Range of ankle motion is a contributing factor to falls among the elderly. Suppose a team of researchers is studying how combining compression bandages or compression hosiery with different types of footwear affects range of ankle motion. They suspect that more than half of all adults wearing compression bandages and no shoes will see decrease in range of ankle motion of at least 2° compared to when they are not wearing compression bandages or compression hosiery and are barefoot. They collect sample data from a random sample of 29 adults and determine that 17 see such a decrease in range of ankle motion. They compute a sample proportion of 17 = 0.586 %3D 29 The researchers conduct a one-sample z-test for a proportion, testing Ho : p = 0.500 against H1 : p > 0.500, where p is the proportion of adults whose range of angle motion decreases at least 2° while wearing compression bandages with no shoes. The lower limit of a 95% confidence interval for p is 0.436. Based on this interval, what should the researchers conclude about their z-test? The researchers should fail to reject Ho at a significance level of a = 0.10 - because || 0.586 > 0.436| a = 0.95 0.500 > 0.436 να=0. 10 v 0.586 > 0.436 0.586 > 0.500 a = 0.05
Range of ankle motion is a contributing factor to falls among the elderly. Suppose a team of researchers is studying how combining compression bandages or compression hosiery with different types of footwear affects range of ankle motion. They suspect that more than half of all adults wearing compression bandages and no shoes will see decrease in range of ankle motion of at least 2° compared to when they are not wearing compression bandages or compression hosiery and are barefoot. They collect sample data from a random sample of 29 adults and determine that 17 see such a decrease in range of ankle motion. They compute a sample proportion of 17 = 0.586 %3D 29 The researchers conduct a one-sample z-test for a proportion, testing Ho : p = 0.500 against H1 : p > 0.500, where p is the proportion of adults whose range of angle motion decreases at least 2° while wearing compression bandages with no shoes. The lower limit of a 95% confidence interval for p is 0.436. Based on this interval, what should the researchers conclude about their z-test? The researchers should fail to reject Ho at a significance level of a = 0.10 - because || 0.586 > 0.436| a = 0.95 0.500 > 0.436 να=0. 10 v 0.586 > 0.436 0.586 > 0.500 a = 0.05
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
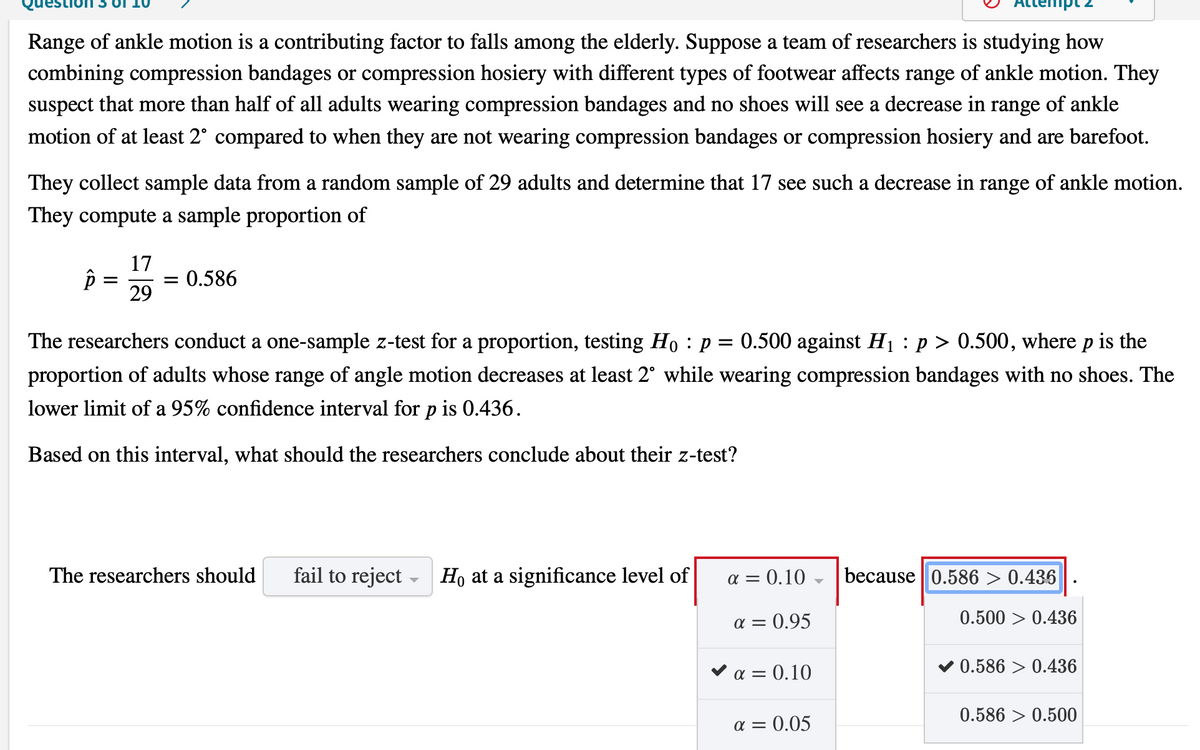
Transcribed Image Text:Range of ankle motion is a contributing factor to falls among the elderly. Suppose a team of researchers is studying how
combining compression bandages or compression hosiery with different types of footwear affects range of ankle motion. They
suspect that more than half of all adults wearing compression bandages and no shoes will see a decrease in range of ankle
motion of at least 2° compared to when they are not wearing compression bandages or compression hosiery and are barefoot.
They collect sample data from a random sample of 29 adults and determine that 17 see such a decrease in range of ankle motion.
They compute a sample proportion of
17
0.586
29
The researchers conduct a one-sample z-test for a proportion, testing Ho : p = 0.500 against H1 :p > 0.500, where p is the
proportion of adults whose range of angle motion decreases at least 2° while wearing compression bandages with no shoes. The
lower limit of a 95% confidence interval for p is 0.436.
Based on this interval, what should the researchers conclude about their z-test?
The researchers should
fail to reject - Ho at a significance level of
a = 0.10
because 0.586 > 0.436
a = 0.95
0.500 > 0.436
v a = 0.10
0.586 > 0.436
0.586 > 0.500
a = 0.05
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman