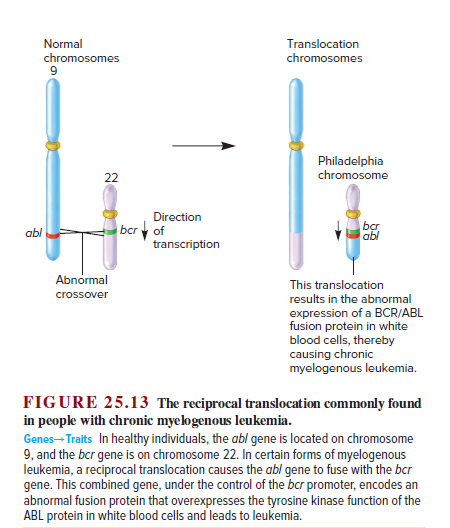
Normal Translocation chromosomes chromosomes Philadelphia chromosome 22 Direction bcry of bạr abl abl transcription Abnormal This translocation crossover results in the abnormal expression of a BCR/ABL fusion protein in white blood cells, thereby causing chronic myelogenous leukemia. FIGURE 25.13 The reciprocal translocation commonly found in people with chronic myelogenous leukemia. Genes-Traits In healthy individuals, the abl gene is located on chromosome 9, and the bcr gene is on chromosome 22. In certain forms of myelogenous leukemia, a reciprocal translocation causes the abl gene to fuse with the bcr gene. This combined gene, under the control of the bcr promoter, encodes an abnormal fusion protein that overexpresses the tyrosine kinase function of the ABL protein in white blood cells and leads to leukemia.
Normal Translocation chromosomes chromosomes Philadelphia chromosome 22 Direction bcry of bạr abl abl transcription Abnormal This translocation crossover results in the abnormal expression of a BCR/ABL fusion protein in white blood cells, thereby causing chronic myelogenous leukemia. FIGURE 25.13 The reciprocal translocation commonly found in people with chronic myelogenous leukemia. Genes-Traits In healthy individuals, the abl gene is located on chromosome 9, and the bcr gene is on chromosome 22. In certain forms of myelogenous leukemia, a reciprocal translocation causes the abl gene to fuse with the bcr gene. This combined gene, under the control of the bcr promoter, encodes an abnormal fusion protein that overexpresses the tyrosine kinase function of the ABL protein in white blood cells and leads to leukemia.
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Michael Cummings
Chapter7: Development And Sex Determination
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 19QP: Equalizing the Expression of X Chromosome Genes in Males and Females Individuals with an XXY...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Why does this translocation cause leukemia rather than cancer in a different tissue type, such as the lung?
Transcribed Image Text:Normal
Translocation
chromosomes
chromosomes
Philadelphia
chromosome
22
Direction
bcry of
bạr
abl
abl
transcription
Abnormal
This translocation
crossover
results in the abnormal
expression of a BCR/ABL
fusion protein in white
blood cells, thereby
causing chronic
myelogenous leukemia.
FIGURE 25.13 The reciprocal translocation commonly found
in people with chronic myelogenous leukemia.
Genes-Traits In healthy individuals, the abl gene is located on chromosome
9, and the bcr gene is on chromosome 22. In certain forms of myelogenous
leukemia, a reciprocal translocation causes the abl gene to fuse with the bcr
gene. This combined gene, under the control of the bcr promoter, encodes an
abnormal fusion protein that overexpresses the tyrosine kinase function of the
ABL protein in white blood cells and leads to leukemia.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning