
Concept explainers
Algers Company produces dry fertilizer. At the beginning of the year, Algers had the following
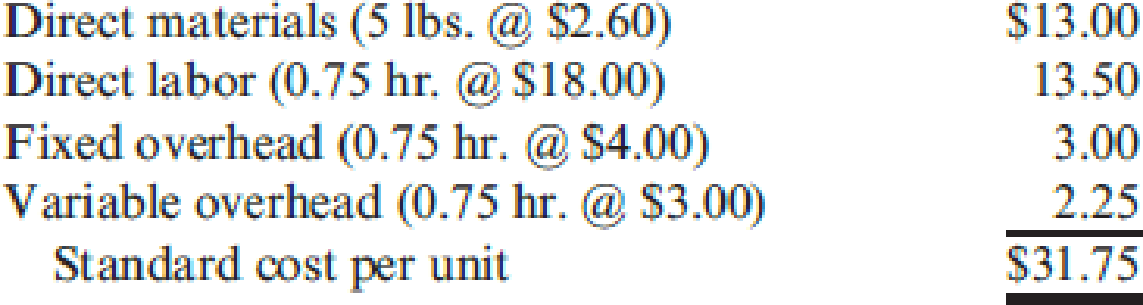
Algers computes its
- a. Units produced: 53,000
- b. Direct materials purchased: 274,000 pounds at $2.50 per pound
- c. Direct materials used: 270,300 pounds
- d. Direct labor: 40,100 hours at $17.95 per hour
- e. Fixed overhead: $161,700
- f. Variable overhead: $122,000
Required:
- 1. Compute price and usage variances for direct materials.
- 2. Compute the direct labor rate and labor efficiency variances.
- 3. Compute the fixed overhead spending and volume variances. Interpret the volume variance.
- 4. Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances.
- 5. Prepare
journal entries for the following:- a. The purchase of direct materials
- b. The issuance of direct materials to production (Work in Process)
- c. The addition of direct labor to Work in Process
- d. The addition of overhead to Work in Process
- e. The incurrence of actual overhead costs
- f. Closing out of variances to Cost of Goods Sold
1.
Compute the direct materials price variance and the direct materials usage variance.
Explanation of Solution
Direct material price variance: The variation in between actual price and estimated price paid for materials multiplied by the actual quantity is called material price variance. It is used to determine difference in price paid for material the price that was supposed to be paid for material.
The following formula is used to calculate direct material price variance:
Direct material usage (efficiency) variance: It is a measure that determines the variation in between actual and standard quantity of input multiplied by the standard unit price is called material usage variance.
The following formula is used to calculate direct material usage variance:
Compute the direct materials price variance:
Compute the direct materials usage variance:
Working note 1: Calculate the standard quantity:
Therefore, the direct materials price variance and the usage variance is $27,400 F and $613,780 U respectively.
2.
Calculate the direct labor rate variance and labor efficiency variance.
Explanation of Solution
Direct Labor Rate Variance: The direct labor rate variance is a measure to determine the variation in the estimated cost of the direct labor and the actual cost of the direct labor and is multiplied by the actual hours is called direct labor rate variance.
The following formula is used to calculate the direct labor rate variance:
Direct labor efficiency variance is a measure that determines the difference between the estimated labor hours and the actual labor hours used and is multiplied by the standard rate per hour is called material usage variance.
The following formula is used to calculate direct labor efficiency variance:
Calculate the direct labor rate variance:
Calculate the labor efficiency variance:
Working note 2: Calculate the standard hours:
Therefore, the direct labor rat variance and the efficiency variance are $2,005 F and $6,300 U respectively.
3.
Calculate the fixed overhead spending and volume variance.
Explanation of Solution
Fixed overhead spending variance: It is the difference between actual fixed overhead and the budgeted fixed overhead.
Favorable variance occurs only when the fixed overhead is less than the budgeted overhead. Unfavorable variance occurs only when the fixed overhead is more than the budgeted overhead.
The following formula is used to calculate fixed overhead spending variance:
Fixed overhead volume variance: It is the difference between budgeted fixed overhead and the applied fixed overhead.
The following formula is used to calculate fixed overhead volume variance:
Calculate the fixed overhead spending volume variance:
Fixed overhead spending:
Step 1: Compute the budgeted fixed overhead.
Step 2: Calculate the fixed overhead spending variance.
Working note 3: Calculate the standard fixed overhead rate:
Working note 4: Calculate the direct labor hour per unit:
Working note 5: Calculate the actual hours:
Volume variance:
Step 1: Compute the applied fixed overhead.
Step 2: Compute the volume variance.
Working note 6: Calculate the standard fixed overhead rate:
Working note 7: Calculate the direct labor hour per unit:
Working note 8: Calculate the standard hours:
Therefore, the fixed overhead spending and volume variance are $300 F and $3,000 U respectively.
4.
Calculate the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances.
Explanation of Solution
Overhead Variance: The overhead variance is the difference arising between the real overhead consumed in the production of a product, and the estimated overhead determined in the production of that product.
Spending variances: It arises when management pays an amount which is different from the standard price for purchasing an item. The variable overhead spending variance measures the total effect of differences in the actual variable overhead rate (AVOR) and the standard variable overhead rate (SVOR).
Efficiency variances: It arises when standard direct labor hours expected for actual production different from labor the actual direct labor hours used.
Variable overhead efficiency variance tells managers how much of the total variable manufacturing overhead variance is due to using more or fewer machine hours than anticipated for the actual volume of output.
Compute the variable overhead spending variance:
Step 1: Compute the budgeted variable overhead cost.
Step 2: Compute the variable overhead spending variance.
Compute the variable overhead efficiency variance:
Step 1: Compute the applied variable overhead.
Step 2: Compute the variable overhead efficiency variance.
Working note 9: Calculate the direct labor hour per unit:
Working note 10: Calculate the standard hours:
Therefore, the variable overhead spending and efficiency variance are $1,700 U and $1,050 U respectively.
5.
Prepare journal entries for the given.
Explanation of Solution
Journalizing: It is the process of recording the transactions of an organization in a chronological order. Based on these journal entries recorded, the amounts are posted to the relevant ledger accounts.
Accounting rules for journal entries:
- To increase balance of the account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit all liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To decrease balance of the account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit all liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
Prepare journal entries for direct materials and direct labor:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| a. | Direct Materials | 712,400 | |
| Direct Materials Price variance | 27,400 | ||
| Accounts Payable | 685,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of direct materials) | |||
| b. | Work in Process | 689,000 | |
| Direct Materials Usage Variance | 13,780 | ||
| Direct Materials | 702,780 | ||
| (To record the usage of direct materials) | |||
| c. | Work in Process | 715,500 | |
| Direct Labor Efficiency Variance | 6,300 | ||
| Direct Labor Rate Variance | 2,005 | ||
| Wages Payable | 719,795 | ||
| (To record the use of direct labor) | |||
| d. | Work in Process | 278,250 | |
| Variable Overhead Control | 119,250 | ||
| Fixed Overhead Control | 159,000 | ||
| (To record assign overhead to the production) | |||
| e. | Variable Overhead Control | 122,000 | |
| Fixed Overhead Control | 161,700 | ||
| Miscellaneous Accounts | 283,700 | ||
| (To record incurrence of actual overhead) | |||
| Closing direct materials and direct labor variances: | |||
| f. | Direct Materials Price variance | 27,400 | |
| Direct Labor Rate Variance | 2,005 | ||
| Direct Materials Usage Variance | 13,780 | ||
| Direct Labor Efficiency Variance | 6,300 | ||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 9,325 | ||
| (To close the direct materials and direct labor variances) | |||
| Closing overhead variances: | |||
| Fixed Overhead Volume Variance | 3,000 | ||
| Variable Overhead Spending Variance | 1,700 | ||
| Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance | 1,050 | ||
| Fixed Overhead Spending Variance | 300 | ||
| Fixed Overhead Control | 2,700 | ||
| Variable Overhead Control | 2,750 | ||
| (To close the overhead variances) | |||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 5,750 | ||
| Fixed Overhead Volume Variance | 3,000 | ||
| Variable Overhead Spending Variance | 1,700 | ||
| Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance | 1,050 | ||
| (To close the overhead variances) | |||
| Fixed Overhead Spending Variance | 300 | ||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 300 | ||
| (To close the cost of goods sold) | |||
Table (1)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- Box Springs. Inc., makes two sizes of box springs: queen and king. The direct material for the queen is $35 per unit and $55 is used in direct labor, while the direct material for the king is $55 per unit, and the labor cost is $70 per unit. Box Springs estimates it will make 4,300 queens and 3,000 kings in the next year. It estimates the overhead for each cost pool and cost driver activities as follows: How much does each unit cost to manufacture?arrow_forwardWyandotte Company provided the following information for the last calendar year: During the year, direct materials purchases amounted to 256,900, direct labor cost was 176,000, and overhead cost was 308,400. There were 40,000 units produced. Required: 1. Calculate the total cost of direct materials used in production. 2. Calculate the cost of goods manufactured. Calculate the unit manufacturing cost. 3. Of the unit manufacturing cost calculated in Requirement 2, 6.62 is direct materials and 7.71 is overhead. What is the prime cost per unit? Conversion cost per unit?arrow_forwardEllerson Company provided the following information for the last calendar year: During the year, direct materials purchases amounted to 278,000, direct labor cost was 189,000, and overhead cost was 523,000. During the year, 100,000 units were completed. Required: 1. Calculate the total cost of direct materials used in production. 2. Calculate the cost of goods manufactured. Calculate the unit manufacturing cost. 3. Of the unit manufacturing cost calculated in Requirement 2, 2.70 is direct materials and 5.30 is overhead. What is the prime cost per unit? Conversion cost per unit?arrow_forward
- The Lubbock plant of Morrils Small Motor Division produces a major subassembly for a 6.0 horsepower motor for lawn mowers. The plant uses a standard costing system for production costing and control. The standard cost sheet for the subassembly follows: During the year, the Lubbock plant had the following actual production activity: (a) Production of motors totaled 50,000 units, (b) The company used 82,000 direct labor hours at a total cost of 1,066,000. (c) Actual fixed overhead totaled 556,000. (d) Actual variable overhead totaled 860,000. The Lubbock plants practical activity is 60,000 units per year. Standard overhead rates are computed based on practical activity measured in standard direct labor hours. Required: 1. Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. 2. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Compute the fixed overhead spending and volume variances. Interpret the volume variance. What can be done to reduce this variance?arrow_forwardColonels uses a traditional cost system and estimates next years overhead will be $480,000, with the estimated cost driver of 240,000 direct labor hours. It manufactures three products and estimates these costs: If the labor rate is $25 per hour, what is the per-unit cost of each product?arrow_forwardBusiness Specialty, Inc., manufactures two staplers: small and regular. The standard quantities of direct labor and direct materials per unit for the year are as follows: The standard price paid per pound of direct materials is 1.60. The standard rate for labor is 8.00. Overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor hours. A plantwide rate is used. Budgeted overhead for the year is as follows: The company expects to work 12,000 direct labor hours during the year; standard overhead rates are computed using this activity level. For every small stapler produced, the company produces two regular staplers. Actual operating data for the year are as follows: a. Units produced: small staplers, 35,000; regular staplers, 70,000. b. Direct materials purchased and used: 56,000 pounds at 1.5513,000 for the small stapler and 43,000 for the regular stapler. There were no beginning or ending direct materials inventories. c. Direct labor: 14,800 hours3,600 hours for the small stapler and 11,200 hours for the regular stapler. Total cost of direct labor: 114,700. d. Variable overhead: 607,500. e. Fixed overhead: 350,000. Required: 1. Prepare a standard cost sheet showing the unit cost for each product. 2. Compute the direct materials price and usage variances for each product. Prepare journal entries to record direct materials activity. 3. Compute the direct labor rate and efficiency variances for each product. Prepare journal entries to record direct labor activity. 4. Compute the variances for fixed and variable overhead. Prepare journal entries to record overhead activity. All variances are closed to Cost of Goods Sold. 5. Assume that you know only the total direct materials used for both products and the total direct labor hours used for both products. Can you compute the total direct materials and direct labor usage variances? Explain.arrow_forward
- The Lubbock plant of Morrils Small Motor Division produces a major subassembly for a 6.0 horsepower motor for lawnmowers. The plant uses a standard costing system for production costing and control. The standard cost sheet for the subassembly follows: During the year, the Lubbock plant had the following actual production activity: a. Production of subassemblies totaled 50,000 units. b. A total of 260,000 pounds of raw materials was purchased at 4.70 per pound. c. There were 60,000 pounds of raw materials in beginning inventory (carried at 5 per lb.) There was no ending inventory. d. The company used 82,000 direct labor hours at a total cost of 1,066,000. The Lubbock plants practical activity is 60,000 units per year. Standard overhead rates are computed based on practical activity measured in standard direct labor hours. Required: 1. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Compute the materials price and usage variances. Of the two materials variances, which is viewed as the more controllable? To whom would you assign responsibility for the usage variance in this case? Explain. 2. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Compute the labor rate and efficiency variances. Who is usually responsible for the labor efficiency variance? What are some possible causes for this variance? 3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Assume that the purchasing agent for the small motors plant purchased a lower-quality raw material from a new supplier. Would you recommend that the plant continue to use this cheaper raw material? If so, what standards would likely need revision to reflect this decision? Assume that the end products quality is not significantly affected. 4. Prepare all possible journal entries.arrow_forwardBobcat uses a traditional cost system and estimates next years overhead will be $800.000, as driven by the estimated 25,000 direct labor hours. It manufactures three products and estimates the following costs: If the labor rate is $30 per hour, what is the per-unit cost of each product?arrow_forwardMoleno Company produces a single product and uses a standard cost system. The normal production volume is 120,000 units; each unit requires 5 direct labor hours at standard. Overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor hours. The budgeted overhead for the coming year is as follows: At normal volume. During the year, Moleno produced 118,600 units, worked 592,300 direct labor hours, and incurred actual fixed overhead costs of 2,150,400 and actual variable overhead costs of 1,422,800. Required: 1. Calculate the standard fixed overhead rate and the standard variable overhead rate. 2. Compute the applied fixed overhead and the applied variable overhead. What is the total fixed overhead variance? Total variable overhead variance? 3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Break down the total fixed overhead variance into a spending variance and a volume variance. Discuss the significance of each. 4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Compute the variable overhead spending and efficiency variances. Discuss the significance of each.arrow_forward
- Carsen Company produces handcrafted pottery that uses two inputs: materials and labor. During the past quarter, 24,000 units were produced, requiring 96,000 pounds of materials and 48,000 hours of labor. An engineering efficiency study commissioned by the local university revealed that Carsen can produce the same 24,000 units of output using either of the following two combinations of inputs: The cost of materials is 8 per pound; the cost of labor is 12 per hour. Required: 1. Compute the output-input ratio for each input of Combination F1. Does this represent a productivity improvement over the current use of inputs? What is the total dollar value of the improvement? Classify this as a technical or an allocative efficiency improvement. 2. Compute the output-input ratio for each input of Combination F2. Does this represent a productivity improvement over the current use of inputs? Now, compare these ratios to those of Combination F1. What has happened? 3. Compute the cost of producing 24,000 units of output using Combination F1. Compare this cost to the cost using Combination F2. Does moving from Combination F1 to Combination F2 represent a productivity improvement? Explain.arrow_forwardShumaker Company manufactures a line of high-top basketball shoes. At the beginning of the year, the following plans for production and costs were revealed: During the year, a total of 50,000 units were produced and sold. The following actual costs were incurred: There were no beginning or ending inventories of raw materials. In producing the 50,000 units 63,000 hours were worked, 5% more hours than the standard allowed for the actual output. Overhead costs are applied to production using direct labor hours. Required: 1. Using a flexible budget, prepare a performance report comparing expected costs for the actual production with actual costs. 2. Determine the following: (a) Fixed overhead spending and volume variances and (b) Variable overhead spending and efficiency variances.arrow_forwardNatur-Gro, Inc., manufactures composters. Based on past experience, Natur-Gro has found that its total annual overhead costs can be represented by the following formula: Overhead cost = 264,000 + 1.42X, where X equals number of composters. Last year, Natur-Gro produced 30,000 composters. Actual overhead costs for the year were as expected. Total overhead for per unit was a. 1.42 b. 8.80 c. 11.63 d. 10.22arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub




