
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305577206
Author: Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
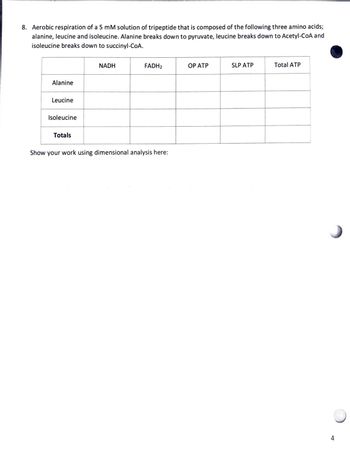
Transcribed Image Text:8. Aerobic respiration of a 5 mM solution of tripeptide that is composed of the following three amino acids;
alanine, leucine and isoleucine. Alanine breaks down to pyruvate, leucine breaks down to Acetyl-CoA and
isoleucine breaks down to succinyl-CoA.
Alanine
NADH
FADH2
OP ATP
SLP ATP
Total ATP
Leucine
Isoleucine
Totals
Show your work using dimensional analysis here:
4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- GTP or ATP is produced during the conversion of isocitrate into ketoglutarate succinyl CoA into succinate fumarate into malate malate into oxaloacetatearrow_forwardEnergetic of Fructose-1 ,6-bis P Hydrolysis (Integrates with Chapter 3.) The standard free energy change (G) for hydrolysis of fructose-1. 6-bisphosphate (FBP) to fructose-S-phosphate (F-6-P) and P: is -16.7 KJ/mol: FBP + H2O fructose-6-P + Pi The standard free energy change (G) for ATP hydrolysis is -30.5 KJ/mol: ATP + H2O ADP + Pj What is the standard free energy change for the phosphofructokinase reaction: ATP + fructose-6-P ADP + FBP b. What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction? c. Assuming the intracellular concentrations of [ATP] and (ADP] are maintained constant at 4 mM and 1.6 mM, respectively, in a rat liver cell, what will be the ratio of [FBP]/[fructose-6-P] when the phosphofructokinase reaction reaches equilibrium?arrow_forwardUnderstanding the Mechanism of Hemolytic Anemia Genetic defects in glycolytic enzymes can have serious consequences for humans For example, defects in the gene for pyruvate kinase can result in a condition known as hemolytic anemia. Consult a reference to learn about hemolytic anemia, and discuss why such genetic defects lead to this condition.arrow_forward
- Comparing Glycolysis Entry Points for Sucrose Sucrose can enter glycolysis by either of two routes: Sucrose phosphorylase: Sucrose + Pi fructose + glucose-1-phosphate Invertase: Sucrose + H20 fructose + glucose Would either of these reactions offer Jin advantage over the other In the preparation of hexoses fur entry into glycolysis?arrow_forwardHow much ATP will be produced during the following metabolic scenario: Aerobic respiration of a 5mM lipid solution that is made up of one glycerol and an 8-carbon fatty acid and 12-carbon fatty acid. Recall that when glycerol breaks down to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate it costs one ATP but your get an extra FADH2. Every two carbons of a fatty acid break down to one acetyl-CoA. (pathways will be provided on the exam) Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forwardHow much ATP will be produced during the following metabolic scenario: Aerobic respiration of a 5mM lipid solution that is made up of one glycerol and an 8-carbon fatty acid and 12-carbon fatty acid. Recall that when glycerol breaks down to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate it costs one ATP but your get an extra FADH2. Every two carbons of a fatty acid break down to one acetyl-CoA. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forward
- Figure 27.3 illustrates the response of R (ATP-regenerating) and U (ATP-utilizing) enzymes to energy charge. a. Would hexokinase be an R enzyme or a U enzyme? Would glutamine: PRPP amidotransferase, the second enzyme in purine biosynthesis, be an R enzyme or a U enzyme? b. If energy charge = 0.5: Is the activity of hexokinase high or low? Is ribose-5-P pyrophosphokinase activity high or low? c. If energy charge = 0.95: Is the activity of hexokinase high or low? Is ribose-5-P pyrophosphokinase activity high or low?arrow_forwardStudy Figure 19.18 and decide which of the following statements is false. Pyruvate dehydrogenase is inhibited by· NIADH. Pyruvate dehydrogenase is inhibited by AΤΡ. Citrate synthase is inhibited by NADH. Succinyl-CoA activates citrate synthase. Acetyl-CoA activates pyruvate carboxylase.arrow_forwardExplaining the Stoichiometry of Fatty Acid Synthesis Carefully count and account for each of the atoms and charges in the equations for the synthesis of palmitoyl-CoA, the synthesis of malonyl-CoA, and the overall reaction for the synthesis of palmitoyl-CoA from acetyl-CoA.arrow_forward
- Distinguishing the Mechanisms of Class I and Class I Aldolases Fructose bisphosphate aldolase in animal muscle is a class 1 aldolase, which forms a Schiff base intermediate between substrate (for example. fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate or dihydroxyacetone phosphate) and a lysine at the active site (see Figure I8.12). The chemical evidence for this intermediate conies from studies with aldolase and the reducing agent sodium borohydride, NaBH4. Incubation of the enzyme with dihydroxyacetone phosphate and NaBH4 inactivates the enzyme. Interestingly, no inactivation is observed if NabH4 is added to the enzyme in the absence of substrate. Write a mechanism that explains these observations and provides evidence for the formation of a Schiff base intermediate in the aldolase reaction.arrow_forwardUnderstanding the Stoichiometry of Cholesterol Synthesis Write a Balanced, stoichiometric reaction for the synthesis of cholesterol from acetyl-CoA.arrow_forwardEthanol as a Source of Metabolic Energy (Integrates with Chapters 19 and 20.) Acetate produced in ethanol metabolism can be transformed into acetyl-COA by the acetyl thiokinase reaction: Acetate+ATP+CoASHacetyleCoA+AMP+PPiAcetyle-CoA then can enter the citric acid cycle and undergo oxidation to 2 CO2by this route, assuming oxidative phosphorylation is part of the process? (Assume all reactions prior to acetyl-CoA entering the citric acid cycle occur outside the mitochondrion). Per carbon atom, which is a better metabolic fuel, ethanol or glucose? That is, how many ATP equivalents per carbon atom are generated by combustion of glucose versus ethanol to CO2?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College
