
a.
Compute the differences in samples of matched pairs Sample-1– Sample-2.
a.
Answer to Problem 10E
The differences in samples of matched pairs Sample-1– Sample-2 is,
| S.no | Difference |
| 1 | –6 |
| 2 | –1 |
| 3 | –9 |
| 4 | –1 |
| 5 | –5 |
| 6 | –1 |
| 7 | –4 |
| 8 | –8 |
| 9 | –2 |
| 10 | –9 |
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The data represents the sample of a five matched pairs.
Let
The differences in samples of matched pairs Sample-1– Sample-2 is,
| S.no | Sample-1 | Sample-2 | |
| 1 | 28 | 34 | |
| 2 | 29 | 30 | |
| 3 | 22 | 31 | |
| 4 | 25 | 26 | |
| 5 | 26 | 31 | |
| 6 | 29 | 30 | |
| 7 | 27 | 31 | |
| 8 | 24 | 32 | |
| 9 | 27 | 29 | |
| 10 | 28 | 37 |
b.
Find the value of t-test statistic.
b.
Answer to Problem 10E
The value of test statistic is –4.3948.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The test hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no significant difference between the population mean1 and population mean2.
Alternate hypothesis:
That is, there is a significant difference between the population mean1 and population mean2.
Mean and standard deviation of differences:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the mean and standard deviation using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic statistic > Display
descriptive statistics . - In Variables, enter the column of Differences.
- In Statistics, select mean, standard deviation and N total.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
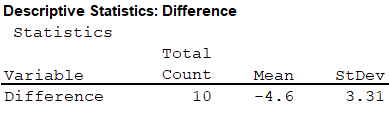
From the MINITAB output, the mean and standard deviation are –4.6 and 3.31.
The mean and standard deviation of the differences is –4.6 and 3.31.
The test statistic is obtained as follows,
Thus, the test statistic is –4.3948.
c.
Check whether the null hypothesis is rejected at
c.
Answer to Problem 10E
There is enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis
Explanation of Solution
Degrees of freedom:
The degrees of freedom for the test statistic is,
Thus, the degree of freedom is 9.
P-value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the P-value using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot.
- Choose View Probability > OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘t’ distribution.
- In Degrees of freedom, enter 9.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose X value and Both Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- In X-value enter –4.3948.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
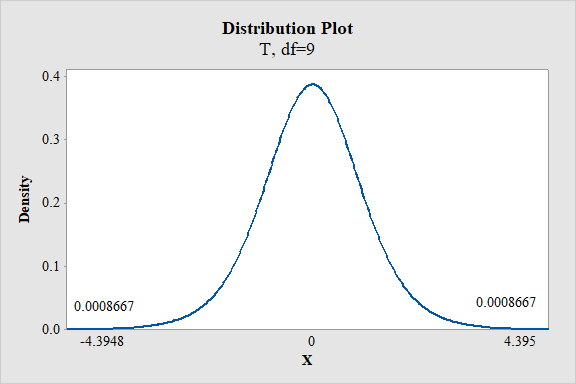
From the MINITAB output, the P-value is
Thus, the P-value is 0.0017.
Decision rule based on P-value:
If
If
Here, the level of significance is
Conclusion based on P-value approach:
The P-value is 0.0017 and
Here, P-value is less than the
That is,
By the rejection rule, reject the null hypothesis.
Thus, there is enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis
d.
Check whether the null hypothesis is rejected at
d.
Answer to Problem 10E
There is enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis
Explanation of Solution
From part (c), the P-value is 0.0017.
Decision rule based on P-value:
If
If
Here, the level of significance is
Conclusion based on P-value approach:
The P-value is 0.0017 and
Here, P-value is less than the
That is,
By the rejection rule, reject the null hypothesis.
Thus, there is enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Essential Statistics
- In a separate experiment, a significance test was performed to test the null hypothesis `H_o`: `\mu` = 24.56 versus the alternative hypothesis `H_a`: `\mu` < 24.56. The test statistic is t = -2.05 with a sample size of 81. What is the p-value of the test?arrow_forwardConsider the following hypothesis statement using α=0.10 and the following data from two independent samples. Complete parts a and b below. H0: p1−p2≥0 x1=74 x2=76 H1: p1−p2<0 n1=125 n2=170 a. Calculate the appropriate test statistic and interpret the result. What is the test statistic? What is/are the critical value(s)? b. Calculate the p-value and interpret the result. What is the p-value?arrow_forwardDr. Stevenson reported the following in a journal: “F (4, 106) = 10.09, p = .04.” Should Dr. Stevenson state that there are significant differences among the variable means at a .01 alpha level?arrow_forward
- For which of the following pairs of significance levels and pp-values are the results statistically significant? That is, for each αα, should H0H0 be rejected based on the given pp-value? Select all cases where H0H0 should be rejected: α=α=0.001; pp-value==0.004 α=α=0.003; pp-value==0.168 α=α=0.010; pp-value==0.056 α=α=0.100; pp-value==0.027 α=α=0.025; pp-value==0.012 α=α=0.050; pp-value==0.002arrow_forwardUse the dataset HT_2448.xls. Using Excel, conduct a t-test (at the alpha = 0.01 significance level) on whether the mean of X1 is equal to 100. What do you conclude from this sample data? Is the population mean equal to 100? Group of answer choices: a-You cannot reject the null hypothesis. You conclude that the population mean is equal to 100. b-You reject the null hypothesis. You conclude that the population mean is equal to 100. c-You reject the null hypothesis. You conclude that the population mean is not equal to 100. d-You cannot reject the null hypothesis. You conclude that the population mean is not equal to 100. Data set HT_2448.xls X1 X2102.04 96.13100.47 97.63103.17 95.4295.09 104.41103.81 102.0895.36 103.33103.38 112.25100.26 96.9397.24 100.1999.61 102.7096.00 106.94100.69 102.29100.50 100.0098.81 97.6795.15 99.09100.01 98.57102.88 97.70101.36 108.11103.05 106.9496.17…arrow_forwardWith reference to Exercise 13.30 below, show that if the first measurement is recorded incorrectly as 16.0 instead of 14.5, this will reverse the result. Explain the apparent paradox that even though the difference between the sample mean and μ0 has increased, it is no longer significant. 13.30. Five measurements of the tar content of a certain kind of cigarette yielded 14.5, 14.2, 14.4, 14.3, and14.6 mg/cigarette. Assuming that the data are a random sample from a normal population, show that at the 0.05 level of significance the null hypothesis μ=14.0 must be rejected in favor of the alternative μ is not equal to 14.0.arrow_forward
- Use HT_5038.xls. Using Excel, conduct a t-test (at the alpha = 0.10 significance level) on whether the mean of X2 is equal to 100. What do you conclude from this sample data? Is the population mean equal to 100? Group of answer choices a-You cannot reject the null hypothesis. You conclude that the population mean is not equal to 100. b-You reject the null hypothesis. You conclude that the population mean is equal to 100. c-You reject the null hypothesis. You conclude that the population mean is not equal to 100. d-You cannot reject the null hypothesis. You conclude that the population mean is equal to 100. HT 5038.xls X1 X299.06 97.6698.75 109.37101.43 98.72107.65 93.69100.63 98.82101.65 95.5797.25 97.8194.15 100.24102.03 103.08101.38 102.12100.62 102.5298.30 103.25108.59 109.5198.22 95.2399.30 110.33100.63 97.6796.31 104.7698.86 98.85101.54 105.94100.90 101.1397.73 102.4599.41 99.6698.50…arrow_forwardThe following results are for two independent samples taken from the two populations. Sample 1 Sample 2 n1 = 40 n2 = 50 x-bar1 = 25.5 x-bar2 = 22.8 σ1 = 5.2 σ2 = 6.0 What is the value of the test statistic? What is the p-value? With α = 0.05, what is your hypothesis testing conclusion?arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





