrow_forward
- A small textile company makes several types of sweat-ers. Demand is very seasonal, as shown by the follow-ing quarterly demand estimates. Demand is estimated interms of standard hours of production required.An hour of regular time costs the company $12. Employees are paid $18 per hour on overtime, andlabor can be subcontracted from the outside at $14per hour. A maximum of 1000 overtime hours isavailable in any month. A change in the regular level of production (increase or decrease) incurs a one-time cost of $5 per hour for adding or subtracting anhour of labor. It costs 2 percent per month to carry an hour of finished work in inventory. Materials and overhead costs in inventory are equal to the directlabor costs. At the beginning of the fall quarter,there are 5000 standard hours in inventory and theworkforce level is equivalent to 10,000 standardhours.a. Suppose management sets the level of regular work-ers for the year equal to the average demand andsubcontracts out the rest. What is…arrow_forwardAn engineering plant has developed the accompanying supply, demand, cost and inventory data. The engineering plant has a constant workforce and meets all its demands. Allocate production capacity to satisfy demand at a minimum cost. What is the cost of this plan? (Assume that back ordering is not a viable alternative for the plant) Demand forecast Period Demand (Unit) 1 650 2 700 3 900 Supply Capacity available (units) Period Regular time Overtime Subcontract 1 350 100 250 2 450 100 250 3 500 100 250 Other Data Initial Inventory 100 units Regular-time cost per unit R 50 Overtime cost per unit R 65 Subcontract cost per unit R 80 Carrying cost per unit per period R 1 Back order cost per unit per period R 4arrow_forward• S7.25 Zan Azlett and Angela Zesiger have joined forcesto start A&Z Lettuce Products, a processor of packaged shredded lettuce for institutional use. Zan has years of food processingexperience, and Angela has extensive commercial food preparation experience. The process will consist of opening crates oflettuce and then sorting, washing, slicing, preserving, and finallypackaging the prepared lettuce. Together, with help from vendors,they think they can adequately estimate demand, fixed costs, revenues, and variable cost per 5-pound bag of lettuce. They think alargely manual process will have monthly fixed costs of $37,500and variable costs of $1.75 per bag. A more mechanized processwill have fixed costs of $75,000 per month with variable costs of$1.25 per 5-pound bag. They expect to sell the shredded lettucefor $2.50 per 5-pound bag.a) What is the break-even quantity for the manual process?b) What is the revenue at the break-even quantity for the manualprocess?c) What is the…arrow_forward
- KLG is a textile manufacturer in Shanghai. They want to expand their t-shirt business into the United States. They have dedicated a factory in KLG to making the tshirts, and the production rate at that facility is 250 pallets of t-shirts per day. KLG's factory uses a just-in time production model so they store no safety stock at their manufacturing facility in Shanghai, The cost of space at the Shanghai facility is $30 per pallet per year. Each pallet has a value of $2000. KLG is opening a distribution center in Los Angeles from which they will serve the American demand for 250 pallets of t-shirts per day. They keep a safety stock of 1200 pallets of t-shirts at the distribution center. The cost of space at the LA facility is $40 per pallet per year. Each pallet has a value of $2200. KLG hires you as a logistics consultant to help them decide whether to transport the t-shirts from Shanghai to Los Angeles using sea or air. KLG uses a holding cost rate of 20%. FlyHigh Airline has…arrow_forwardA manager has prepared a forecast of expected aggregate demand for the next six months. Develop an aggregate plan to meet this demand given this additional information: A level production rate of 500 units per month can be used. Backorders are allowed, and they are charged at the rate of $20 per unit per month. Inventory holding costs are $1 per unit per month in ending inventory. Determine the cost of this plan if regular time cost is $10 per unit and beginning inventory is zero. Overtime costs $16 per unit and subcontracting costs $20 per unit. In the 4th month, overtime is not possible. While outsourcing is not possible in the 3rd month. Overtime capacity is 50 units and subcontracting capacity is 50 units. Month Forecast 1 400 2 480 3 560 4 720 5…arrow_forwardThis company has the following aggregate demand requirements and other data for the upcoming four quarters. Quarter Demand Previous quarter's output 1500 units 1 1400 Beginning inventory 200 units 2 1000 Stockout cost $50 per unit 3 1500 Inventory holding cost $8 per unit at end of quarter 4 1300 Hiring workers $5 per unit Laying off workers $10 per unit Unit cost $30 per unit Overtime $10 extra per unit Which of the following production plans is better: Plan 1—chase demand by hiring and layoffs; or Plan 2—produce at a constant rate of 1200 and obtain the remainder from overtime? Finish the calculation. Plan 1. Demand Regular Time Capacity Regular Time Production Hire Fire Initial Inventory Period 1 1,400 1200 Period 2 1,000 Period 3 1,500 Period 4 1,300…arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





