
To discuss:
Annual average return and standard deviation.
Introduction:
Return: In financial context, return is seen as percentage that represents the profit in an investment.
Explanation of Solution
The annual average
Using equation (1) the annual average return of Miller’s Fund (MF) is calculated as follows:
The annual average return of Miller’s Fund (MF) is 24.325%..
Using equation (1) the annual average return of S&P is calculated as follows:
The annual average return of S&P is 14.925%.
By the annual average returns, Miller’s Fund performed better than the S&P over the given period of time.
If money investment of $1,000 is made in Miller’s Fund in 2009, the money reaped at the end of 2012 would be $1,243.25
If money investment of $1,000 is made in S&P in 2009, the money reaped at the end of 2012 would be $1,149.25
The standard deviation of Miller’s Fund can be calculated as follows using excel functions as in table1.
Table 1
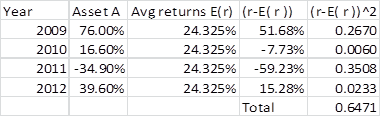
The standard deviation of Miller’s Fund is calculated as follows:
The standard deviation of Miller’s Fund is 46.44%.
The standard deviation of S&P can be calculated as follows using excel functions as in table 2.
Table 2
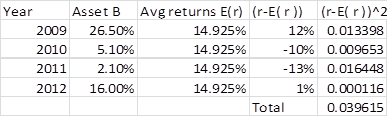
The standard deviation of S&P is calculated as follows:
The standard deviation of S&P is 11.5%.
By the value of standard deviation, Millers Fund is more volatile than S&P.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF MANAGERIAL FINANCE
- Suppose that you initially invested 10,000 in the Stivers mutual fund and 5,000 in the Trippi mutual fund. The value of each investment at the end of each subsequent year is provided in the table: Which of the two mutual funds performed better over this time period?arrow_forwardIn a recent 5-year period, mutual fund manager Diana Sauros produced the following percentage rates of return for the Mesozoic Fund. Rates of return on the market index are given for comparison. 1 2 3 4 5 Fund -1.4 23.2 41.1 10.1 0.5 Market index -0.6 18.0 30.6 11.4 -0.4 a. Calculate (a) the average return on both the Fund and the index, and (b) the standard deviation of the returns on each. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) b. Did Ms. Sauros do better or worse than the market index on these measures?arrow_forwardIn a recent 5tear period, mutual fund manager Diana sharks produced the following percentage rates of return for the Mesozoic fund. Rates of return on the market index are given for comparison. A. Calculate the average return on both the fund and the index and the standard deviation of the returns on each. Did Ms. Sauros do better or worse than the market index on these measures?arrow_forward
- A local mutual fund says it has expertise in identifying stocks that are undervalued because they are under researched or unpopular. To prove its point, the fund produces evidence that it returns over the past four years was 3% above the return on the market index. a) What does efficient market hypothesis (EMH) say about undervalued stock? b) Does the fund’s evidence contradict the EMH?arrow_forwardThe Retired Fund is an open-ended mutual fund composed of $500 million in U.S. bonds and U.S. Treasury bills. This fund has had a portfolio duration (including T-bills) of between 3 and 9 years. Retired has shown first-quartile performance over the past five years, as measured by an independent fixed-income measurement service. However, the directors of the fund would like to measure the market timing skill of the fund’s sole bond investor manager. An external consulting firm has suggested the following three methods:a. Method I examines the value of the bond portfolio at the beginning of every year, then calculates the return that would have been achieved had that same portfolio been held throughout the year. This return would then be compared with the return actually obtained by the fund.b. Method II calculates the average weighting of the portfolio in bonds and T-bills for each year. Instead of using the actual bond portfolio, the return on a long-bond market index and T-bill index…arrow_forwarda. A mutual fund is a professionally managed type of collective investment scheme that pools money from many investors and invests in stocks, bonds, short-term money market instruments and other securities. The performance of these mutual funds and the portfolio they build needs to be evaluated as frequently as possible. Evaluating the performance of these mutual funds is important for both existing and potential investors. The Table below provides the average return, standard deviation and betas of selected equity mutual funds over a period of three years. The average risk free rate for the period is estimated at 15%. Portfolio Average return Standard Deviation Beta Portfolio A 27.62 16 1.2 Portfolio B 20.12 15 0.9 Portfolio C 26.25 12 1.05 GSE return(benchmark) 16.18 10 1.0 Required:Estimate and compare the performance of the funds with the market using:i. Treynor’s measureii. Sharpe’s measureiii. Jensen’s Measure b. The issuing of security goes through a number of…arrow_forward
- The following data relates to the portfolios of a fund’s two equity managers Total Return Beta Manager A 24 % 1.0 Manager B 30.0 % 1.5 S&P 500 21.0 Lehman 31.0 91 day Treasury bills 12.0 Calculate and compare the risk-adjusted performance of the two managers relative to each other and to the S&P 500. Explain the reasons why the conclusions drawn from this calculation may be misleading.arrow_forwardYou have been given the following return information for two mutual funds (Papa and Mama), the market index, and the risk-free rate. Year Papa Fund Mama Fund Market Risk-Free 2011 –12.6 % –22.6 % –24.5 % 1 % 2012 25.4 18.5 19.5 3 2013 8.5 9.2 9.4 2 2014 15.5 8.5 7.6 4 2015 2.6 –1.2 –2.2 2 Calculate the Sharpe ratio, Treynor ratio, Jensen’s alpha, information ratio, and R-squared for both funds. (Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter all answers as a decimal value rounded to 4 decimal places.) PAPA MAMA SHARPE RATIO: TREYNOR RATIO JENSEN'S ALPHA INFORMATION RATIO R-SQUAREDarrow_forwardI need someone to check my answer In a recent 5-year period, mutual fund manager Diana Sauros produced the following percentage rates of return for the Mesozoic fund. Rates of return on the market index are given for comparison Year Fund Return (%) Standard deviation mean Deviation 2 Market index return (%) Standard Deviation (Mean) Deviation2 1 -1.4 -16.52 272.91 -0.5 -11.8 139.24 2 24.0 8.88 77.44 16.0 4.7 22.09 3 41.9 26.78 717.17 31.4 20.1 404.01 4 10.9 -4.22 17.81 9.9 -1.4 1.96 5 0.2 -14.92 222.61 -0.3 -11.6 134.56 TOTAL 75.6 1,307.94 56.5 701.86 AVERAGE 15.12 261.59 11.3 140.37 SD 16.17 11.85 Calculate The average return on Mesozoic Fund Return and Market Portfolio Return Fund return = (-1.4+24+41.9+10.9+0.2)/5 = 15.12 Market index return = -0.5+16+31.4+9.9+ (-0.3)]/5 =…arrow_forward
 Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning
Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning


