
Concept explainers
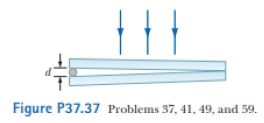
Many cells are transparent anti colorless. Structures of great interest in biology and medicine can be practically invisible to ordinary microscopy. To indicate the size and shape of cell structures, an interference micro-scope reveals a difference in index of refraction as a shift in interference fringes. The idea is exemplified in the following problem. An air wedge is formed between two glass plates in contact along one edge and slightly separated at the opposite edge as in Figure P37.37. When the plates are illuminated with monochromatic light from above, the reflected light has 85 dark fringes. Calculate the number of dark fringes that appear if water (n = 1.33) replaces the air between the plates.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 37 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
- A beam of 580-nm light passes through two closely spaced glass plates at close to normal incidence as shown in Figure P27.23. For what minimum nonzero value of the plate separation d is the transmitted light bright?arrow_forwardCoherent light rays of wavelength strike a pair of slits separated by distance d at an angle 1, with respect to the normal to the plane containing the slits as shown in Figure P27.14. The rays leaving the slits make an angle 2 with respect to the normal, and an interference maximum is formed by those rays on a screen that is a great distance from the slits. Show that the angle 2 is given by 2=sin1(sin1md) where m is an integer.arrow_forwardIn Figure P37.18, let L = 120 cm and d = 0.250 cm. The slits are illuminated with coherent 600-nm light. Calculate the distance y from the central maximum for which the average intensity on the screen is 75.0% of the maximum.arrow_forward
- Solar cells are often coated with a transparent, thin film of silicon monoxide (n = 1.45) to minimize reflective losses from the surface. Suppose a silicon solar cell (n= 3.5) is coated with a thin film of silicon monoxide. Determine the minimum film thickness that produces the least reflection at a wavelength of 550 nm. ANS = 94.8 nm 180° phase change 180° phase change Air n = 1 SiO n = 1.45 Si n = 3.5 (a) Thomen ghe bdatenarrow_forwardThe walls of a soap bubble have about the same index of refraction as that of plain water, n = 1.33. There is air both inside and outside the bubble. What wavelength (in air) of visible light is most strongly reflected from a point on a soap bubble where its wall is 340. nm thick? Note: Your answer is assumed to be reduced to the highest power possible.arrow_forwardYour friend has been given a laser for her birthday. Unfortunately, she did not receive a manual with it and so she doesn't know the wavelength that it emits. You help her by performing a double-slit experiment, with slits separated by 0.36 mm. You find that the two m=1 bright fringes are 5.5 mm apart on a screen 1.6 mm from the slits. What is the wavelength the laser emits?arrow_forward
- Ch26,P24arrow_forwardYou are working in an optical research laboratory. One of your projects involves the use of a double slit through which you pass orange laser light of wavelength 590 nm. Unfortunately, because of budget cuts, there are a lot of researchers in the same room, with lots of equipment stuffed in theroom, and, in particular, lots of laser beams flying around the room. One day, you find that a second laser beam of unknown origin and different color is entering your double slit along with your orange beam and you are seeing an interference pattern that is the sum of those due to the twobeams. You notice that the combined pattern is pretty much a mess, but wait! The m = 3 maximum of your orange laser beam pattern is pure; there is absolutely no mixture of the other color at that point. From this fact, you determine the wavelength of the offending laser light so that you can figure out which other researcher to ask to modify the aiming of his laser.arrow_forwardA common lens coating material is magnesium fluoride 1MgF22, with n = 1.38. What thickness should a nonreflective coating have for 550 nm light if it is applied to glass with n = 1.52?arrow_forward
- ress SA A thin film of magnesium fluoride (n = 1.38) is applied to glass (n = 1.50) with a thickness of 100 nm. For what visible wavelength of light will this coating act as nonreflecting? Assume normal incidence. O 491 nm O 600 nm O 504 nm 552 pm Q Search 15 40 %5 6 Il app.honorlock.com is sharing your screen. Stop, sharing Hide 99+ 3+ hp 103 a malip 8arrow_forwardA Newton's ring experiment uses a glass lens having radius of curvature 1.0 m. The apparatus is illuminated separately by light having two different wavelengths. Suppose that one of the wavelengths is 550 nm. The 6th bright ring of the 550 nm fringe system coincides with the 5th bright ring of the other. The value of second wavelength isarrow_forwardA microscope with an objective lens of diameter 7.70 mm is used to view samples of light of wavelength 650 nm.What is the limiting resolutions of this microscope with this objective lens.?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


