
Concept explainers
Given the following probability distributions:
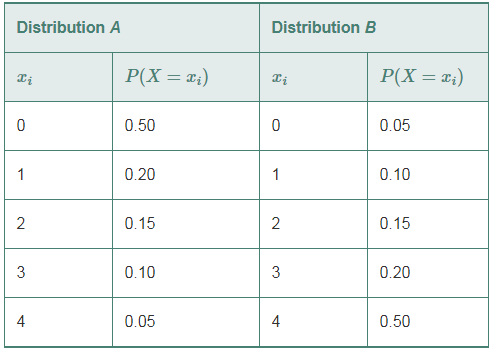
- Compute the expected value for each distribution.
- Compute the standard deviation for each distribution.
- Compare the results of distributions A and B.
(a)
To find: The expected values for both the distributions.
Answer to Problem 5.1LB
The expected values are 1 and 3 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The probability distributions are:
| Distribution A | Distribution B | ||
| 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.05 |
| 1 | 0.2 | 1 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 0.15 | 2 | 0.15 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 3 | 0.2 |
| 4 | 0.05 | 4 | 0.5 |
Formula used:
The formula to compute the expected mean is:
Here,
The formula to compute the standard deviation is:
Calculation:
The expected values for both the distributions can be calculated as:
Distribution A:
Distribution B:
Thus, the required expected values are 1 and 3 respectively.
(b)
To find: The standard deviation for each distribution.
Answer to Problem 5.1LB
The standard deviations are 1.225 and 1.225 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
The standard deviation for each distribution can be computed as:
Distribution A:
Distribution B:
Thus, the required standard deviations are 1.225 and 1.225 respectively.
(c)
To compare: The provided distributions.
Explanation of Solution
From the above two parts, it is clear that the mean of distribution B is greater than the mean of distribution B but there is no difference in the standard deviation of two distributions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Business Statistics: A First Course (7th Edition)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Research Methods for the Behavioral Sciences (MindTap Course List)
Introductory Statistics (2nd Edition)
Business Analytics
Statistics Through Applications
Elementary Statistics Using The Ti-83/84 Plus Calculator, Books A La Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Business Statistics: A First Course (8th Edition)
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





