(d) In what ways are the two sampling distributions of parts (b) and (c) similar? In what ways are they different? (Select all that apply.) Their means are equal. One distribution is not symmetrical. They are both symmetrical. Their means are different. They both cover the same range. One distribution covers a larger range.
(d) In what ways are the two sampling distributions of parts (b) and (c) similar? In what ways are they different? (Select all that apply.) Their means are equal. One distribution is not symmetrical. They are both symmetrical. Their means are different. They both cover the same range. One distribution covers a larger range.
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8CR
Related questions
Question
Just answer the last part (D) Please answer correctly and I'll leave a like
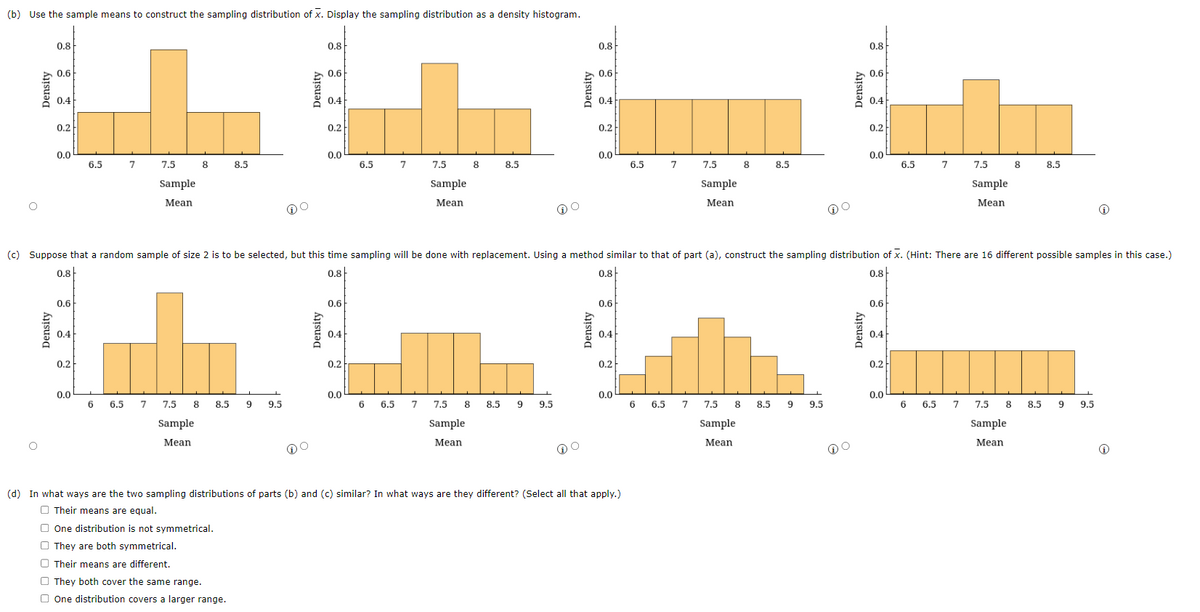
Transcribed Image Text:(b) Use the sample means to construct the sampling distribution of x. Display the sampling distribution as a density histogram.
Density
0.8
Density
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
0.6
0.4
0.2
6.5
0.0
6
7
6.5
7.5
Sample
Mean
8
7 7.5
Sample
Mean
8 8.5
8.5
9 9.5
Density
DO
0.8
Density
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
0.6
0.4
0.2
6.5
0.0
7
6 6.5
7.5
Sample
Mean
8
8.5
7 7.5 8 8.5 9
Sample
Mean
9.5
Density
(c) Suppose that a random sample of size 2 is to be selected, but this time sampling will be done with replacement. Using a method similar to that of part (a), construct the sampling distribution of X. (Hint: There are 16 different possible samples in this case.)
0.8
0.8
0.8
0.8
o
0.8
Density
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
6.5 7
(d) In what ways are the two sampling distributions of parts (b) and (c) similar? In what ways are they different? (Select all that apply.)
Their means are equal.
One distribution is not symmetrical.
They are both symmetrical.
Their means are different.
They both cover the same range.
One distribution covers a larger range.
6
7.5
Sample
Mean
6.5
8
8.5
7 7.5 8 8.5 9
Sample
Mean
9.5
Density
DO
0.8
Density
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
0.6
0.4
0.2
6.5
0.0
6
7
6.5
7.5 8
Sample
Mean
8.5
7 7.5 8 8.5 9
Sample
Mean
9.5
Ⓡ
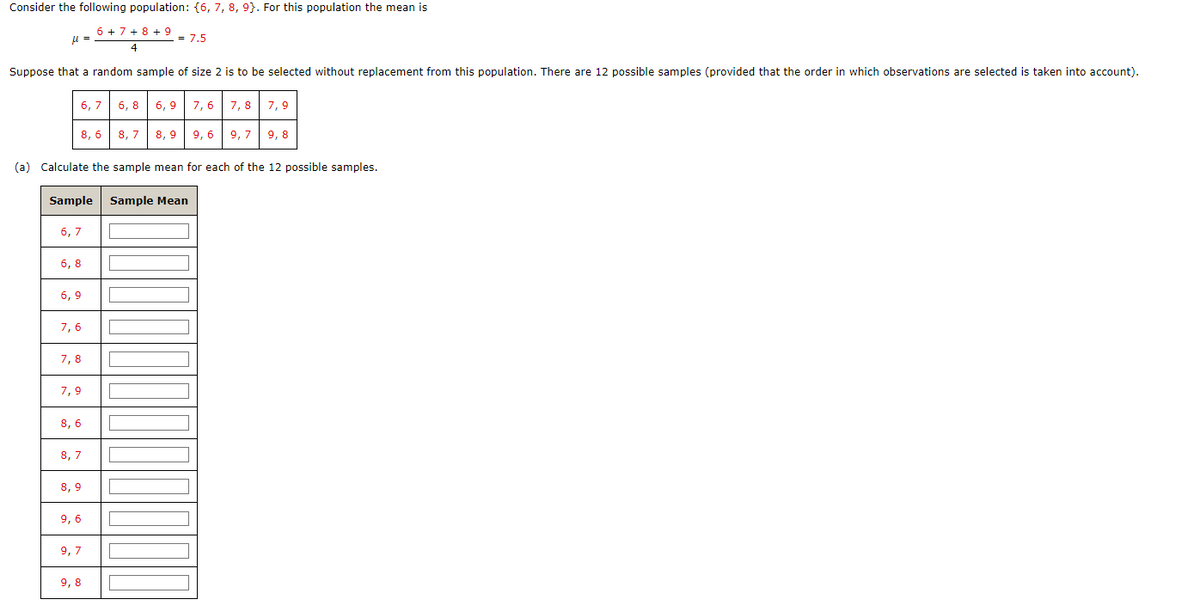
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following population: {6, 7, 8, 9). For this population the mean is
6 + 7 + 8 + 9
4
μ =
Suppose that a random sample of size 2 is to be selected without replacement from this population. There are 12 possible samples (provided that the order in which observations are selected is taken into account).
8,6
6,7
6,7
6,8
(a) Calculate the sample mean for each of the 12 possible samples.
Sample Sample Mean
6,9
7,6
7,8
7,9
8,6
8,7
8,9
= 7.5
9,6
9,7
6,8 6,9 7,6
9,8
7,8 7,9
8,7 8,9 9,6 9,7 9,8
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill