Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, and Times-Interest-Earned Ratio The following data is from the current accounting records of Florence Company: Cash $360 Accounts receivable (net of allowance of $120) 600 450 240 Inventory Other current assets Accounts payable Other current liabilities 319 510 The president of the company is concerned that the company is in violation of a debt covenant that requires the company to maintain a minimum current ratio of 2.0. He believes the best way to rectify this is to reverse a bad debt write-off in the amount of $30 that the company just recorded. He argues that the write-off was done too early and that the collections department should be given more time to collect the outstanding receivables. The CFO argues that this will have no effect on the current ratio, so a better idea is to use $30 of cash to pay accounts payable early. Florence Company uses the allowance method to account for bad debts. a. Calculate the current ratio under the following scenarios: Round answers to two decimal places. Current ratio (with no action) Current ratio (after reversal of bad debt) Current ratio (after paydown of accounts payable) Which action, if any, should Florence Company take to maintain a minimum 2.0 current ratio? b. Will either the quick ratio or the times-interest-earned ratios be affected by at least one of these ideas? Quick ratio Times-interest-earned ratio 90
Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, and Times-Interest-Earned Ratio The following data is from the current accounting records of Florence Company: Cash $360 Accounts receivable (net of allowance of $120) 600 450 240 Inventory Other current assets Accounts payable Other current liabilities 319 510 The president of the company is concerned that the company is in violation of a debt covenant that requires the company to maintain a minimum current ratio of 2.0. He believes the best way to rectify this is to reverse a bad debt write-off in the amount of $30 that the company just recorded. He argues that the write-off was done too early and that the collections department should be given more time to collect the outstanding receivables. The CFO argues that this will have no effect on the current ratio, so a better idea is to use $30 of cash to pay accounts payable early. Florence Company uses the allowance method to account for bad debts. a. Calculate the current ratio under the following scenarios: Round answers to two decimal places. Current ratio (with no action) Current ratio (after reversal of bad debt) Current ratio (after paydown of accounts payable) Which action, if any, should Florence Company take to maintain a minimum 2.0 current ratio? b. Will either the quick ratio or the times-interest-earned ratios be affected by at least one of these ideas? Quick ratio Times-interest-earned ratio 90
Chapter9: Accounting For Receivables
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6PA: Funnel Direct recorded $1,345,780 in credit sales for the year and $695,455 in accounts receivable....
Related questions
Question
Ef 403.
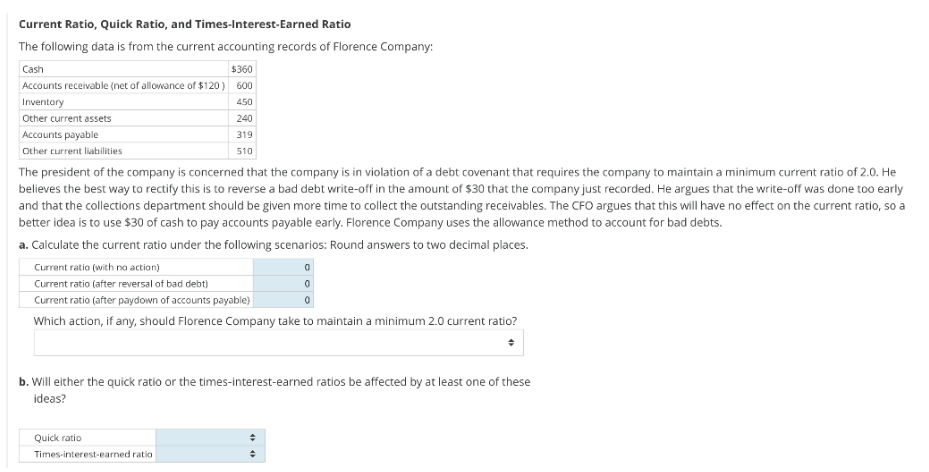
Transcribed Image Text:Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, and Times-Interest-Earned Ratio
The following data is from the current accounting records of Florence Company:
Cash
$360
Accounts receivable (net of allowance of $120) 600
Inventory
450
Other current assets
Accounts payable
Other current liabilities
240
319
510
The president of the company is concerned that the company is in violation of a debt covenant that requires the company to maintain a minimum current ratio of 2.0. He
believes the best way to rectify this is to reverse a bad debt write-off in the amount of $30 that the company just recorded. He argues that the write-off was done too early
and that the collections department should be given more time to collect the outstanding receivables. The CFO argues that this will have no effect on the current ratio, so a
better idea is to use $30 of cash to pay accounts payable early. Florence Company uses the allowance method to account for bad debts.
a. Calculate the current ratio under the following scenarios: Round answers to two decimal places.
Current ratio (with no action)
Current ratio (after reversal of bad debt)
Current ratio (after paydown of accounts payable)
Which action, if any, should Florence Company take to maintain a minimum 2.0 current ratio?
Quick ratio
Times-interest-earned ratio
b. Will either the quick ratio or the times-interest-earned ratios be affected by at least one of these
ideas?
0
0
+
÷
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172685
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337115773
Author:
Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337794756
Author:
HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305666160
Author:
James A. Heintz, Robert W. Parry
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning