
Concept explainers
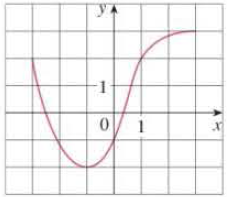
FIGURE FOR PROBLEM 1
1. The graph of a function f is given at the left
- (a) State the value of f(−1)
- (b) Estimate the value of f(2)
- (c) For what values of x is f(x) = 2?
- (d) Estimate the values of x such that f(x) = 0.
- (e) State the domain and range of f.
(a)
To state: The value of
Answer to Problem 1CDT
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Spot the point
To find the value of
Now the intersecting point of the graph of the function and the line
From the figure, it is clear that the value of
Thus, the value of
(b)
To estimate: The value of
Answer to Problem 1CDT
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Spot the point
To find the value of
Now the intersecting point of the graph of the function and the line
From the figure, it is clear that the value of
Thus, the value of
(c)
To find: The value of x such that
Answer to Problem 1CDT
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Spot the point
To find the value of
Now the x-coordinate of the intersecting point of the graph of the function and the line
From the figure, it is clear that the value of
Thus, the value of
(d)
To estimate: The value of x such that
Answer to Problem 1CDT
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Spot the point
To find the value of
Now the x-coordinate of the intersecting point of the graph of the function and the line
From the figure, it is clear that the value of
Thus, the value of
(e)
To state: The domain and range of the function
Explanation of Solution
The set of all possible values of the independent variables in a function is called the domain of the function.
From the figure, it is clear that the function
Thus, the domain of the function
The resulting set of possible values of the dependent variable is called the range.
From the figure, it is clear that the function
Thus, the range of the function
Chapter T Solutions
Single Variable Calculus: Concepts and Contexts, Enhanced Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Calculus: Single And Multivariable
Precalculus: A Unit Circle Approach
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Precalculus: A Unit Circle Approach (3rd Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





