A spring with spring constant 20 N/m is compressed a distance of 6.0 cm by a ball with a mass of 215.5 g (see figure below). The ball is then released and rolls without slipping along a horizontal surface, leaving the spring at point A. The process is repeated, using a block instead, with a mass identical to that of the ball. The block compresses the spring by 6.0 cm and is also released, leaving the spring at point A. Assume the ball rolls, but ignore other effects of friction. (Assume that the ball is a solid ball.) B A (a) What is the speed of the ball at point B? m/s (b) What is the speed of the block at point B? m/s
A spring with spring constant 20 N/m is compressed a distance of 6.0 cm by a ball with a mass of 215.5 g (see figure below). The ball is then released and rolls without slipping along a horizontal surface, leaving the spring at point A. The process is repeated, using a block instead, with a mass identical to that of the ball. The block compresses the spring by 6.0 cm and is also released, leaving the spring at point A. Assume the ball rolls, but ignore other effects of friction. (Assume that the ball is a solid ball.) B A (a) What is the speed of the ball at point B? m/s (b) What is the speed of the block at point B? m/s
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter13: Rotation Ii: A Conservation Approach
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 33PQ: A spring with spring constant 25 N/m is compressed a distance of 7.0 cm by a ball with a mass of...
Related questions
Question
Subject :- Accounting
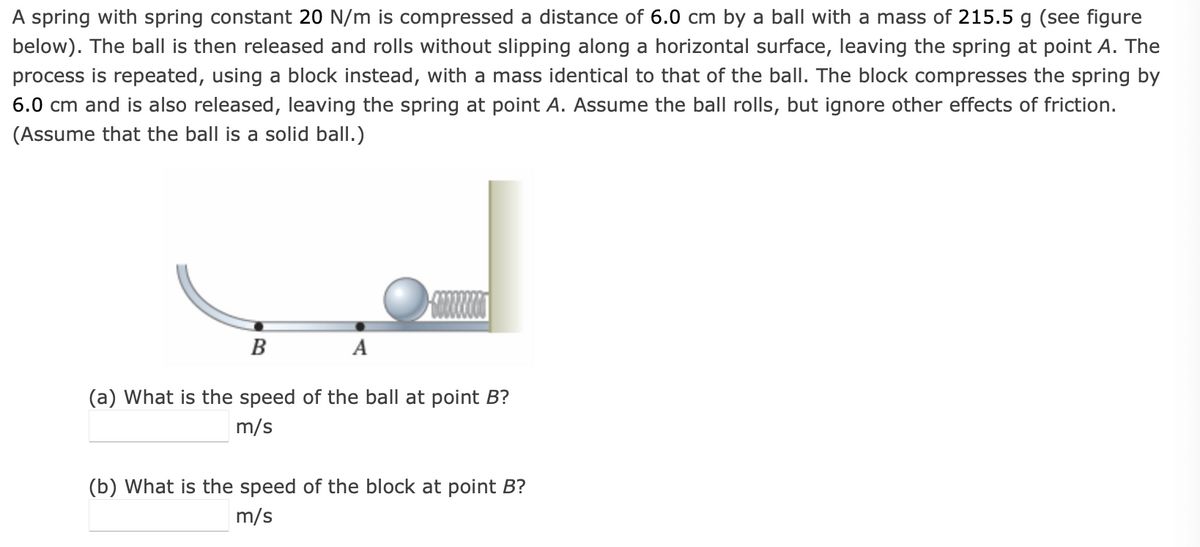
Transcribed Image Text:A spring with spring constant 20 N/m is compressed a distance of 6.0 cm by a ball with a mass of 215.5 g (see figure
below). The ball is then released and rolls without slipping along a horizontal surface, leaving the spring at point A. The
process is repeated, using a block instead, with a mass identical to that of the ball. The block compresses the spring by
6.0 cm and is also released, leaving the spring at point A. Assume the ball rolls, but ignore other effects of friction.
(Assume that the ball is a solid ball.)
B
(a) What is the speed of the ball at point B?
m/s
(b) What is the speed of the block at point B?
m/s
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning