
Concept explainers
(A)
The point
Answer to Problem 1AR
The point
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The point is
Calculation:
The ordered pair
The point
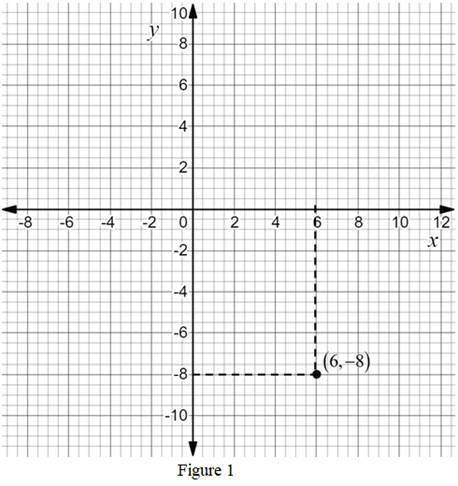
Thus, the point
Conclusion:
The point
(B)
The point
Answer to Problem 1AR
The point
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The point is
Calculation:
The ordered pair
The point
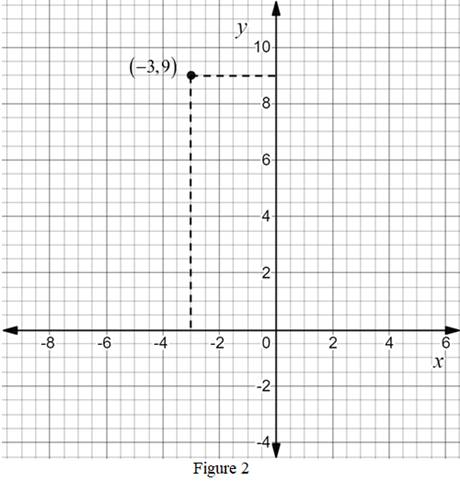
Thus, the point
Conclusion:
The point
(c)
The point
Answer to Problem 1AR
The point
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The point is
Calculation:
The ordered pair
The point
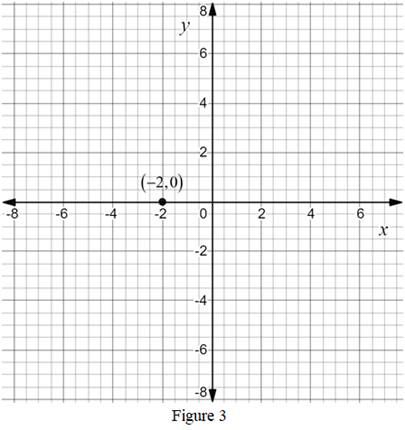
Thus, the point
Conclusion:
The point
(D)
The point
Answer to Problem 1AR
The point
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The point is
Calculation:
The ordered pair
The point
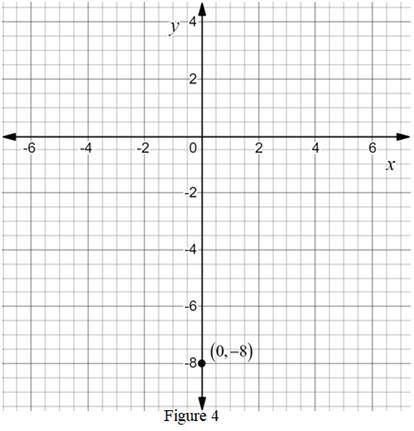
Thus, the point
Conclusion:
The point
(e)
The point
Answer to Problem 1AR
The point
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The point is
Calculation:
The ordered pair
The point
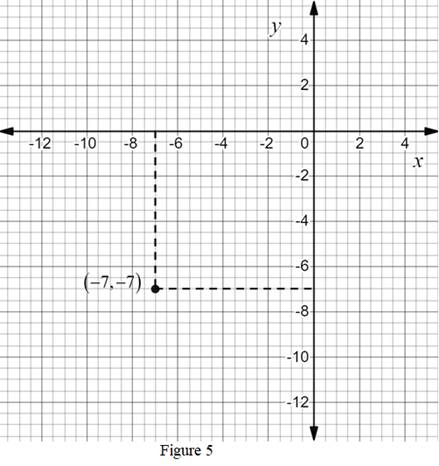
Thus, the point
Conclusion:
The point
(f)
The point
Answer to Problem 1AR
The point
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The point is
Calculation:
The ordered pair
The point
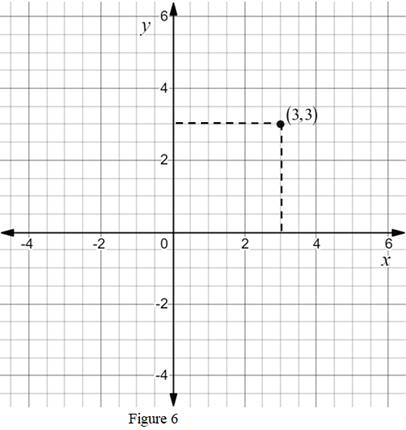
Thus, the point
Conclusion:
The point
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 88 Solutions
Mathematics For Machine Technology
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,






