
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
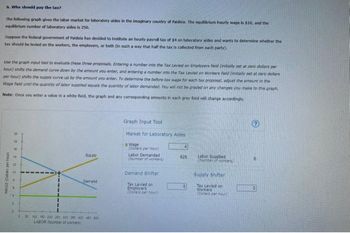
Transcribed Image Text:6. Who should pay the tax?
The following graph gives the labor market for laboratory aides in the imaginary country of Paideia. The equilibrium hourly wage is $10, and the
equilibrium number of laboratory aides is 250.
Suppose the federal government of Paidela has decided to institute an hourly payroll tax of $4 on laboratory aldes and wants to determine whether the
tax should be levied on the workers, the employers, or both (in such a way that half the tax is collected from each party).
Use the graph input tool to evaluate these three proposals. Entering a number into the Tax Levied on Employers field (initially set at zero dollars per
hour) shifts the demand curve down by the amount you enter, and entering a number into the Tax Levied on Workers field (initially set at zer dollars
per hour) shifts the supply curve up by the amount you enter. To determine the before-tax wage for each tax proposal, adjust the amount in the
Wage field until the quantity of labor supplied equals the quantity of labor demanded. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph.
Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly.
WAGE (Dallars per hour
22:22.
10
Supply
Derrand
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 800
LABOR (Number of workers)
Graph Input Tool
Market for Laboratory Aides
Wage
(Dollars per hour)
Labor Demanded
(Number of workers)
Demand Shifter
Tax Levied on
Employers
(Dollars per hour)
4
625
0
Labor Supplied
(Number of workers,
Supply Shifter
Tax Levied on
Workers
(Dollars per hour)
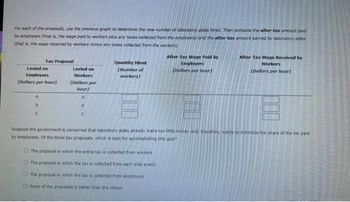
Transcribed Image Text:For each of the proposals, use the previous graph to determine the new number of laboratory aides hired. Then compute the after-tax amount paid
by employers (that is, the wage paid to workers plus any taxes collected from the employers) and the after-tax amount earned by laboratory aides
(that is, the wage received by workers minus any taxes collected from the workers).
Tax Proposal
Levied on
Employers
(Dollars per hour)
0
2
Levied on
Workers
(Dollars per
hour)
0
4
2
Quantity Hired
(Number of
workers)
After-Tax Wage Paid by
Employers
(Dollars per hour)
O The proposal in which the entire tax is collected from workers
The proposal in which the tax is collected from each side evenly
The proposal in which the tax is collected from employers
O None of the proposals is better than the others
After-Tax Wage Received by
Workers
(Dollars per hour)
Suppose the government is concerned that laboratory aides already make too little money and, therefore, wants to minimize the share of the tax paid
by employees. Of the three tax proposals, which is best for accomplishing this goal?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- sation NQF Level 4 monstrate knowledge and application of ethical conduct in a business environment Activity 17.5 In your groups work through the following case studies: Case Study 1: Employee Absence By Stephen Adams Graphics and Commercial Art Joan, an employee of Great American Market, was warned about her excessive absenteeism several times, both verbally and in writing. The written warning included notice that "further violations will result in disciplinary actions," including suspension or discharge. A short time after the written warning was issued, Joan called work to say she was not going to be in because her babysitter had called in sick and she had to stay home and care for her young child. Joan's supervisor, Sylvia, told her that she had already exceeded the allowed number of absences and warned that if she did not report to work, she could be suspended. When Joan did not report for her shift, Sylvia suspended her for fifteen days. In a subsequent hearing, Joan argued that…arrow_forwardPLS HELP ASAP ON BOTHarrow_forwardOther Companies (Part 2) You directed your research department to do some research on the demand for Tesla sedans. They selected BMW i3 Sedans and Chevy Bolts as comparative offerings. Using regression analysis, the research department comes up the following estimate for yearly demand. Qx = -40,000 -1*Px +0.02*M +2*PB +2*PC Where: Px = $70,000, M = $150,000, PB = $65,000, PC = $40,000 a. Is the own price elasticity of demand for Tesla sedans at the point defined above elastic or inelastic? If Mr. Musk decides to raise his prices, what will happen to his revenue. b. PB and PC represent the price for i3 sedans and Bolt sedans respectively. Are these items compliments or substitutes when compared to Teslas? Give evidence to support your answer. c. Is the demand for Tesla sedans elastic or inelastic to price changes of BMW i3 and Bolt at the price points given in the problem? Interpret the result you find and explain what it means.arrow_forward
- The revenue from the sale of a product is, in dollars, R = 1500x + 3000(2x+3)-1 - 1000 where x is the number of units sold. Find the marginal revenue when 200 units are sold. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) $ Interpret your result. If the sales go from 200 units sold to units sold, the revenue will increase by about $ Suppose that the weekly sales volume y (in thousands of units sold) depends on the price per unit (in dollars) of the product according to the following formula. y = 30(3p+ 1) −2/5, p > 0 (a) What is the rate of change in sales volume when the price is $24? (Round your answer to three decimal places.) dy = dp (b) Interpret your answer to part (a). (Round your answer to the nearest whole number.) If the price increases $1, the sales volume will decrease by If the demand for q units of a product priced at $p per unit is described by the equation p = 500 √29 + 7 find the rate of change of p with respect to q. dp = dq 1 units.arrow_forwardFamily Flowers employs 17 people, of whom 14 earn gross pay of $640.00 each and 3 earn gross pay of $720.00 each on a weekly basis. What is the employer's share of total social security and Medicare taxes for the first quarter of the year? (Social security tax is 6.2% of wages up to $128,400. Medicare tax is 1.45% of all wages.)arrow_forwardCould someone walk me through this problem? Thank you for your help!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education