A parent of mass m₂ = 60 kg sits on a uniform beam seesaw of mass M = 40 kg, at a distance r₁ = 1.0 m to the right of the pivot P (as pictured below). Each end of the beam is equidistant from P. a) What distance r, to the left should a child of mass m, = 30 kg sit in order to balance the seesaw (hint: the center of mass of the beam is right at its center, since it is taken to be uniform)? Show any equations you use, or justify your intuition. m₂ = 30 kg m, = 60 kg M = 40 kg P √₂ = ? r₁=1.0 m b) What is the torque exerted by the weight of the parent, the torque from the child's weight, and the torque from the seesaw weight (magnitude and direction for each case, with direction indicated as into or out of the paper, and state the proper units)?
A parent of mass m₂ = 60 kg sits on a uniform beam seesaw of mass M = 40 kg, at a distance r₁ = 1.0 m to the right of the pivot P (as pictured below). Each end of the beam is equidistant from P. a) What distance r, to the left should a child of mass m, = 30 kg sit in order to balance the seesaw (hint: the center of mass of the beam is right at its center, since it is taken to be uniform)? Show any equations you use, or justify your intuition. m₂ = 30 kg m, = 60 kg M = 40 kg P √₂ = ? r₁=1.0 m b) What is the torque exerted by the weight of the parent, the torque from the child's weight, and the torque from the seesaw weight (magnitude and direction for each case, with direction indicated as into or out of the paper, and state the proper units)?
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter10: Rotational Motion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5OQ: Assume a single 300-N force is exerted on a bicycle frame as shown in Figure OQ10.5. Consider the...
Related questions
Question
I would really appreciate the solution for these parts.

Transcribed Image Text:A parent of mass m₂ = 60 kg sits on a uniform beam seesaw of mass M = 40 kg, at a distance r = 1.0 m to the right of the pivot P (as pictured below).
Each end of the beam is equidistant from P.
a) What distance r, to the left should a child of mass m₂ = 30 kg sit in order to balance the seesaw (hint: the center of mass of the beam is right at its
center, since it is taken to be uniform)? Show any equations you use, or justify your intuition.
m₂ = 30 kg
m₁ = 60 kg
M = 40 kg
P
r₂ = ?
r₁=1.0 m
b) What is the torque exerted by the weight of the parent, the torque from the child's weight, and the torque from the seesaw weight (magnitude
and direction for each case, with direction indicated as into or out of the paper, and state the proper units)?
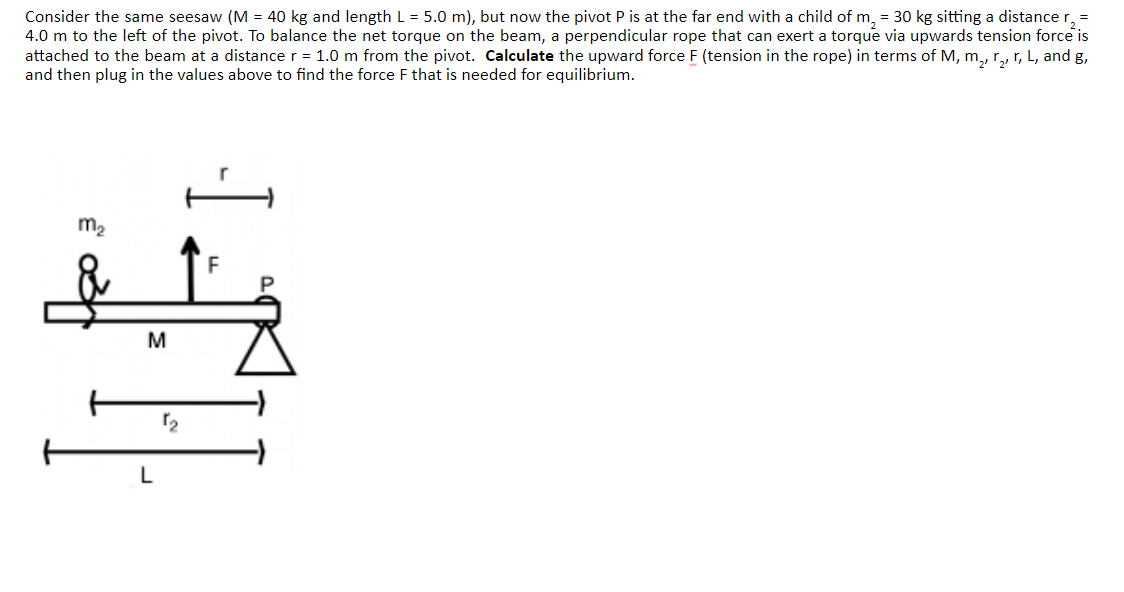
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the same seesaw (M = 40 kg and length L = 5.0 m), but now the pivot P is at the far end with a child of m₂ = 30 kg sitting a distance r, =
4.0 m to the left of the pivot. To balance the net torque on the beam, a perpendicular rope that can exert a torque via upwards tension force is
attached to the beam at a distance r = 1.0 m from the pivot. Calculate the upward force F (tension in the rope) in terms of M, m₂, r₂, r, L, and g,
and then plug in the values above to find the force F that is needed for equilibrium.
m₂
M
L
2
-I
F
P
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning