
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
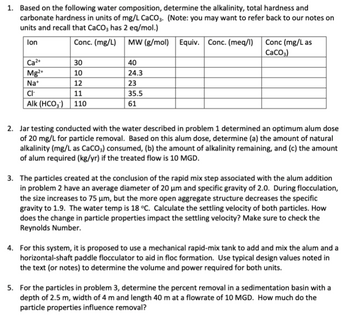
Transcribed Image Text:1. Based on the following water composition, determine the alkalinity, total hardness and
carbonate hardness in units of mg/L CaCO3. (Note: you may want to refer back to our notes on
units and recall that CaCO3 has 2 eq/mol.)
lon
Conc. (mg/L) MW (g/mol) Equiv. Conc. (meq/l)
Ca²+
30
Mg2+
10
Na+
12
CI-
11
Alk (HCO3) 110
40
24.3
23
35.5
61
Conc (mg/L as
CaCO3)
2. Jar testing conducted with the water described in problem 1 determined an optimum alum dose
of 20 mg/L for particle removal. Based on this alum dose, determine (a) the amount of natural
alkalinity (mg/L as CaCO3) consumed, (b) the amount of alkalinity remaining, and (c) the amount
of alum required (kg/yr) if the treated flow is 10 MGD.
3. The particles created at the conclusion of the rapid mix step associated with the alum addition
in problem 2 have an average diameter of 20 µm and specific gravity of 2.0. During flocculation,
the size increases to 75 µm, but the more open aggregate structure decreases the specific
gravity to 1.9. The water temp is 18 °C. Calculate the settling velocity of both particles. How
does the change in particle properties impact the settling velocity? Make sure to check the
Reynolds Number.
4. For this system, it is proposed to use a mechanical rapid-mix tank to add and mix the alum and a
horizontal-shaft paddle flocculator to aid in floc formation. Use typical design values noted in
the text (or notes) to determine the volume and power required for both units.
5. For the particles in problem 3, determine the percent removal in a sedimentation basin with a
depth of 2.5 m, width of 4 m and length 40 m at a flowrate of 10 MGD. How much do the
particle properties influence removal?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 14 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 1.7 The composition of a natural gas is shown in Table 1. 3. The reservoir conditions is 8.3 MPa and 32 C. Table 1.3 Component CH, C,H, C, H, C,H, 10 Mole fraction 96. 23 1. 85 0. 83 0.41 Calculate: (1) Gas compressibility factor. (2) Gas formation volume factor. (3) If a gas well produces 10 000 standard m' of gas per day, calculate the volume of gas in reservoir conditions. (4) The coefficient of isothermal compressibility of the gas mixture. (5) Gas viscosity.arrow_forwardConsider the following samples of gas.Select the set of graphs below that show the distributions of the speed of the atoms in each sample (please take a photo of the correct graph).arrow_forwardA cylindrical pressure vessel of diameter 50 cm and height 1.2 m is used to store a gas mixture consisting of 75 mole % nitrogen and 25 mole % carbon dioxide at 30 bar and 20°C. i) Find the mass of gas present. ii) Find the density of the gas mixture under these conditions. iii) Use the Gibbs Phase Rule to find the number of degrees of freedom in the system.arrow_forward
- QUESTION 16 Calculate the freezing point. in degrees Celsius, of a solution containing 58.5 grams of CHCI3 (molar mass-119.38 g/mol) and 644.4 grams of eucalyptol C10H180 (molar mass-154.24 g/mol), a fragrant substance found in the leaves of eucalyptus trees. The molal-freezing point depression constant for C10H180 is 4.68°C/m and pure C10H180 freezes at -63.5°Cc. Express your answer to ene decimal place.arrow_forwardCompound TA has a molar mass of 180. g/mol and is a triester. Calculate the minimum volume (in mL) of 0.100 N NaOH (aq) solution needed to completely hydrolyzed 0.192 g of compound TA. Show Work & Units!!!arrow_forwardNeed neat and clean handwritten solution explaining every parts. Don't give copied solution from cheggarrow_forward
- The density of carbon tetrachloride (CC14) is used as a reference density at a specific condition to measure the specific gravity of the liquid substance Select one: O True O Falsearrow_forwardAt a certain temperature and pressure, a 1.00 mol sample of argon gas is pumped into a 22.4 L rigid box that already contains 1.00 mol of nitrogen gas. We would expect the argon gas to: Group of answer choices decrease the total gas pressure in the box by a factor of 2 occupy the entire 22.4 L volume of the box. increase the total gas pressure in the box by a factor of less than 2. spread out into the box, but the actual volume occupied but he gas cannot be known without pressure information. occupy only 11.2 L of the box.arrow_forwardFind the molar concentration in mol litre-1 of a solution if 46 kg of acompound (relative mass = 110) is present in a solution whose volume is36 litres.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The