
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The orbital interaction that represents hyperconjugation in
Concept introduction:
Relative stabilities of carbocations are explained by hyperconjugation. In the case of primary carbocations like
Answer to Problem D.1P
The orbital interaction that represents hyperconjugation in
The hyperconjugation leads to greater stabilization for the
Explanation of Solution
In
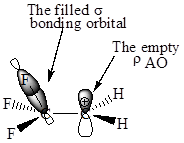
Also, in
The orbital interactions for both
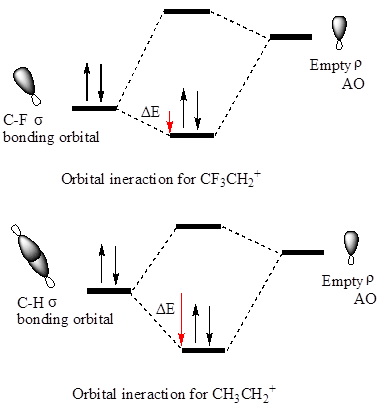
The F atom is more electronegative than H, therefore the
The cation in which hyperconjugation would leads to greater stabilization is determined on the basis of orbital interactions shown above.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter D Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- How many of the following molecules and ions have a bondorder of 1/2: H2, H2+, H2-, and He22 + ?(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 (e) 4arrow_forwardWhich compound in each of the following pairs would you expect to have the greaterdipole moment μ? Why?(a) HF or HCl (d) CHCl3 or CCl3F(b) HF or BF3 (e) CH3NH2 or CH3OH(c) (CH3)3CH or (CH3)3CCl (f) CH3NH2 or CH3NO2arrow_forwardSketch the geometry of (a) tans-[Cu(Br)2(H2O)4] (b) [Zn(OH)2I22-](tetrahedral) (c) [Pt(NH3)42+](square planar) (d) cis-[Ni(H2O)2(C2O4]22- (e) [Au(CN)(NH3)]arrow_forward
- Using cartoon representations, draw a molecular orbital mixing diagram for a CO bond. In your picture, consider the relative energies of C and O and how this changes the resulting bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals relative to a CC bond.arrow_forwardwhich is more polar, H-Cl or H-O?arrow_forwardWhich one of the following would be paramagnetic? Group of answer choices C2 B2 F2 N2arrow_forward
- why do you have -k2 in the L.H.S and -(-w)2 in the R.H.S ?arrow_forwardWhich of the compounds below are cis/trans isomerism applicable? Choices: A. 2 onlyB.2 and 3C. all 3D. 1 and 2E. 3 onlyarrow_forwardThere are two compounds of the formula Pt(NH3)2Cl2: The compound on the right is called cisplatin, and the compoundon the left is called transplatin. (a) Which compoundhas a nonzero dipole moment? (b) One of these compoundsis an anticancer drug, and one is inactive. The anticancerdrug works by its chloride ions undergoing a substitutionreaction with nitrogen atoms in DNA that are close together,forming a N—Pt—N angle of about 90°. Which compoundwould you predict to be the anticancer drug?arrow_forward
- Which of the following central atoms would be expected to accommodate more than four electron pairs in some of its compounds?Simply explain your answer in a seperate sheet as well. F Br O Narrow_forward1. How many molecular orbitals describe 2,4,6-Octatriene ?arrow_forwardHow many anti-bonding pi-type molecular orbitals does 1,3-butadiene contain?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning




