
To analyze:
In terms of the central dogma of molecular biology, explain:
The meaning of biological terminology, “gene”?
The reason behind genes for rRNA and tRNA is considered to be genes even though they do not produce polypeptides.
Introduction:
DNA is the genetic material present in all organisms. Gene is a unit of heredity that transfers from parents to offsprings. In other terms, it is a physical and functional unit of heredity.
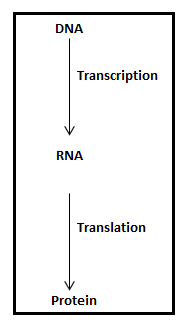
Central dogma – It is the directional flow of information from DNA to RNA to Protein. The process of copying DNA information into RNA is called Transcription while the process of translating the message copied into proteins is called Translation.
Explanation of Solution
Central dogma – It is the flow of the formation of a functional product that includes copying of genetic material into RNA and then the translation of copied sequence into proteins.
A unit of heredity that is passed from one generation to the next generation or from parents to offsprings is called a gene.
Genes instruct for a functional product or proteins according to the need of a cell. These proteins are joined together and form polypeptides. Genes that specify the polypeptides are called protein-coding genes.
Not all the genes specify polypeptides; some code for other molecules, too. Few genes instruct the production of RNA molecules like tRNA (Transfer RNA) and rRNA (Ribosomal RNA) that play crucial roles in the translation.
The gene is the structural and functional unit of DNA which transmit from one generation to the next generation. The gene contains necessary information for the formation of the specific protein.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- Use the information uploaded in the picture to help with this question. Would you conclude that IP-1383 induces mutations or not? Briefly (one or two sentences) explain how or why you came to your conclusion.arrow_forwardGive typing answer with explanation and conclusion lets say, you treat a bacteria with an unknown antibiotic. After three short days, the bacteria becomes resistant to the antibiotic. Mind you, after three days you measure the S12 protein mutations and they highly increased those three days. what is most likey the antibiotic identity and why?arrow_forwardGive typing answer with explanation and conclusion to all parts Consider the following DNA mRNA sequence: 5’-ACTGATCCATGCCAGGGGTTTTCAACTAAAATGAAA-3’ a) What is the template sequence this mRNA was transcribed from? Include 5’ and 3’ labels. b) Based on this sequence, what you predict would be the resulting peptide sequence from it. c) In examining this sequence what is the proper reading frame of the open reading frame? (+1, +2, +3, -1, -2, or -3). d) What would you predict the peptide sequence to be if there was the following mutation that led to a base change: 5’-ACTGATGCATGCCAGGGGTTTTCAACTAAAATGAAA-3’arrow_forward
- What is Transcriptome analysis? In your answer, also explain, what are the steps and primary methods used in Transcriptome analysis, and what are some important applications of Transcriptome analysis.arrow_forwardGive only typing answer with explanation and conclusion which of these choices represents one possible corresponding mRNA sequence that can be transcribed by RNA polymerase, and later translated by ribosomes from the following DNA template? 5'- CTGTATCCTAGCACCCAAATCGCAT - 3'; A. 5'- CTA GCA CCC AAA TCG CAT TAG - 3', B. 5' - AUG CGA UUU GGG UGC UAG - 3', C. 5' - AUG CGA UUU GGG UGC - 3', D. 5- ATG CGA TTT GGG TCG TAG - 3'arrow_forwardUse the sequences below to determine what type of mutation has occurred by comparing the normal sequence to the mutated sequence. Normal Gene Sequence: 3'- ATAGCTAAGCCCATGCGG-5' Mutated Gene Sequence 3'-ATAGCTAAGCCCAGGTGCGG-5'arrow_forward
- Give typing answer with explanation and conclusion α-Amanitin is a poison found in the mushroom Amanita phalloides, and this is the most common form of mushroom poisoning in the world. What is the mechanism of action of α-Amanitin on RNA polymerase?arrow_forwardGive typing answer with explanation and conclusion The following gene codes for a liver enzyme. Changing the A/T base pair to which of the following would result in a missense mutation? 5’ GCCTAATATGCCCGTATGC(AGC)nCGAATAAAATAGTACGGTCGTCGC 3’ 3’ CGGATTATACGGGCATACG(TCG)nGCTTATTTT ATCATGCCAGCAGCG5’ A. C/G B. T/A C. G/C D. Any of the above E. 2 of the above F. None of the abovearrow_forwardRefer to the DNA sequence provided: 3’ -TACTGAAGCGGCAGCCCCGCATGAGTAGACCTTACT-5’ a. What is the mRNA transcript of the anticoding strand of the DNA model? b. What is the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain that will be translated from the mRNA in (a)?arrow_forward
- Give typing answer with explanation and conclusion 5'ATTAGGAGGTGCGTTATGCAGGCATGTTACGTACGTACG,TAAGATAAGTACT3’ 3' TAATCCTCCACGCAATACGTCCGTACAATGCATGCATGCATTCTATTCATGA5’ In the above piece of double stranded DNA, how many potential translations start sites exist if an mRNA could be synthesized from any portion of this DNA? Indicate where they are in the DNA above and explain how you found this number.arrow_forwardQuestion:- Often a given mutation or variant will have slightly different phenotypes in different groups of patients. “Genetic Background” is frequently used to explain how the same exact mutation could exhibit different phenotypes in different populations. Please explain.arrow_forwardexplain about the Exceptional genetic codesarrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
