
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (MindTap Course List)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781305117396
Author: Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
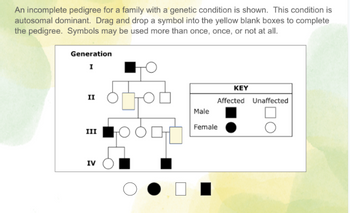
Transcribed Image Text:An incomplete pedigree for a family with a genetic condition is shown. This condition is
autosomal dominant. Drag and drop a symbol into the yellow blank boxes to complete
the pedigree. Symbols may be used more than once, once, or not at all.
Generation
I
II
III
IV
Sod
KEY
Affected Unaffected
Male
Female
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A proband female with an unidentified disease seeks the advice of a genetic counselor before starting a family. Based on the following data, the counselor constructs a pedigree encompassing three generations: (1) The maternal grandfather of the proband has the disease. (2) The mother of the proband is unaffected and is the youngest of five children, the three oldest being male. (3) The proband has an affected older sister, but the youngest siblings are unaffected twins (boy and girl). (4) All the individuals who have the disease have been revealed. Duplicate the counselors featarrow_forwardKlinefelter syndrome XXY can be easily diagnosed by _______ . a. pedigree analysis c. karyotyping b. aneuploidy d. phenotypic treatmentarrow_forwardGiven the karyotype shown at right, is this a male or a female? Normal or abnormal? What would the phenotype of this individual be?arrow_forward
- A couple was referred for genetic counseling because they wanted to know the chances of having a child with dwarfism. Both the man and the woman had achondroplasia (MIM 100800), the most common form of short-limbed dwarfism. The couple knew that this condition is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, but they were unsure what kind of physical manifestations a child would have if it inherited both mutant alleles. They were each heterozygous for the FGFR3 (MIM 134934) allele that causes achondroplasia. Normally, the protein encoded by this gene interacts with growth factors outside the cell and receives signals that control growth and development. In achrodroplasia, a mutation alters the activity of the receptor, resulting in a characteristic form of dwarfism. Because both the normal and mutant forms of the FGFR3 protein act before birth, no treatment for achrondroplasia is available. The parents each carry one normal allele and one mutant allele of FGRF3, and they wanted information on their chances of having a homozygous child. The counsellor briefly reviewed the phenotypic features of individuals with achondroplasia. These include facial features (large head with prominent forehead; small, flat nasal bridge; and prominent jaw), very short stature, and shortening of the arms and legs. Physical examination and skeletal X-ray films are used to diagnose this condition. Final adult height is approximately 4 feet. Because achondroplasia is an autosomal dominant condition, a heterozygote has a 1-in-2, or 50%, chance of passing this trait to his or her offspring. However, about 75% of those with achondroplasia have parents of average size who do not carry the mutant allele. In these cases, achondroplasia is due to a new mutation. In the couple being counseled, each individual is heterozygous, and they are at risk for having a homozygous child with two copies of the mutated gene. Infants with homozygous achondroplasia are either stillborn or die shortly after birth. The counselor recommended prenatal diagnosis via ultrasounds at various stages of development. In addition, a DNA test is available to detect the homozygous condition prenatally. What is the chance that this couple will have a child with two copies of the dominant mutant gene? What is the chance that the child will have normal height?arrow_forwardA couple was referred for genetic counseling because they wanted to know the chances of having a child with dwarfism. Both the man and the woman had achondroplasia (MIM 100800), the most common form of short-limbed dwarfism. The couple knew that this condition is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, but they were unsure what kind of physical manifestations a child would have if it inherited both mutant alleles. They were each heterozygous for the FGFR3 (MIM 134934) allele that causes achondroplasia. Normally, the protein encoded by this gene interacts with growth factors outside the cell and receives signals that control growth and development. In achrodroplasia, a mutation alters the activity of the receptor, resulting in a characteristic form of dwarfism. Because both the normal and mutant forms of the FGFR3 protein act before birth, no treatment for achrondroplasia is available. The parents each carry one normal allele and one mutant allele of FGRF3, and they wanted information on their chances of having a homozygous child. The counsellor briefly reviewed the phenotypic features of individuals with achondroplasia. These include facial features (large head with prominent forehead; small, flat nasal bridge; and prominent jaw), very short stature, and shortening of the arms and legs. Physical examination and skeletal X-ray films are used to diagnose this condition. Final adult height is approximately 