
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The structure of naturally occurring
Concept introduction: A compound exhibits number of stereoisomers when it contains more than one stereogenic centers. The maximum number of stereoisomers a compound with
Answer to Problem 5.51P
The structure of naturally occurring
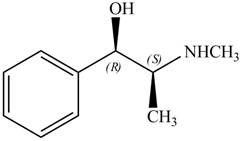
Explanation of Solution
The structure of given compoundis shown below.
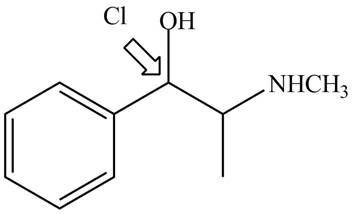
Figure 1
The stereochemistry of the compound is determined by prioritizing the groups attached to its stereogenic center. The groups are prioritizedon the basis ofatomic number of their atoms. The group that contains atom with a the higher
The configuration at the first stereocenter of
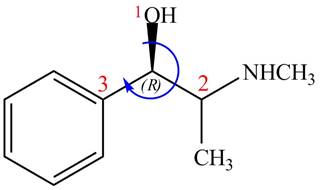
Figure 2
The above structure implies that the configuration at the first stereocenter of
The configuration at the second stereocenter of
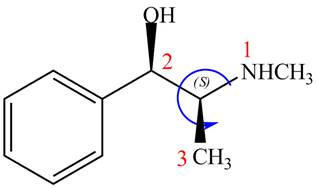
Figure 3
The above structure implies that the configuration at the second stereocenter of
The configuration at both the stereocenters of
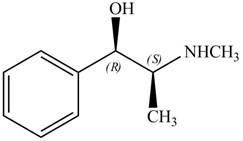
Figure 4
The configurations at the first and second stereocenters of
The structure of naturally occurring
(b)
Interpretation: The structure of naturally occurring
Concept introduction: A compound exhibits number of stereoisomers when it contains more than one stereogenic centers. The maximum number of stereoisomers a compound with
Answer to Problem 5.51P
The structure of naturally occurring
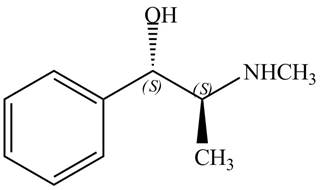
Explanation of Solution
The structure of naturally occurring
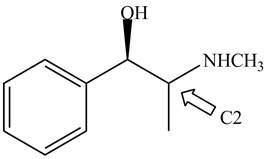
Figure 5
The stereochemistry of the compound is determined by prioritizing the groups attached to its stereogenic center. The groups are prioritizedon the basis of atomic number of their atoms. The group that contain atom with higher atomic number is givenhigher priority. Complete the circle in decreasing order of priorityfrom
The configuration at first chiral center of
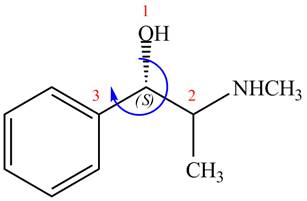
Figure 6
The above structure implies that the configuration at the first stereocenter of
The configuration at the second chiral center of
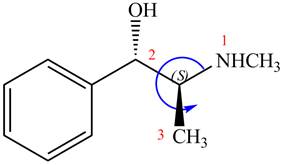
Figure 7
The above structure implies that the configuration at the second stereocenter of
The configuration at the first and second chiral centers of
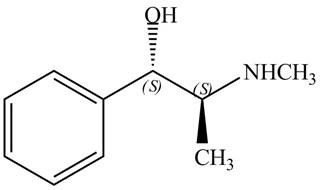
Figure 8
The configurations at the first and second carbon atoms of
The structure of naturally occurring
(c)
Interpretation: The relationship between ephedrine and pseudoephedrine is to be identified.
Concept introduction: A compound exhibits number of stereoisomers when it contains more than one stereogenic centers. The maximum number of stereoisomers a compound with
Answer to Problem 5.51P
Ephedrine and pseudoephedrine are related as diastereomers.
Explanation of Solution
The relationship between ephedrine and pseudoephedrine is shown below.
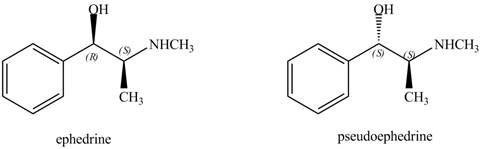
Figure 9
One stereocenter in both the compounds has opposite configuration, while the other stereogenic center has the same configuration. Therefore, both the compounds are related as diastereomer.
Ephedrine and pseudoephedrine are related as diastereomers.
(d)
Interpretation: All the stereoisomers of
Concept introduction: A compound exhibits number of stereoisomers when it contains more than one stereogenic centers. The maximum number of stereoisomers a compound with
Answer to Problem 5.51P
The stereoisomers of
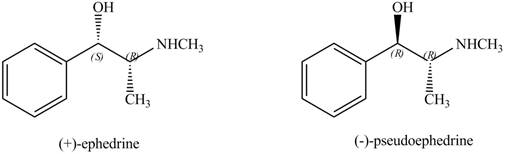
Explanation of Solution
The stereoisomers of
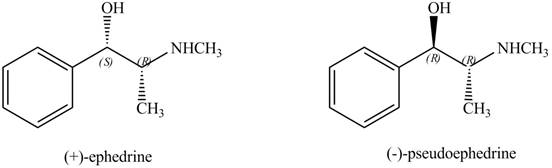
Figure 10
Both the stereoisomers have two stereocenters. One stereocenter in both the compounds has the same configuration, while the other stereocenter in both the compounds has opposite configuration.
The stereoisomers of
(e)
Interpretation: The relationship between each compound drawn in part (d) and
Concept introduction: A compound exhibits number of stereoisomers when it contains more than one stereogenic centers. The maximum number of stereoisomers a compound with
Answer to Problem 5.51P
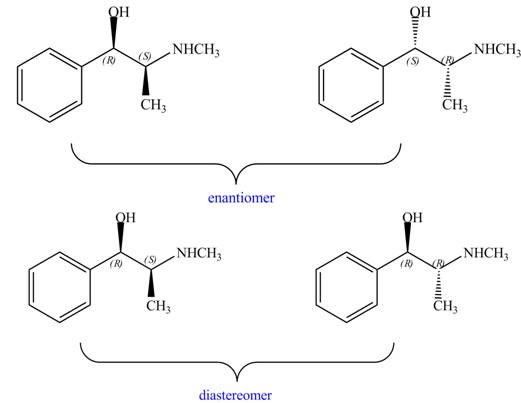
The relationship between each compound drawn in part (d) and
Explanation of Solution
The relationship between each compound drawn in part (d) and

Figure 11
The compounds
The relationship between each compound drawn in part (d) and
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- (a) Draw the products of molecular formula C3H4Cl2, including stereoisomers, formed when chlorocyclopropane is heated with Cl2. (b)Assuming that compounds that have different physical properties are separable, how many fractions would be present if the mixture of products were distilled using an efficient fractional distillation? (c) How many fractions would be optically active?arrow_forward(a) Draw all stereoisomers of molecular formula C5H10Cl2 formed when (R)-2-chloropentane is heated with Cl2. (b) Assuming that products having different physical properties can be separated into fractions by some physical method (such as fractional distillation), how many different fractions would be obtained? (c) Which of these fractions would be optically active?arrow_forwardWhich of the following are aromatic?arrow_forward
- A chemist isolated an aromatic compound with molecular formula C6H4Br2. He treated this compound with nitric acid and sulfuric acid and isolated threedifferent isomers, in different amounts, with molecular formula C6H3Br2NO2. What was the structure of the original compound?arrow_forwardI need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forwardThe cis ketone A is isomerized to a trans ketone B with aqueous NaOH. A similar isomerization does not occur with ketone C. (a) Draw the structure of B using a chair cyclohexane. (b) Label the substituents in C as cis or trans, and explain the difference in reactivity.arrow_forward
- For each alkene, indicate the direction of the dipole moment. For each pair, determine which compound has the largerdipole moment.(a) cis-1,2-difluoroethene or trans-1,2-difluoroethenearrow_forward1 Provide the IUPAC name of the following compounds, with clear indication of stereochemistry for stereocenters and alkene. (a) (b) Br (c) Me. (d) Mearrow_forward1. (a) Describe aromaticity, Kekule structure and resonance structure for benzene. (b) Why is benzene more stable than aliphatic alkenes?arrow_forward
- Ciprofloxacin is a member of the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics.(a) Which of its rings are aromatic?arrow_forward(a) which if the structure of trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane? (b) which is the most stable conformation of 1-bromo-2-ethylcyclohexane? (c) which is the least stable conformation of 1-bromo-2-ethylcyclohexane? (d) which is the more stable configuration of 1,3-dimethylcyclopentane? *Et = ethylarrow_forwardAn optically active unknown compound B, whose molecular formula is C6H10, reacts with H2/Ni produce compound C, whose molecular formula is C6H14. Compound C is optically inactive. What are the structures of compound B and C ?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





