The following graph shows a hypothetical economy in long-run equilibrium at an expected price level of 120 and a natural output level of $300 billion. Suppose a stock market boom increases household wealth and causes consumers to spend more. Using the graph, shift the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve or the aggregate demand (AD) curve to show the short-run impact of the stock market boom. PRICE LEVEL 3 AS 200 AD -α- 180 8 0 100 200 300 AD 400 500 600 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) AS (?) In the short run, the increase in consumption spending associated with the stock market expansion causes the price level to level people expected and the quantity of output to the price the natural level of output. The stock market boom will cause the unemployment rate to ▼the natural rate of unemployment in the short run. Again, the following graph shows a hypothetical economy experiencing long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and natural output level of $300 billion, prior to the increase in consumption spending associated with the stock market expansion. Along the transition from the short run to the long run, price-level expectations will ▼curve will shift to the ▼ and the Using the graph, illustrate the long-run impact of the stock market boom by shifting both the aggregate demand (AD) curve and the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve in the appropriate directions. PRICE LEVEL 240 AS AD 200 160 120 100 200 300 AD 400 500 600 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) AS , the quantity of output the natural level of the natural rate. In the long run, due to the stock market boom, the price level output, and the unemployment rate
The following graph shows a hypothetical economy in long-run equilibrium at an expected price level of 120 and a natural output level of $300 billion. Suppose a stock market boom increases household wealth and causes consumers to spend more. Using the graph, shift the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve or the aggregate demand (AD) curve to show the short-run impact of the stock market boom. PRICE LEVEL 3 AS 200 AD -α- 180 8 0 100 200 300 AD 400 500 600 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) AS (?) In the short run, the increase in consumption spending associated with the stock market expansion causes the price level to level people expected and the quantity of output to the price the natural level of output. The stock market boom will cause the unemployment rate to ▼the natural rate of unemployment in the short run. Again, the following graph shows a hypothetical economy experiencing long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and natural output level of $300 billion, prior to the increase in consumption spending associated with the stock market expansion. Along the transition from the short run to the long run, price-level expectations will ▼curve will shift to the ▼ and the Using the graph, illustrate the long-run impact of the stock market boom by shifting both the aggregate demand (AD) curve and the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve in the appropriate directions. PRICE LEVEL 240 AS AD 200 160 120 100 200 300 AD 400 500 600 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) AS , the quantity of output the natural level of the natural rate. In the long run, due to the stock market boom, the price level output, and the unemployment rate
Economics (MindTap Course List)
13th Edition
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Roger A. Arnold
Chapter9: Classical Macroeconomics And The Self Regulating Economy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 15QP
Related questions
Question
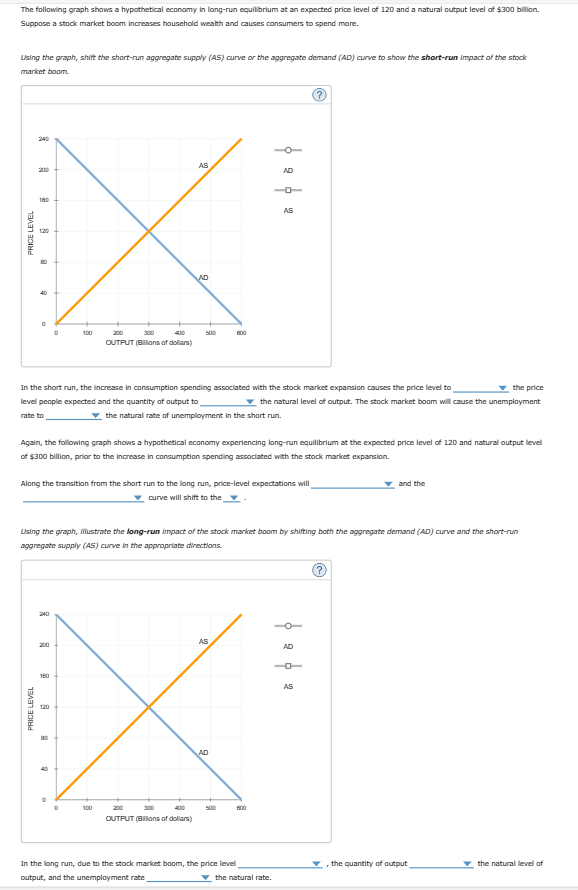
Transcribed Image Text:The following graph shows a hypothetical economy in long-run equilibrium at an expected price level of 120 and a natural output level of $300 billion.
Suppose a stock market boom increases household wealth and causes consumers to spend more.
Using the graph, shift the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve or the aggregate demand (AD) curve to show the short-run impact of the stock
market boom.
PRICE LEVEL
3
AS
200
AD
-α-
180
8
0
100
200
300
AD
400
500
600
OUTPUT (Billions of dollars)
AS
(?)
In the short run, the increase in consumption spending associated with the stock market expansion causes the price level to
level people expected and the quantity of output to
the price
the natural level of output. The stock market boom will cause the unemployment
rate to
▼the natural rate of unemployment in the short run.
Again, the following graph shows a hypothetical economy experiencing long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and natural output level
of $300 billion, prior to the increase in consumption spending associated with the stock market expansion.
Along the transition from the short run to the long run, price-level expectations will
▼curve will shift to the ▼
and the
Using the graph, illustrate the long-run impact of the stock market boom by shifting both the aggregate demand (AD) curve and the short-run
aggregate supply (AS) curve in the appropriate directions.
PRICE LEVEL
240
AS
AD
200
160
120
100
200
300
AD
400
500
600
OUTPUT (Billions of dollars)
AS
, the quantity of output
the natural level of
the natural rate.
In the long run, due to the stock market boom, the price level
output, and the unemployment rate
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337617383
Author:
Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:
Cengage Learning




