
Concept explainers
Referto Figure 8-2. Replace the values shown with the following. Solvefor all theunknownvalues.
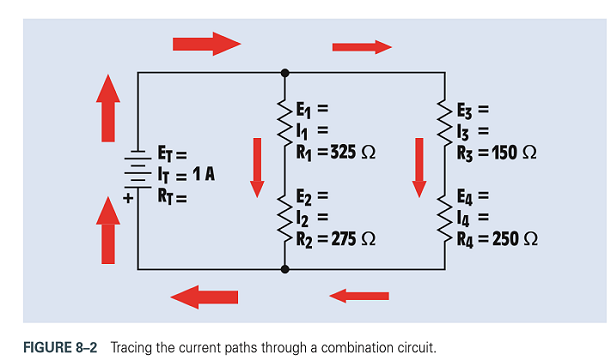
Solve for the unknown values in the figure.
Answer to Problem 1RQ
| ET = 264.47 V | E1 = 149.87 V | E2 = 114.79 V | E3 = 143.48 V | E4 = 120.98 V |
| IT = 0.6 A | I1 = 0.3186 A | I2 = 0.3186 A | I3 = 0.2813 A | I4 = 0.2813 A |
| RT = 440.79 Ω | R1 = 470 Ω | R2 = 360 Ω | R3 = 150 Ω | R4 = 250Ω |
Explanation of Solution
The circuit diagram is redrawn with given data;
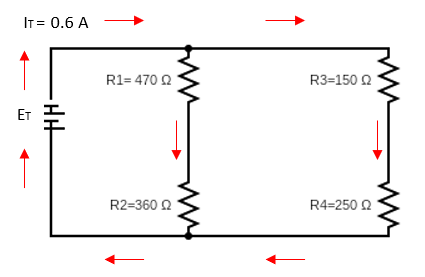
Description:
For the given combination circuit, total resistance will be series combination of R1 and R2 in parallel combination with series combination of R3 and R4. Calculations are shown below,
Using the current IT and resistance RT, we calculate the voltage ET
The individual voltage drops can be calculated using the voltage divider rule.
Since R1 and R2 are series connected, the same current flows through them. Hence, I1=I2
Similarly, R3 and R4 are series connected, therefore I3=I4
Conclusion:
The unknown values have been calculated using rules for combination circuit and ohm’s law.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
- Find the unknown values in the circuit if the total current is 1.2 A and the resistors have the following values: R1=75R2=47R3=220R4=160ETE1E2E3E4RTI1I2I3I4 FIGURE 8-25 A parallel-series circuit.arrow_forwardRefer to Figure 8-21. Assume that the resistors have the following values: R1=150R2=120R3=47R4=220 Assume that an ohmmeter connected across the entire circuit indicates a value of 245 . Does this reading indicate that there is a problem with the circuit and, if so, what is the most likely problem? FIGURE 8-21 Series-parallel circuit.arrow_forwardRefer to the circuit shown in Figure 8-25 to solve the following problems. 4. Find the unknown values in the circuit if the total current is 0.8 A and the resistors have the following values: FIGURE 8-25 A parallel-series circuit.arrow_forward
- ET E1 E2 E3 E41.248V IT I1 I2 I3 I4 RT R1 R2 R3 R4 PT0.576W P10.0806W P20.0461W P30.00184W P4 E5 E6 E7 E8 E9 I5 I6 I7 I8 I9 R5 R6 R7 R8 R9 P50.0203W P60.00995W P70.0518W P80.0726W P90.288W FIGURE 8-26 A combination circuit.arrow_forwardA series RL circuit with R=50 Ohms and L=10 H has a constant voltage V=100 V at t=0 by closing of a switch. Find the current at t=0.5 seconds. PLS show complete and clean solutionarrow_forward8. 7.8 In the circuit , the voltage and current expressions are v=400e−5tV, t≥0+;i=10e−5tA, t≥0.1. a) Rarrow_forward
- Find Io. Use Mesh and Nodal Analysis only. Explain each step.arrow_forwardDetermine Vx in this circuit using Norton's theorem. Draw illustrations if needed. Show complete solution. Answer must be Vx= 29.36<62.88 Varrow_forwardFind the current in the RLC circuit, assuming that E(t) = 0 for t > 0 R = 4 ohms; L = .05 henrys; C = .008 farads; Q0 = -1 coulombs; I0 = 2 amperes I need helparrow_forward
- notes: u(t) = 0 for t<0 = 1 for t>=0 u(-t) = 1 for t<0 = 0 for t>=0 Assume components are ideal, unless otherwise specified. Assume circuits had been on/running for a long time before a change in the circuit happens, unless otherwise specified. Allow for round off errors for the final answer that you get (vs. the indicated final answer)arrow_forwardChoose the correct answer fitting the following circuit: a. ib= -0.5A b. -193+ 4ia+ 2.5ib- 0.5+ 7.5ib+ 6ia=0 c. ib=0.5Aarrow_forwardThe lead storage batteries A and B are connected in parallel. Battery A has an open circuitvoltage of 12.6 V and internal resistance of 0.2 ohms. Battery B has an open circuit voltage of12.2 V and internal resistance of 0.3 ohms. If two batteries together deliver power to a 0.5-ohmpower resistor. Neglecting effects of temperature, how much current is contributed by batteryA(IA)? Solve the problem using Thevenin’s and Norton’s theorem. (Ia= 12.84 A)arrow_forward
 Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