4 feet. Because achondroplasia is an autosomal dominant condition, a heterozygote has a 1-in-2, or 50%, chance of passing this trait to his or her offspring. However, about 75% of those with achondroplasia have parents of average size who do not carry the mutant allele. In these cases, achondroplasia is due to a new mutation. In the couple being counseled, each individual is heterozygous, and they are at risk for having a homozygous child with two copies of the mutated gene. Infants with homozygous achondroplasia are either stillborn or die shortly after birth. The counselor recommended prenatal diagnosis via ultrasounds at various stages of development. In addition, a DNA test is available to detect the homozygous condition prenatally. Should the parents be concerned about the heterozygous condition as well as the homozygous mutant condition?arrow_forwardA couple was referred for genetic counseling because they wanted to know the chances of having a child with dwarfism. Both the man and the woman had achondroplasia (MIM 100800), the most common form of short-limbed dwarfism. The couple knew that this condition is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, but they were unsure what kind of physical manifestations a child would have if it inherited both mutant alleles. They were each heterozygous for the FGFR3 (MIM 134934) allele that causes achondroplasia. Normally, the protein encoded by this gene interacts with growth factors outside the cell and receives signals that control growth and development. In achrodroplasia, a mutation alters the activity of the receptor, resulting in a characteristic form of dwarfism. Because both the normal and mutant forms of the FGFR3 protein act before birth, no treatment for achrondroplasia is available. The parents each carry one normal allele and one mutant allele of FGRF3, and they wanted information on their chances of having a homozygous child. The counsellor briefly reviewed the phenotypic features of individuals with achondroplasia. These include facial features (large head with prominent forehead; small, flat nasal bridge; and prominent jaw), very short stature, and shortening of the arms and legs. Physical examination and skeletal X-ray films are used to diagnose this condition. Final adult height is approximately 4 feet. Because achondroplasia is an autosomal dominant condition, a heterozygote has a 1-in-2, or 50%, chance of passing this trait to his or her offspring. However, about 75% of those with achondroplasia have parents of average size who do not carry the mutant allele. In these cases, achondroplasia is due to a new mutation. In the couple being counseled, each individual is heterozygous, and they are at risk for having a homozygous child with two copies of the mutated gene. Infants with homozygous achondroplasia are either stillborn or die shortly after birth. The counselor recommended prenatal diagnosis via ultrasounds at various stages of development. In addition, a DNA test is available to detect the homozygous condition prenatally. What if the couple wanted prenatal testing so that a normal fetus could be aborted?arrow_forward
- Achondroplasia is a rare dominant autosomal defect resulting in dwarfism. The unaffected brother of an individual with achondroplasia is seeking counsel on the likelihood of his being a carrier of the mutant allele. What is the probability that the unaffected client is carrying the achondroplasia allele?arrow_forwardAn allele responsible for Marfan syndrome Section 13.4 is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. What is the chance that a child will inherit the allele if one parent does not carry it and the other is heterozygous?arrow_forwardThe following pedigree shows the pattern of inheritance of red-green color blindness in a family. Females are shown as circles and males as squares; the squares or circles of individuals affected by the trait are filled in black. What is the chance that a son of the third-generation female indicated by the arrow will be color blind if the father is not color blind? If he is color blind?arrow_forward
- As it turned out, one of the tallest Potsdam Guards had an unquenchable attraction to short women. During his tenure as guard, he had numerous clandestine affairs. In each case, children resulted. Subsequently, some of the childrenwho had no way of knowing that they were relatedmarried and had children of their own. Assume that two pairs of genes determine height. The genotype of the 7-foot-tall Potsdam Guard was A9A9B9B9, and the genotype of all of his 5-foot clandestine lovers was AABB. An A9 or B9 allele in the offspring each adds 6 inches to the base height of 5 feet conferred by the AABB genotype. a. What were the genotypes and phenotypes of all the F1 children? b. Diagram the cross between the F1 offspring, and give all possible genotypes and phenotypes of the F2 progenyarrow_forwardThe genotype XXY corresponds to: a. Klinefelter syndrome b. Turner syndrome c. Tripto-X d. Jacob syndromearrow_forwardKlinefelter syndrome (XXY) can most be easily diagnosed by _______. a. pedigree analysis. b. aneuploidy c. karyotyping d. phenotypic treatmentarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781337408332
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning