
Intercorporate Inventory and Debt Transfers (Effective Interest Method)
Puzzle Corporation purchased 75 percent of Sunday Company’s common stock at underlying book value on January 1, 20X3. At that date, the fair value of the noncontrolling interest was equal to 25 percent of Sunday’s book value.
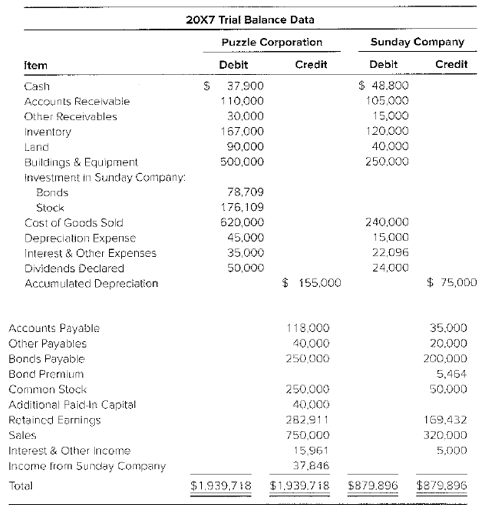
During 20X7, Puzzle resold inventory purchased from Sunday in 20X6. It had cost Sunday $44,000 to produce the inventory, and Puzzle had purchased it for $59,000. In 20X7, Puzzle had purchased inventory for $40,000 and sold it to Sunday for $60,000. At December 31, 20X7. Sunday continued to hold $27,000 of the inventory.
Sunday had issued $200,000 of 8 percent, 10−year bonds on January 1, 20X4, at 104. Puzzle had purchased $80,000 of the bonds from one of the original owners for $78,400 on December 31, 20X5. Interest is paid annually on December 31. Assume Puzzle uses the fully adjusted equity method.
Required
a. What amount of cost of goods sold will be reported in the 20X7 consolidated income statement?
b. What inventory balance will be reported in the December 31, 20X7, consolidated balance sheet?
c. Prepare the
d. Prepare the journal entry to record interest income for Puzzle for 20X7.
e. What amount will be assigned to the noncontrolling interest in the consolidated balance sheet prepared at December 31, 20X7?
f. Prepare all consolidation entries needed at December 31, 20X7, to complete a three−part consolidation worksheet.
g. Prepare a consolidation worksheet for 20X7 in good form.
a
Introduction: When one business organization holds majority shareholdings in another company, the management can transfer resources between these two businesses. One way of resource transfer is debt transfer from one affiliate to another without third party involvement. Debt transfer may also include setoff of trade receivable, payables arising from the intercompany sale of inventory on credit and the issue of notes payable to each other in exchange for operating funds.
Amount of cost of goods sold to be reported in consolidated income statement.
Answer to Problem 8.25P
Cost of goods sold to be reported in consolidated income statement is $794,000
Explanation of Solution
| $ | $ | |
| Amount of cost of goods reported by P corporation | 620,000 | |
| Amount of cost of goods reported by S corporation | 240,000 | |
| Adjustment of unrealized profit on inventory purchased by P from S | (15,000) | |
| Adjustment of inventory purchased from subsidiary and resold 20X7 | ||
| CGS intercompany sales recorded by P | 40,000 | |
| CGS intercompany sales recorded by S | 33,000 | |
| Total | 73,000 | |
| CGS based on P’s cost 40,000 x (33,000 /60,000) | (22,000) | |
| Required adjustment | (51,000) | |
| Cost of goods sold | 794,000 |
b.
Introduction: When one business organization holds majority shareholdings in another company, the management can transfer resources between these two businesses. One way of resource transfer is debt transfer from one affiliate to another without third party involvement. Debt transfer may also include setoff of trade receivable, payables arising from the intercompany sale of inventory on credit and the issue of notes payable to each other in exchange for operating funds.
Inventory balance to be reported in consolidated balance sheet December 31 20X7
Answer to Problem 8.25P
Consolidated inventory balance to be reported in consolidated balance sheet is $278,000
Explanation of Solution
| $ | |
| Amount of inventory reported by P | 167,000 |
| Amount of inventory reported by S | 120,000 |
| Total | 287,000 |
| Less: Unrealized profit in ending inventory held by S | (9,000) |
| Consolidated inventory balance | 278,000 |
c.
Introduction: When one business organization holds majority shareholdings in another company, the management can transfer resources between these two businesses. One way of resource transfer is debt transfer from one affiliate to another without third party involvement. Debt transfer may also include setoff of trade receivable, payables arising from the intercompany sale of inventory on credit and the issue of notes payable to each other in exchange for operating funds.
Journal entry to record interest expenses by S
Explanation of Solution
| Particulars | Debit $ | Credit $ |
| Interest expense | 15,200 | |
| Bond premium | 800 | |
| Cash | 16,000 | |
| (Paid cash on account of interest expense) |
Computation of interest expenses
| Par value of bond issued | $200,000 |
| Annual Interest | $16,000 |
| Annual amortization of premium ($4,800 /6 years) | (800) |
| Interest expenses | $15,200 |
d.
Introduction: When one business organization holds majority shareholdings in another company, the management can transfer resources between these two businesses. One way of resource transfer is debt transfer from one affiliate to another without third party involvement. Debt transfer may also include setoff of trade receivable, payables arising from the intercompany sale of inventory on credit and the issue of notes payable to each other in exchange for operating funds.
Journal entry to record interest income for S
Explanation of Solution
| Particulars | Debit $ | Credit $ |
| Cash | $6,400 | |
| Investment in A company bond | 200 | |
| Interest income | 6,600 | |
| (Received cash on account of interest income and premium on bond amortized) |
Computation of interest income
| Annual payment received | $6,400 |
| Amortization of discount | 200 |
| Interest income | $6,600 |
e.
Introduction: When one business organization holds majority shareholdings in another company, the management can transfer resources between these two businesses. One way of resource transfer is debt transfer from one affiliate to another without third party involvement. Debt transfer may also include setoff of trade receivable, payables arising from the intercompany sale of inventory on credit and the issue of notes payable to each other in exchange for operating funds.
The income assigned to non-controlling interest in consolidated balance sheet
Answer to Problem 8.25P
Amount of income assigned to non-controlling interest $15,620
Explanation of Solution
| $ | |
| Net income reported by S | 48,000 |
| Adjustment for realization of profit on inventory sold to P | 15,000 |
| Adjustment of gain on bond retirement | (520) |
| Realized net income | 62,480 |
| Income assigned to non-controlling interest | 15,620 |
Computation of gain on bond retirement
| $ | $ | |
| Par value of bond | 200,000 | |
| Amortization per year | 800 | |
| Premium maturity value Dec 31 20X5 | 6,400 | |
| Book value of bond | 206,400 | |
| Book value of bond purchase | 82,560 | |
| Purchase price | (78,400) | |
| Gain | 4,160 |
f.
Introduction: When one business organization holds majority shareholdings in another company, the management can transfer resources between these two businesses. One way of resource transfer is debt transfer from one affiliate to another without third party involvement. Debt transfer may also include setoff of trade receivable, payables arising from the intercompany sale of inventory on credit and the issue of notes payable to each other in exchange for operating funds.
Preparation of consolidation entries needed at December 31 20X7 to complete consolidation worksheet.
Explanation of Solution
| Particulars | Debit $ | Credit $ |
| To eliminate income from subsidiary | ||
| Income from subsidiary | 36,000 | |
| Dividends declared | 18,000 | |
| Investment in S company stock | 18,000 | |
| (Income from subsidiary eliminated by reversal) | ||
| Assign income to non-controlling interest. | ||
| Income to non-controlling interest | 15,620 | |
| Dividends declared | 6,000 | |
| Non-controlling interest | 9,620 | |
| (Income assigned to non-controlling interest) | ||
| Eliminate beginning investment balance | ||
| Common stock S company | 50,000 | |
| Retained earnings January 1 | 170,000 | |
| Investment in A’s stock | 165,000 | |
| Non-controlling interest | 55,000 | |
| (Beginning investment in S stock eliminated by reversal) | ||
| Eliminating beginning inventory profit | ||
| Retained earnings, January 1 | 11,250 | |
| Non-controlling interest | 3,750 | |
| Cost of goods sold | 15,000 | |
| (Unrealized profit on beginning inventory eliminated) | ||
| Eliminating intercompany sale of inventory by P | ||
| Sales | 60,000 | |
| Cost of goods sold | 51,000 | |
| Inventory | 9,000 | |
| (Intercompany profit on sale of inventory eliminated) | ||
| Eliminating intercompany bond holdings | ||
| Bond payable | 80,000 | |
| Bond premium | 1,920 | |
| Interest income | 6,600 | |
| Investment on S company’s bonds | 78,800 | |
| Interest expenses | 6,080 | |
| Retained earnings, January 1 | 2,730 | |
| Non-controlling interest | 910 | |
| (Intercompany bond holdings eliminated by reversal) |
- Income from subsidiary is eliminated by debiting to income from subsidiary account.
- Assignment of income to non-controlling interest
Realized net income by S company
| Net income reported by S | $48,000 |
| Realization of profit on inventory sold to P(59,000 − 44,000) | $15,000 |
| Adjustment of gain on bond retirement ($4,160 / 8 years) | (520) |
| Realized net income | 62,480 |
- Common stock and retained earnings in the beginning of the year was $170,000 and 50,000 which is $220,000 eliminating by crediting to investment in S account and non- controlling interest account in the ratio of parental and subsidiary holdings.
- Beginning inventory profit of $15,000 is eliminated as required by debiting retained earnings at 75% and non-controlling interest by 25%.
- Intercompany sale of inventory is eliminated by posting reversal entry.
- Eliminating corporate bond holding
Bond premium:
| Bond premium given | $4,800 |
| P bond discount 80,000 − 78,400 | (1,600) |
| Net premium on bond | $3,200 |
Calculation of bond investment value:
| Bonds purchase consideration | $78,400 |
| Amortization of discount (1,600 / 8 years) | 200 |
| Bond investment value | $78,800 |
Calculation of interest expenses:
| $6,400 | |
| Less amortization of premium ($3,200 / 10 years) | (320) |
| Interest expenses | $6,080 |
g.
Introduction: When one business organization holds majority shareholdings in another company, the management can transfer resources between these two businesses. One way of resource transfer is debt transfer from one affiliate to another without third party involvement. Debt transfer may also include setoff of trade receivable, payables arising from the intercompany sale of inventory on credit and the issue of notes payable to each other in exchange for operating funds.
The preparation of consolidation worksheet for 20X7
Answer to Problem 8.25P
The following are the balances reported in consolidation work sheet for 20X7:
- Retained earnings $337,040
- Total Assets $1,274,700
Explanation of Solution
P Corporation and S Corporation
Consolidation worksheet
December 31, 20X7
| Elimination | |||||
| P $ | S $ | Debit $ | Credit $ | Consolidation $ | |
| Sales | 750,000 | 320,000 | 60,000 | 1,010,000 | |
| Interest and other income | 16,000 | 5,000 | 6,600 | 14,400 | |
| Income from subsidiary | 36,000 | 36,000 | |||
| 802,000 | 325,000 | 1,024,400 | |||
| Less: Cost of goods sold | (620,000) | (240,000) | 15,000 | ||
| 51,000 | (794,000) | ||||
| Depreciation expenses | (45,000) | (15,000) | (60,000) | ||
| Interest and other expenses | (35,000) | (22,000) | 6,080 | (50,920) | |
| Consolidated net income | $119,480 | ||||
| Income to NCI | 15,620 | (15,620) | |||
| Net income | 102,000 | 48,000 | 118,220 | 72,080 | 103,860 |
| Retained earnings Jan 1 | 291,700 | 170,000 | 170,000 | 2,730 | |
| 11,250 | 283,180 | ||||
| 393,700 | 218,000 | 387,040 | |||
| Dividends declared | (50,000) | (24,000) | 18,000 | ||
| 6,000 | (50,000) | ||||
| Retained earnings Dec 31 | 343,700 | 194,000 | 299,470 | 98,810 | 337,040 |
| Balance sheet: | |||||
| Cash | 37,900 | 48,800 | 86,700 | ||
| Accounts receivable | 110,000 | 105,000 | 215,000 | ||
| Other receivable | 30,000 | 15,000 | 45,000 | ||
| Inventory | 167,000 | 120,000 | 9,000 | 278,000 | |
| Land | 90,000 | 40,000 | 130,000 | ||
| Investment in S’s bonds | 78,800 | 78,800 | |||
| Investment in S’s Stock | 183,000 | 18,000 | |||
| 165,000 | |||||
| Buildings and Equipment | 500,000 | 250,000 | 750,000 | ||
| Less Accumulated Depreciation | (155,000) | (75,000) | (230,000) | ||
| Total Assets | 1,041,700 | 175,000 | 1,274,700 | ||
| Accounts payable | 118,000 | 35,000 | 153,000 | ||
| Other payable | 40,000 | 20,000 | 60,000 | ||
| Bonds payable | 250,000 | 200,000 | 80,000 | 370,000 | |
| Bonds premium | 4,800 | 1,920 | 2,880 | ||
| Common Stock: | |||||
| P company | 250,000 | 250,000 | |||
| S company | 50,000 | 50,000 | |||
| Additional Paid in capital | 40,000 | 40,000 | |||
| Retained earnings Dec 31 | 343,700 | 194,000 | 299,470 | 98,810 | 337,040 |
| Non-controlling interest | 3,750 | 9,620 | |||
| 55,000 | |||||
| 910 | 61,780 | ||||
| Total Liability and Equity | 1,041,700 | 175,000 | 1,274,700 | ||
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Advanced Financial Accounting
- On January 1, 20x1, ABC Co. acquired 10%, P1,000,000 bonds for P827,135. The bonds mature on December 31, 20x3 and pay annual interest every December 31. ABC Co. incurred transaction costs P80,000 on the acquisition. The effective interest rate adjusted for the effect of the transaction costs is 14%. The bonds are to be held under a "hold to collect and sell" business model. Information on fair values is as follows: December 31, 20x1...............98 December 31, 20x2..............102 December 31, 20x3..............100 9.How much is the carrying amount of the investment on December 31, 20x1? a. 935,134 b. 1,002,000 c. 980,000 d. 965,443 10. How much is the unrealized gain (loss) recognized in other comprehensive income on December 31, 20x1? a. 45,866 b. (45,866) c. (37,899) d. 0 11. How much is the interest income recognized in 20x2? a. 126,999 c. 135,088 b. 130,779 d. 144,388arrow_forwardAssume that Birch made intra-entity inventory transfers to Aspen that have resulted in the following intra-entity gross profits in inventory at the end of each year: Date Amount 12/31/19 $13,000 12/31/20 23,300 12/31/21 30,200 On January 1, 2019, Aspen Company acquired 80 percent of Birch Company's voting stock for $500,000. Birch reported a $490,000 book value, and the fair value of the noncontrolling interest was $125,000 on that date. Then, on January 1, 2020, Birch acquired 80 percent of Cedar Company for $224,000 when Cedar had a $253,000 book value and the 20 percent noncontrolling interest was valued at $56,000. In each acquisition, the subsidiary's excess acquisition-date fair over book value was assigned to a trade name with a 30-year remaining life. These companies report the following financial information. Investment income figures are not included. 2019 2020 2021 Sales: Aspen Company $ 637,500 $ 650,000 $ 732,500 Birch…arrow_forwardPie Corporation acquired 60 percent of Slice Company’s common stock on December 31, 20X5, at underlying book value. The book values and fair values of Slice’s assets and liabilities were equal, and the fair value of the noncontrolling interest was equal to 40 percent of the total book value of Slice. Slice provided the following trial balance data at December 31, 20X5: Debit Credit Cash $ 27,600 Accounts Receivable 64,900 Inventory 91,600 Buildings and Equipment (net) 216,000 Cost of Goods Sold 103,300 Depreciation Expense 24,450 Other Operating Expenses 31,060 Dividends Declared 15,800 Accounts Payable $ 32,000 Notes Payable 127,000 Common Stock 94,800 Retained Earnings 130,000 Sales 190,910 Total $ 574,710 $ 574,710 Required: How much did Pie pay to purchase its shares of Slice? Note: Round your answer to nearest whole dollar amount. If consolidated financial statements are prepared at December 31, 20X5, what amount…arrow_forward
- Paulos Company purchases a controlling interest in Sanjoy Company. Sanjoy had identifiable net assets with a book value of $500,000 and a fair value of $800,000. It was agreed that the total fair value of Sanjoy’s common stock was $1,200,000. Use value analysis schedules to determine what adjustments will be made to Sanjoy’s accounts andwhat new accounts and amounts will be recorded if: a. Paulos purchases 100% of Sanjoy’s common stock for $1,200,000. b. Paulos purchases 80% of Sanjoy’s common stock for $960,000.arrow_forwardQ7- On January 1, 20X8, Zeta Company acquired 85 percent of Theta Company's common stock for $100,000 cash. The fair value of the noncontrolling interest was determined to be 15 percent of the book value of Theta at that date. What portion of the retained earnings reported in the consolidated balance sheet prepared immediately after the business combination assigned to the noncontrolling interest? a- None b- 15 percent c- 100 percent d- Cannot be determined With calculations pleasearrow_forwardSuspect Company issued $1,110,000 of 8 percent first mortgage bonds on January 1, 20X1, at 104. The bonds mature in 20 years and pay interest semiannually on January 1 and July 1. Prime Corporation purchased $740,000 of Suspect’s bonds from the original purchaser on December 31, 20X5, for $736,000. Prime owns 70 percent of Suspect’s voting common stock. Required:a. Prepare the worksheet consolidation entry or entries needed to remove the effects of the intercorporate bond ownership in preparing consolidated financial statements for 20X5 b. Prepare the worksheet consolidation entry or entries needed to remove the effects of the intercorporate bond ownership in preparing consolidated financial statements for 20X6.arrow_forward
- Lorn Corporation purchased inventory from Dresser Corporation for P120,000 on September 20, 20x2, and resold 80% of the purchased inventory to unaffiliated companies prior to December 31, 20x2, for P140,000. Dresser produced the inventory sold to Lorn for P75,000. Lorn owns 70% of Dresser’s voting common stock. The companies had no other transactions during 20x2. What inventory balance will be provided by the consolidated entity on December 31, 20x2? A. P15,000 C. P24, 000B. P16, 800 D. P39, 000arrow_forwardOn January 1, 20X1, Rivera Company (RC) and Caventa Company (CC) each acquired 40% of the ordinaryvoting shares of Tulang Company (TC) for P500,000. They then both agreed to share control of TC.In 20X1, RC purchased goods from TC for P150,000. On December 31, 20X1, P80,000 of the goods purchasedremains in TC’s inventory. TC sells goods at 25% mark-up based on the sale.For the year ended December 31, 20X1, TC reported a profit of P400,000 and declared and paid dividends ofP150,0000. Also, the fair value of each venturer’s investment in TC is P600,000. There is no published quotationfor TC.RC and CC account for jointly controlled entities using the equity method.Required: Determine the following:1. The amount of income RC should recognize from TC.2. The value of RC’s investment in TC at December 31, 20X1.3. The amount of income CC should recognize from TC.4. The value of CC’s investment in TC at December 31, 20X1.arrow_forwardTorres Investments acquired $260,800 of Murphy Corp., 9% bonds at their face amount on October 1, Year 1. The bonds pay interest on October 1 and April 1. On April 1, Year 2, Torres sold $72,400 of Murphy Corp. bonds at 102. Journalize the entries to record the following: Do not round interim calculations. Round final answers to nearest dollar. For a compound transaction, if an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. a. The initial acquisition of the Murphy Corp. bonds on October 1, Year 1. Year 1, Oct. 1 fill in the blank 71bd05f45f95fbb_2 fill in the blank 71bd05f45f95fbb_4 b. The adjusting entry for three months of accrued interest earned on the Murphy Corp. bonds on December 31, Year 1. Year 1, Dec. 31 fill in the blank 96c81afb2ff8068_2 fill in the blank 96c81afb2ff8068_4 c. The receipt of semiannual interest on April 1, Year 2. Year 2, Apr. 1 fill in the blank d8c23f06e01002a_2 fill in the blank…arrow_forward
- On January 1, 20X1, ABC acquired 5,000 of XYZ’s bonds denominated at P1,000, 12% interest rate, 5 years, intending to collect contractual cash flows and sell them. The effective rate in the market at that time is 10%. On December 31, 20X1, the market value of the bonds is P5,200,000. ABC changes its business model in managing this financial asset by collecting contractual cash flows representing principal and interest. On the reclassification date, the initial amount of the newly reclassified investment is (Round off your answer to the nearest peso. Round off PVF into 4 decimals.)arrow_forwardEntity A acquired 75% of the outstanding voting shares of Entity B for P1,800,000. On the acquisition date, Entity B's identifiable assets and liabilities have fair values of P4,000,000 and P1,600,000, respectively. Additional information: Entity A replaces Entity B as a guarantor on a loan of a third party. As of the acquisition date, the third party has defaulted on the loan. However, because negotiations for debt restructuring are ongoing with the lender and the Entity strongly believes that the lender will agree to the proposed terms, no provision was recognized. The fair value of the guarantee is P200,000. Entity A chose to measure the non-controlling interest at the NCI's proportionate share in the acquiree's net identifiable assets. Requirement: Compute for the goodwill.arrow_forwardGonzalez Company acquired $210,000 of Walker Co., 5% bonds on May 1 at their face amount. Interest is paid semiannually on May 1 and November 1. On November 1, Gonzalez Company sold $44,400 of the bonds for 95. Journalize entries to record the following in Year 1: For a compound transaction, if an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. a. The initial acquisition of the bonds on May 1. May 1 fill in the blank 2db398fc5fbefe9_2 fill in the blank 2db398fc5fbefe9_4 b. The semiannual interest received on November 1. Nov. 1 fill in the blank 12a681fdb06bff7_2 fill in the blank 12a681fdb06bff7_4 c. The sale of the bonds on November 1. Nov. 1 fill in the blank cee7ff00dfa3fc5_2 fill in the blank cee7ff00dfa3fc5_3 fill in the blank cee7ff00dfa3fc5_5 fill in the blank cee7ff00dfa3fc5_6 fill in the blank cee7ff00dfa3fc5_8 fill in the blank cee7ff00dfa3fc5_9 d. The accrual of $1,380…arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning



