
Biology 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172517
Author: Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
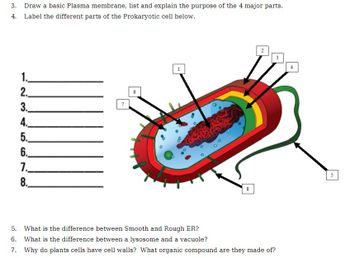
Transcribed Image Text:3. Draw a basic Plasma membrane, list and explain the purpose of the 4 major parts.
4. Label the different parts of the Prokaryotic cell below.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
7
6
5.
What is the difference between Smooth and Rough ER?
6. What is the difference between a lysosome and a vacuole?
7. Why do plants cells have cell walls? What organic compound are they made of?
3
4
5
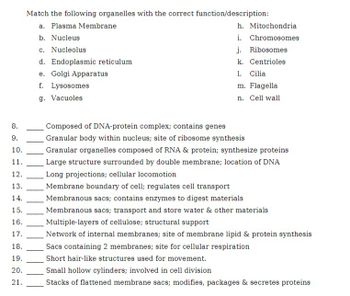
Transcribed Image Text:8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
Match the following organelles with the correct function/description:
a. Plasma Membrane
b. Nucleus
c. Nucleolus
d. Endoplasmic reticulum
e. Golgi Apparatus
f. Lysosomes
g. Vacuoles
▬▬▬▬▬▬
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
h. Mitochondria
i. Chromosomes
j. Ribosomes
k. Centrioles
1. Cilia
m. Flagella
n. Cell wall
Composed of DNA-protein complex; contains genes
Granular body within nucleus; site of ribosome synthesis
Granular organelles composed of RNA & protein; synthesize proteins
Large structure surrounded by double membrane; location of DNA
Long projections; cellular locomotion
Membrane boundary of cell; regulates cell transport
Membranous sacs; contains enzymes to digest materials
Membranous sacs; transport and store water & other materials
Multiple-layers of cellulose; structural support
Network of internal membranes; site of membrane lipid & protein synthesis
Sacs containing 2 membranes; site for cellular respiration
Short hair-like structures used for movement.
Small hollow cylinders; involved in cell division
Stacks of flattened membrane sacs; modifies, packages & secretes proteins
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The eukaryotic cell in the photo on the left is in the process of cytoplasmic division. Is this cell from a plant or an animal? How do you know?arrow_forwardIon pumps and phagocytosis are both examples of ________. a. endocytosis b. passive transport c.active transport d. facilitated diffusionarrow_forwardThe surface-to-volume ratio _______. a. does not apply to prokaryotic cells. b. constrains cell size. c. is part of the cell bodyarrow_forward
- Which of the following are glycoproteins whose function is affected by the common cold birus? a. plasmodesmata b. desmosomes c. cell adhesion molecules d. flagella e. ciliaarrow_forwardUnlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells ________. a. have no plasma membrane b. have RNA but not DNA c. have no nucleus d. a and carrow_forwardWhy is it advantageous for the cell membrane to be fluid in nature?arrow_forward
- What controls the passage of molecules into and out of the nucleus? a. endoplasmic reticulum, an extension of the nucleus b. nuclear pores, which consists of membrane proteins c. nucleoli, in which ribosome subunits are made d. dynamically assembled microtubules e. tight junctionsarrow_forwardThe plasma membrane __________. a. surrounds the cytoplasm b. separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm c. separates the cell interior from the environment d. both a and carrow_forwardExpalin the difference between cytosol and cytoplasm in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.arrow_forward
- In the fluid mosaic model: plasma membrane proteins orient their hydrophilic sides toward the internal bilayer. phospholipids often flip-flop between the inner and outer layers. the mosaic refers to proteins attached to the underlying cytoskeleton. the fluid refers to the phospholipid bilayer. the mosaic refers to the symmetry of the internal membrane proteins and sterols.arrow_forwardFigure 3.13 Why does the cis face of the Golgi not face the plasma membrane?arrow_forwardA typical prokaryotic cell ________ compared to a eukaryotic cell. a. is smaller in size by a factor of 100 b. is similar in size c. is smaller in size by a factor of one million d. is larger in size by a factor of 10arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
 Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax


Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

