
Mary Williams, owner of Williams Products, is evaluating whether to introduce a new product line. After thinking through the production process and the costs of raw materials and new equipment, Williams estimates the variable costs of each unit produced and sold at $6 and the fixed costs per year at $60,000.
- If the selling price is set at $18 each, how many unit must be produced and sold for Williams to break even? Use both graphic and algebraic approaches to get your answer.
- Williams
forecasts sales of 10,000 units for the first year if the selling price is set at $14 each. What would be the total contribution to profits from this new product during the first year? - If the selling price is set at $12.50, Williams forecasts that first-year sales would increase to 15,000 units. Which pricing strategy ($14.00 or $12.50) would result in the greater total contribution to profits?
- What oilier considerations would be crucial to the final decision about making and marketing the new product?
a.
To calculate: The break even quantity using both graphic and algebraic approaches.
Concept Introduction: Break-even point is explained as a point where a company is earning no profits and incurring no losses reflecting that total cost is equivalent to total income.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Variable costs: $6 per unit
Fixed costs: $60,000
Selling price: $18 per unit
Break-even quantity: ?
Calculation of break even quantity:
Hence, the break even quantity is 5,000 units.
Graphic approach for calculating break even quantity:
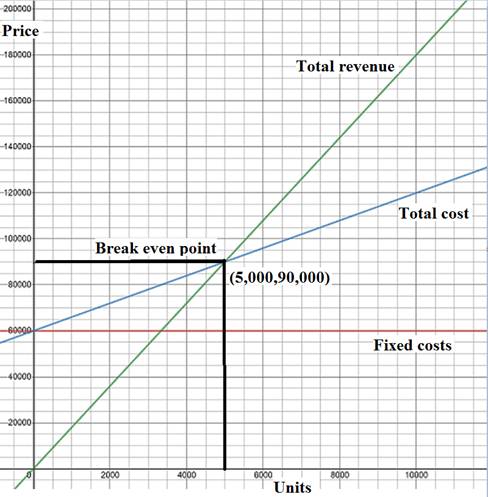
Fig (1)
b.
To calculate: The total contribution to profits from this new product.
Concept Introduction: Profit is explained as surplus of total income over total costs.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Forecasted sales: 10,000 units
Selling price: $14 per unit
Calculation of total contribution to the profits:
Therefore, the total contribution from the new product is $20,000.
c.
To calculate: The total contribution to profits from this new product if selling price is $12.50.
Concept Introduction: Profit is explained as surplus of total income over total costs.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Forecasted sales: 15,000 units
Selling price: $12.50 per unit
Calculation of total contribution to the profits:
Therefore, the total contribution from the new product is $37,500.
If selling price is $14 and forecasted sales are 15,000 units, then,
Calculation of total contribution to the profits:
It can be concluded that when selling price is $14 then it can get a greater total contribution to Company W.
d.
To identify: The other considerations that would be crucial for final decision making for the new product.
Concept Introduction: Decision making is a process in which members of an organization select a particular course of action in response to both problem and opportunity. The objective of decision making is to gain a maximum and profitable result.
Explanation of Solution
Other considerations that would be crucial for final decision making of new product are:
- Company W can identify and evidently state the problems.
- Various other alternatives should be evaluated and for the same information should be collected.
Decisions are taken by organizations on the basis these procedures that are generally performed: break even analysis, decision tree, preference matrix and preference decision tree.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter A Solutions
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Operations and Supply Chain Management 9th edition
Operations Management, Binder Ready Version: An Integrated Approach
Loose-leaf for Operations Management (The Mcgraw-hill Series in Operations and Decision Sciences)
Business in Action (8th Edition)
Principles Of Operations Management
Business in Action
- Scenario 3 Ben Gibson, the purchasing manager at Coastal Products, was reviewing purchasing expenditures for packaging materials with Jeff Joyner. Ben was particularly disturbed about the amount spent on corrugated boxes purchased from Southeastern Corrugated. Ben said, I dont like the salesman from that company. He comes around here acting like he owns the place. He loves to tell us about his fancy car, house, and vacations. It seems to me he must be making too much money off of us! Jeff responded that he heard Southeastern Corrugated was going to ask for a price increase to cover the rising costs of raw material paper stock. Jeff further stated that Southeastern would probably ask for more than what was justified simply from rising paper stock costs. After the meeting, Ben decided he had heard enough. After all, he prided himself on being a results-oriented manager. There was no way he was going to allow that salesman to keep taking advantage of Coastal Products. Ben called Jeff and told him it was time to rebid the corrugated contract before Southeastern came in with a price increase request. Who did Jeff know that might be interested in the business? Jeff replied he had several companies in mind to include in the bidding process. These companies would surely come in at a lower price, partly because they used lower-grade boxes that would probably work well enough in Coastal Products process. Jeff also explained that these suppliers were not serious contenders for the business. Their purpose was to create competition with the bids. Ben told Jeff to make sure that Southeastern was well aware that these new suppliers were bidding on the contract. He also said to make sure the suppliers knew that price was going to be the determining factor in this quote, because he considered corrugated boxes to be a standard industry item. Is Ben Gibson acting legally? Is he acting ethically? Why or why not?arrow_forwardScenario 3 Ben Gibson, the purchasing manager at Coastal Products, was reviewing purchasing expenditures for packaging materials with Jeff Joyner. Ben was particularly disturbed about the amount spent on corrugated boxes purchased from Southeastern Corrugated. Ben said, I dont like the salesman from that company. He comes around here acting like he owns the place. He loves to tell us about his fancy car, house, and vacations. It seems to me he must be making too much money off of us! Jeff responded that he heard Southeastern Corrugated was going to ask for a price increase to cover the rising costs of raw material paper stock. Jeff further stated that Southeastern would probably ask for more than what was justified simply from rising paper stock costs. After the meeting, Ben decided he had heard enough. After all, he prided himself on being a results-oriented manager. There was no way he was going to allow that salesman to keep taking advantage of Coastal Products. Ben called Jeff and told him it was time to rebid the corrugated contract before Southeastern came in with a price increase request. Who did Jeff know that might be interested in the business? Jeff replied he had several companies in mind to include in the bidding process. These companies would surely come in at a lower price, partly because they used lower-grade boxes that would probably work well enough in Coastal Products process. Jeff also explained that these suppliers were not serious contenders for the business. Their purpose was to create competition with the bids. Ben told Jeff to make sure that Southeastern was well aware that these new suppliers were bidding on the contract. He also said to make sure the suppliers knew that price was going to be the determining factor in this quote, because he considered corrugated boxes to be a standard industry item. As the Marketing Manager for Southeastern Corrugated, what would you do upon receiving the request for quotation from Coastal Products?arrow_forwardScenario 4 Sharon Gillespie, a new buyer at Visionex, Inc., was reviewing quotations for a tooling contract submitted by four suppliers. She was evaluating the quotes based on price, target quality levels, and delivery lead time promises. As she was working, her manager, Dave Cox, entered her office. He asked how everything was progressing and if she needed any help. She mentioned she was reviewing quotations from suppliers for a tooling contract. Dave asked who the interested suppliers were and if she had made a decision. Sharon indicated that one supplier, Apex, appeared to fit exactly the requirements Visionex had specified in the proposal. Dave told her to keep up the good work. Later that day Dave again visited Sharons office. He stated that he had done some research on the suppliers and felt that another supplier, Micron, appeared to have the best track record with Visionex. He pointed out that Sharons first choice was a new supplier to Visionex and there was some risk involved with that choice. Dave indicated that it would please him greatly if she selected Micron for the contract. The next day Sharon was having lunch with another buyer, Mark Smith. She mentioned the conversation with Dave and said she honestly felt that Apex was the best choice. When Mark asked Sharon who Dave preferred, she answered, Micron. At that point Mark rolled his eyes and shook his head. Sharon asked what the body language was all about. Mark replied, Look, I know youre new but you should know this. I heard last week that Daves brother-in-law is a new part owner of Micron. I was wondering how soon it would be before he started steering business to that company. He is not the straightest character. Sharon was shocked. After a few moments, she announced that her original choice was still the best selection. At that point Mark reminded Sharon that she was replacing a terminated buyer who did not go along with one of Daves previous preferred suppliers. Ethical decisions that affect a buyers ethical perspective usually involve the organizational environment, cultural environment, personal environment, and industry environment. Analyze this scenario using these four variables.arrow_forward
- Scenario 4 Sharon Gillespie, a new buyer at Visionex, Inc., was reviewing quotations for a tooling contract submitted by four suppliers. She was evaluating the quotes based on price, target quality levels, and delivery lead time promises. As she was working, her manager, Dave Cox, entered her office. He asked how everything was progressing and if she needed any help. She mentioned she was reviewing quotations from suppliers for a tooling contract. Dave asked who the interested suppliers were and if she had made a decision. Sharon indicated that one supplier, Apex, appeared to fit exactly the requirements Visionex had specified in the proposal. Dave told her to keep up the good work. Later that day Dave again visited Sharons office. He stated that he had done some research on the suppliers and felt that another supplier, Micron, appeared to have the best track record with Visionex. He pointed out that Sharons first choice was a new supplier to Visionex and there was some risk involved with that choice. Dave indicated that it would please him greatly if she selected Micron for the contract. The next day Sharon was having lunch with another buyer, Mark Smith. She mentioned the conversation with Dave and said she honestly felt that Apex was the best choice. When Mark asked Sharon who Dave preferred, she answered, Micron. At that point Mark rolled his eyes and shook his head. Sharon asked what the body language was all about. Mark replied, Look, I know youre new but you should know this. I heard last week that Daves brother-in-law is a new part owner of Micron. I was wondering how soon it would be before he started steering business to that company. He is not the straightest character. Sharon was shocked. After a few moments, she announced that her original choice was still the best selection. At that point Mark reminded Sharon that she was replacing a terminated buyer who did not go along with one of Daves previous preferred suppliers. What should Sharon do in this situation?arrow_forwardScenario 4 Sharon Gillespie, a new buyer at Visionex, Inc., was reviewing quotations for a tooling contract submitted by four suppliers. She was evaluating the quotes based on price, target quality levels, and delivery lead time promises. As she was working, her manager, Dave Cox, entered her office. He asked how everything was progressing and if she needed any help. She mentioned she was reviewing quotations from suppliers for a tooling contract. Dave asked who the interested suppliers were and if she had made a decision. Sharon indicated that one supplier, Apex, appeared to fit exactly the requirements Visionex had specified in the proposal. Dave told her to keep up the good work. Later that day Dave again visited Sharons office. He stated that he had done some research on the suppliers and felt that another supplier, Micron, appeared to have the best track record with Visionex. He pointed out that Sharons first choice was a new supplier to Visionex and there was some risk involved with that choice. Dave indicated that it would please him greatly if she selected Micron for the contract. The next day Sharon was having lunch with another buyer, Mark Smith. She mentioned the conversation with Dave and said she honestly felt that Apex was the best choice. When Mark asked Sharon who Dave preferred, she answered, Micron. At that point Mark rolled his eyes and shook his head. Sharon asked what the body language was all about. Mark replied, Look, I know youre new but you should know this. I heard last week that Daves brother-in-law is a new part owner of Micron. I was wondering how soon it would be before he started steering business to that company. He is not the straightest character. Sharon was shocked. After a few moments, she announced that her original choice was still the best selection. At that point Mark reminded Sharon that she was replacing a terminated buyer who did not go along with one of Daves previous preferred suppliers. What does the Institute of Supply Management code of ethics say about financial conflicts of interest?arrow_forwardThe options Outlook has for handling the seasonality of magazine are adding workers during the peak season, subcontracting out some of the work, building up inventory during the slow months, or building up a backlog of orders that will be delivered late to customers. To determine how to best use these options through an aggregate plan, Outlook`s vice president of Marketing starts with the first task-building a demand forecast. Although Outlook could attempt to forecast this demand itself, a much more accurate forecast comes from a collaborative process used by both Outlook and its retailers to produce the forecast shown in Table (a). Outlook sells each book through retailers for Rs.40. The company has a starting inventory in January of 1000 books. At the beginning of January the company has a workforce of 80 employees. The company has a total of 20 working days in each month, and each employee earns Rs 4 per hour regular time. Each employee works eight hours per day on straight time…arrow_forward
- MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning



