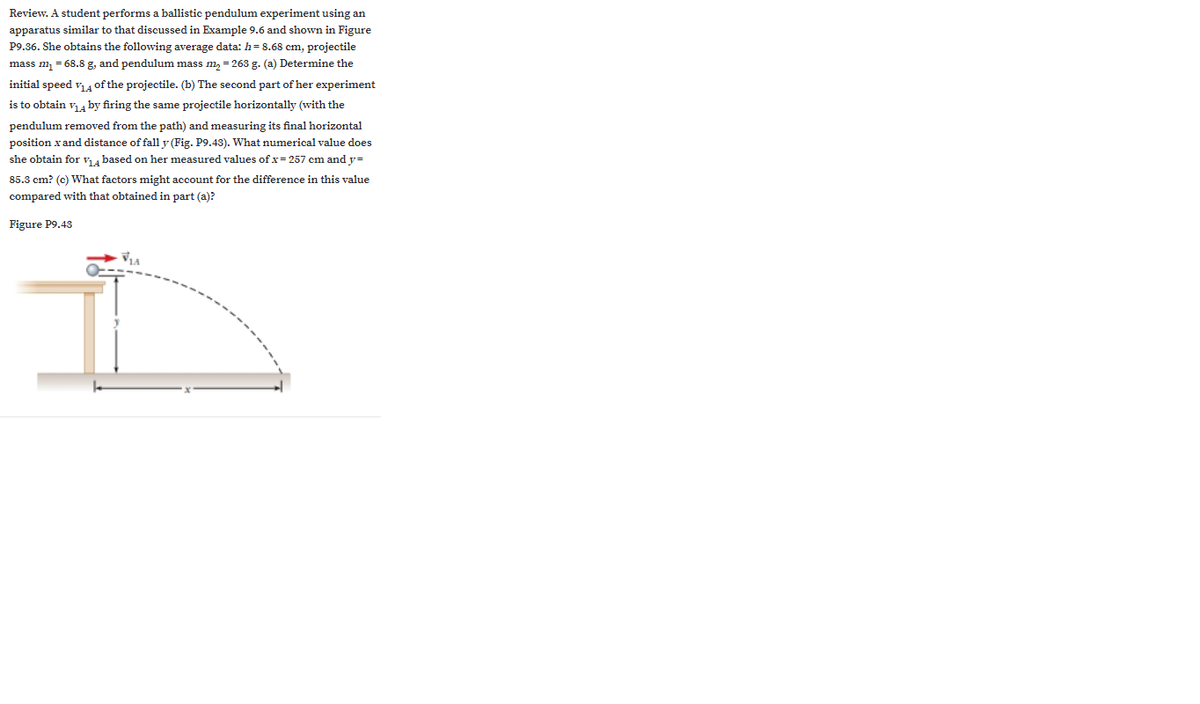
Review. A student performs a ballistic pendulum experiment using an apparatus similar to that discussed in Example 9.6 and shown in Figure P9.36. She obtains the following average data: h=8.68 cm, projectile mass m, = 68.8 g, and pendulum mass m, = 263 g. (a) Determine the initial speed v4 of the projectile. (b) The second part of her experiment is to obtain v4 by firing the same projectile horizontally (with the pendulum removed from the path) and measuring its final horizontal position x and distance of fall y (Fig. P9.43). What numerical value does she obtain for v, based on her measured values of x= 257 cm and y= 85.3 cm? (c) What factors might account for the difference in this value compared with that obtained in part (a)? Figure P9.43 VIA
Review. A student performs a ballistic pendulum experiment using an apparatus similar to that discussed in Example 9.6 and shown in Figure P9.36. She obtains the following average data: h = 8.68 cm, projectile mass m1 = 68.8 g, and pendulum mass m2 = 263 g. (a) Determine the initial speed v1A of the projectile. (b) The second part of her experiment is to obtain v1A by firing the same projectile horizontally (with the pendulum removed from the path) and measuring its final horizontal position x and distance of fall y (Fig. P9.43). What numerical value does she obtain for v1A based on her measured values of x = 257 cm and y = 85.3 cm? (c) What factors might account for the difference in this value compared with that obtained in part (a)?
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images






